本文主要是介绍【深蓝学院】移动机器人运动规划--第4章 动力学约束下的运动规划--作业,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 1. T1
- 1.1 题目
- 1.2 求解
- 1.3 Pontryagin Minimum Principle 的拓展
- 2. T2
- 2.1 题目
- 2.2 求解
- 3. Reference
1. T1
1.1 题目

1.2 求解



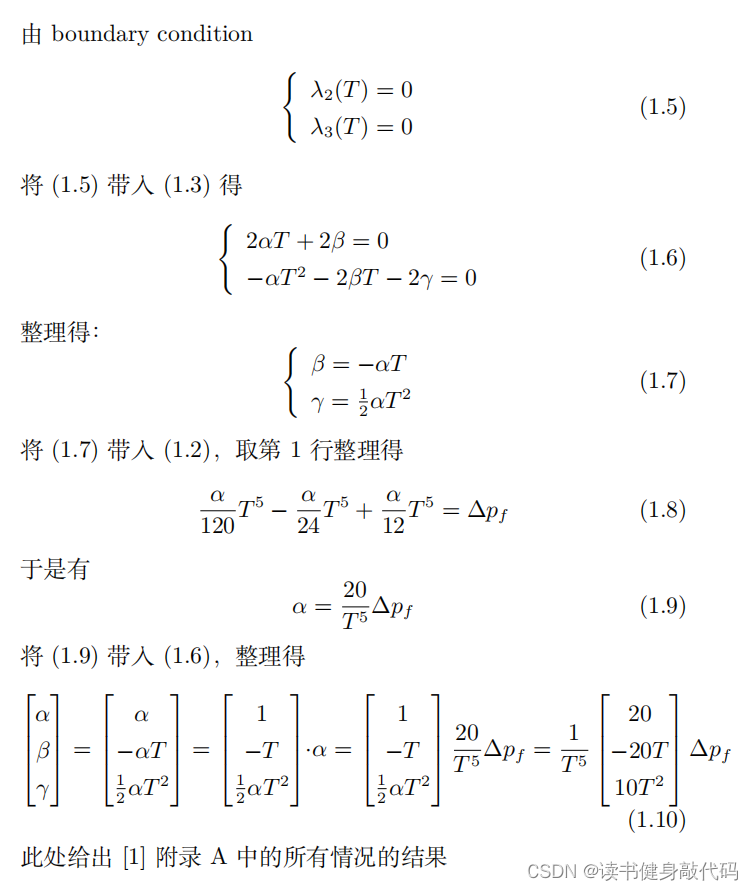
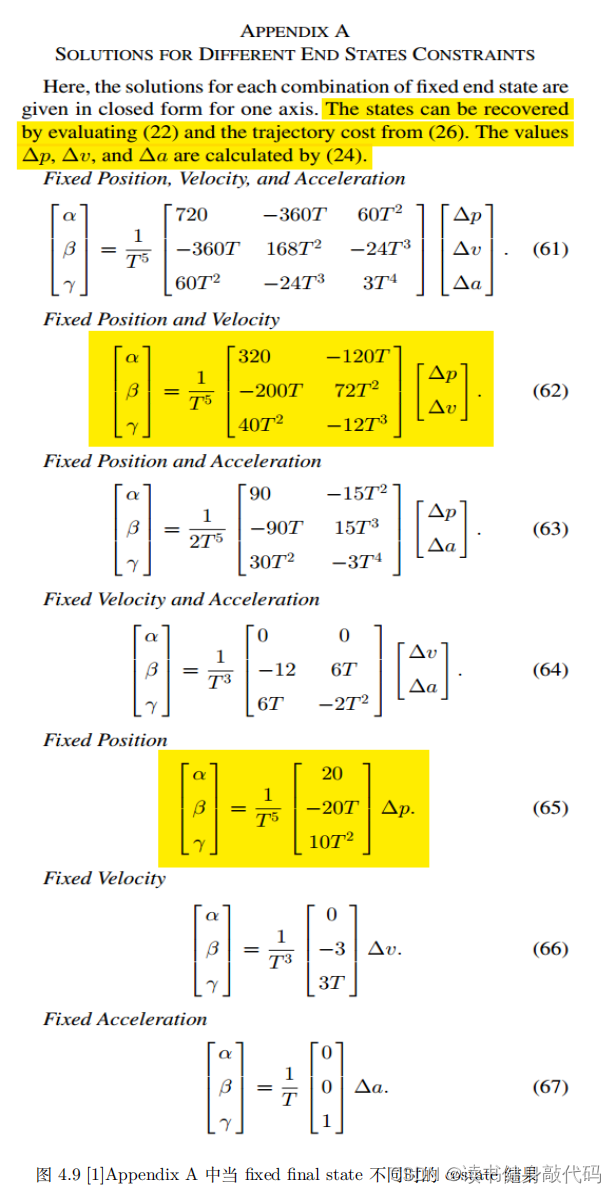
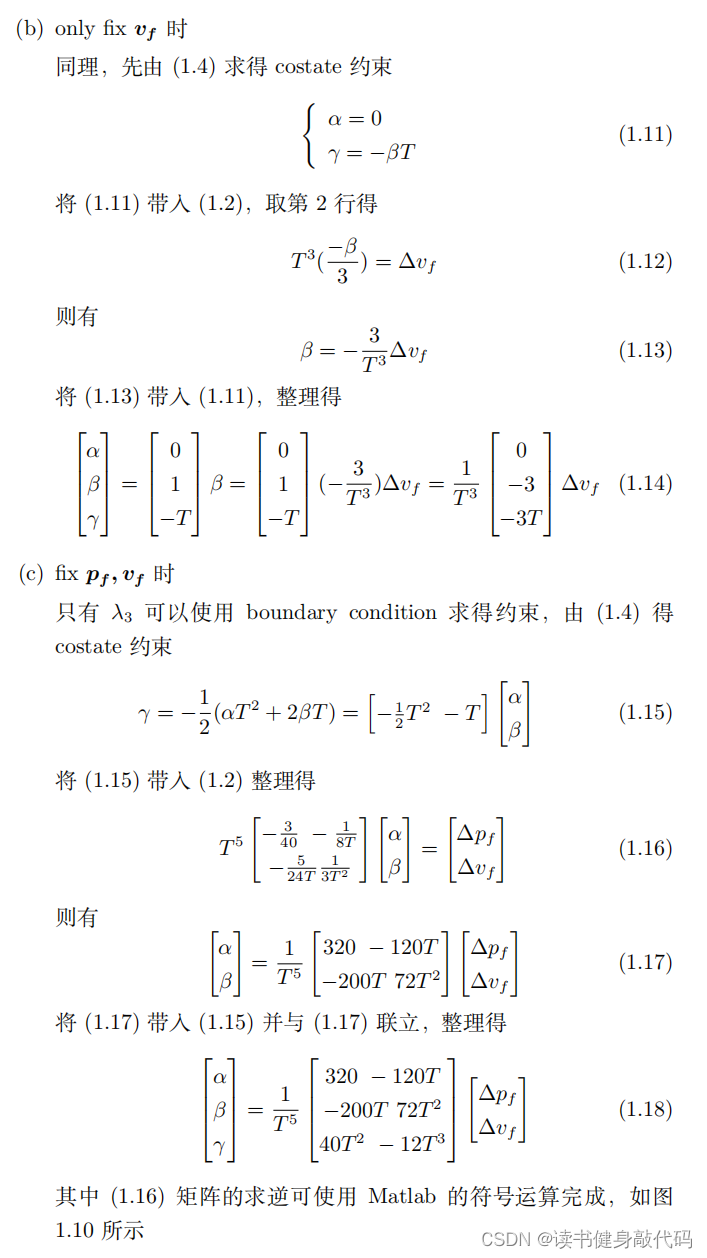

1.3 Pontryagin Minimum Principle 的拓展




2. T2
2.1 题目

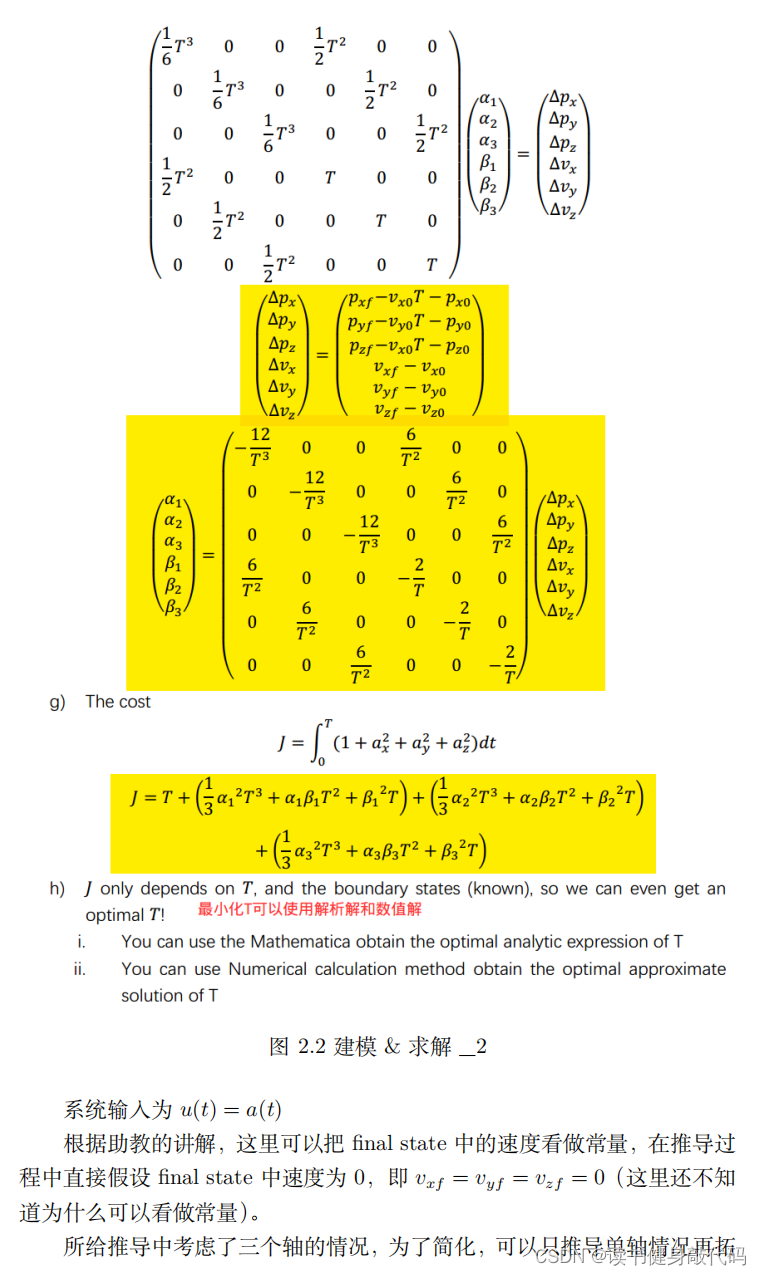
2.2 求解

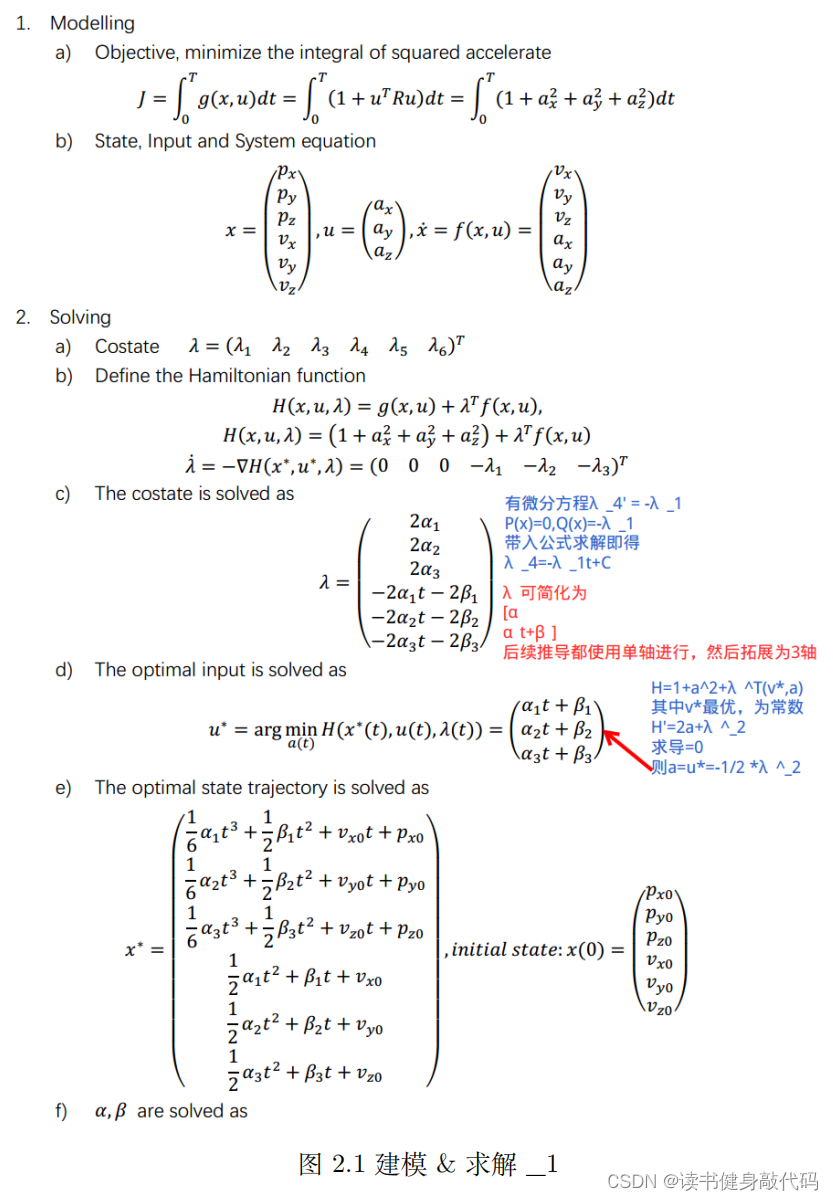


Listing1: demo_node.cpp/trajectoryLibrary()
for(int step=0 ; step<=_time_step ; step ++){/*STEP 1: finish the forward integration, the modelling has been given in the documentthe parameter of forward integration: _max_input_acc|_discretize_step|_time_interval|_time_step all have been givenuse the pos and vel to recored the steps in the trakectory*///使用运动学公式:x=x0+v0t+1/2at^2,v=v0+at//要体现出积分,是accumulate的过程pos(0) = pos(0) + vel(0) * delta_time + 0.5 * acc_input(0) * std::pow(delta_time, 2);pos(1) = pos(1) + vel(1) * delta_time + 0.5 * acc_input(1) * std::pow(delta_time, 2);pos(2) = pos(2) + vel(2) * delta_time + 0.5 * acc_input(2) * std::pow(delta_time, 2);vel(0) = vel(0) + acc_input(0) * delta_time;vel(1) = start_velocity(1) + acc_input(1) * delta_time;vel(2) = start_velocity(2) + acc_input(2) * delta_time;Position.push_back(pos);Velocity.push_back(vel);double coord_x = pos(0);double coord_y = pos(1);double coord_z = pos(2);//check if if the trajectory face the obstacleif(_homework_tool->isObsFree(coord_x,coord_y,coord_z) != 1){collision = true;}
}

Listing2:hw_tool.cpp/OptimalBVP()
double Homeworktool::OptimalBVP(Eigen::Vector3d _start_position,Eigen::Vector3d _start_velocity,Eigen::Vector3d _target_position)
{double optimal_cost = 1000000; // this just to initial the optimal_cost, you can delete it/*STEP 2: go to the hw_tool.cpp and finish the function Homeworktool::OptimalBVPthe solving process has been given in the documentbecause the final point of trajectory is the start point of OBVP, so we input the pos,vel to the OBVPafter finish Homeworktool::OptimalBVP, the Trajctory_Cost will record the optimal cost of this trajectory*///直接求解一元四次方程Eigen::Matrix<double,4,4> mat44;Eigen::Matrix<complex<double>, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic> matrix_eigenvalues;//求出一元四次方程的五个系数abcdedouble v_x0 = _start_velocity(0), v_y0 = _start_velocity(1), v_z0 = _start_velocity(2);double dx = _target_position(0) - _start_position(0);double dy = _target_position(1) - _start_position(1);double dz = _target_position(2) - _start_position(2);double v0_square_sum = v_x0*v_x0 + v_y0*v_y0 + v_z0*v_z0;double v0_dp_sum = v_x0*dx+v_y0*dy+v_z0*dz;double dp_square_sum = dx*dx + dy*dy + dz*dz;double a = 1.0;double b = 0.0;double c = -4 * v0_square_sum;double d = 24 * v0_dp_sum;double e = -36 * dp_square_sum;mat44 <<0, 0, 0, -e,1, 0, 0, -d,0, 1, 0, -c,0, 0, 1, -b;
// ROS_INFO_STREAM("\nmatrix_44: \n" << mat44);matrix_eigenvalues = mat44.eigenvalues();
// ROS_INFO_STREAM("\nmatrix_eigenvalues: \n"<<matrix_eigenvalues);for(int i=0; i<4; ++i) {if(matrix_eigenvalues(i).real() < 0)continue;double T = matrix_eigenvalues(i).real();double tmp_cost = T + 4.0/T * v0_square_sum - 12.0/(std::pow(T,2)) * v0_dp_sum + 12.0/std::pow(T,3) * dp_square_sum;ROS_INFO_STREAM("\nnow optimal_cost=" << optimal_cost <<", tmp_cost= " << tmp_cost);if(tmp_cost < optimal_cost) {ROS_INFO_STREAM("\n======now optimal_cost=" << optimal_cost <<", found lower cost= " << tmp_cost);optimal_cost = tmp_cost;}}ROS_INFO_STREAM("\nreturn optimal_cost=" << optimal_cost);return optimal_cost;
}

3. Reference
[1] A Computationally Efficient Motion Primitive for Quadrocopter Trajectory Generation, Mark W. Mueller,
Markus Hehn, and Raffaello D’Andrea.
[2] Dynamic Programming and Optimal Control, D. P. Bertsekas.
[3] https://blog.csdn.net/fb_941219/article/details/102984587
这篇关于【深蓝学院】移动机器人运动规划--第4章 动力学约束下的运动规划--作业的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







