本文主要是介绍2024 Flutter 重大更新,Dart 宏(Macros)编程开始支持,JSON 序列化有救,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
说起宏编程可能大家并不陌生,但是这对于 Flutter 和 Dart 开发者来说它一直是一个「遗憾」,这个「遗憾」体现在编辑过程的代码修改支持上,其中最典型的莫过于 Dart 的 JSON 序列化。
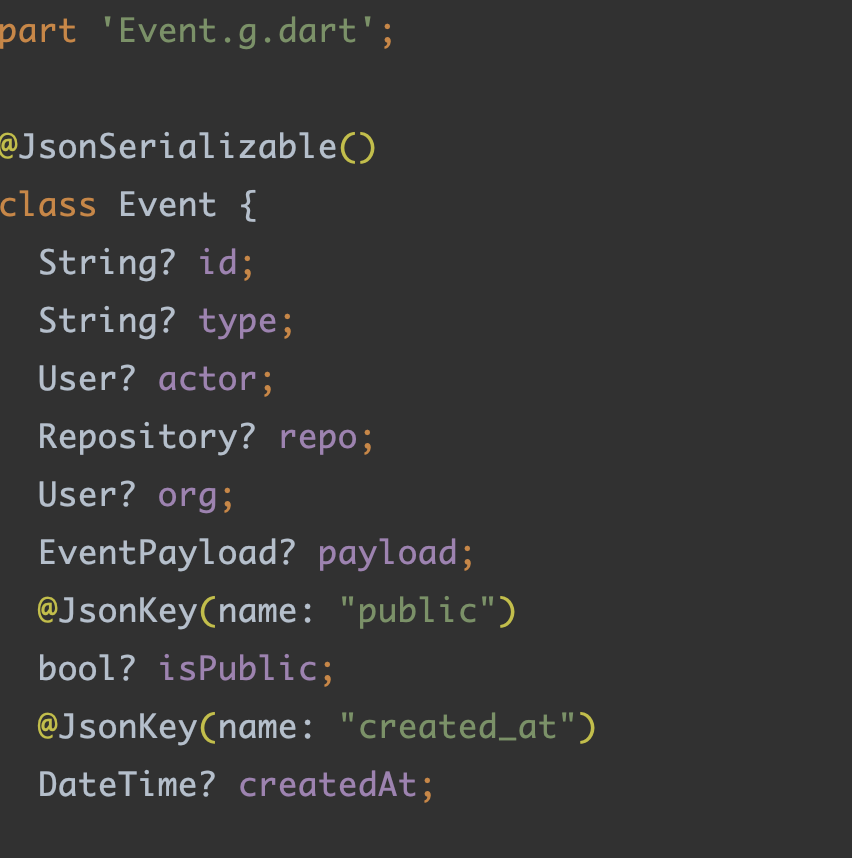
举个例子,目前 Dart 语言的 JSON 序列化高度依赖 build_runner 去生成 Dart 代码,例如在实际使用中我们需要:
- 依赖
json_serializable,通过注解声明一个Event对象 - 运行
flutter packages pub run build_runner build生成文件 - 得到
Event.g.dart文件,在项目中使用它去实现 JSON 的序列化和反序列化
 |  |
|---|
这里最大的问题在于,我们需要通过命令行去生成一个项目文件,并且这个文件我们还可以随意手动修改,从开发角度来说,这并不优雅也不方便。
而宏声明是用户定义的 Dart 类,它可以实现一个或多个新的内置宏接口,Dart 中的宏是用正常的命令式 Dart 代码来开发,不存在单独的“宏语言”。
大多数宏并不是简单地从头开始生成新代码,而是根据程序的现有属性去添加代码,例如向 Class 添加 JSON 序列化的宏,可能会查看 Class 声明的字段,并从中合成一个
toJson(),将这些字段序列化为 JSON 对象。
我们首先看一段官方的 Demo , 如下代码所示,可以看到 :
MyState添加了一个自定义的@AutoDispose()注解,这是一个开发者自己实现的宏声明,并且继承了State对象,带有dispose方法。- 在
MyState里有多个a、a2、b和c三个对象,其中a、a2、b都实现了Disposable接口,都有dispose方法 - 虽然
a、a2、b和MyState的dispose();方法来自不同基类实现,但是基于@AutoDispose()的实现,在代码调用state.dispose();时,a、a2、b变量的dispose方法也会被同步调用
import 'package:macro_proposal/auto_dispose.dart';void main() {var state = MyState(a: ADisposable(), b: BDisposable(), c: 'hello world');state.dispose();
}()
class MyState extends State {final ADisposable a;final ADisposable? a2;final BDisposable b;final String c;MyState({required this.a, this.a2, required this.b, required this.c});String toString() => 'MyState!';
}class State {void dispose() {print('disposing of $this');}
}class ADisposable implements Disposable {void dispose() {print('disposing of ADisposable');}
}class BDisposable implements Disposable {void dispose() {print('disposing of BDisposable');}
}如下图所示,可以看到,尽管 MyState 没用主动调用 a 、a2 、b 变量的 dispose 方法,并且它们和 MyState 的 dispose 也来自不同基类,但是最终执行所有 dispose 方法都被成功调用,这就是@AutoDispose() 的宏声明实现在编译时对代码进行了调整。

如下图所示是 @AutoDispose() 的宏编程实现,其中 macro 就是一个标志性的宏关键字,剩下的代码可以看到基本就是 dart 脚本的实现, macro 里主要是实现 ClassDeclarationsMacro 和buildDeclarationsForClass方法,如下代码可以很直观看到关于 super.dispose(); 和 disposeCalls 的相关实现。
import 'package:_fe_analyzer_shared/src/macros/api.dart';// Interface for disposable things.
abstract class Disposable {void dispose();
}macro class AutoDispose implements ClassDeclarationsMacro, ClassDefinitionMacro {const AutoDispose();void buildDeclarationsForClass(ClassDeclaration clazz, MemberDeclarationBuilder builder) async {var methods = await builder.methodsOf(clazz);if (methods.any((d) => d.identifier.name == 'dispose')) {// Don't need to add the dispose method, it already exists.return;}builder.declareInType(DeclarationCode.fromParts([// TODO: Remove external once the CFE supports it.'external void dispose();',]));}Future<void> buildDefinitionForClass(ClassDeclaration clazz, TypeDefinitionBuilder builder) async {var disposableIdentifier =// ignore: deprecated_member_useawait builder.resolveIdentifier(Uri.parse('package:macro_proposal/auto_dispose.dart'),'Disposable');var disposableType = await builder.resolve(NamedTypeAnnotationCode(name: disposableIdentifier));var disposeCalls = <Code>[];var fields = await builder.fieldsOf(clazz);for (var field in fields) {var type = await builder.resolve(field.type.code);if (!await type.isSubtypeOf(disposableType)) continue;disposeCalls.add(RawCode.fromParts(['\n',field.identifier,if (field.type.isNullable) '?','.dispose();',]));}// Augment the dispose method by injecting all the new dispose calls after// either a call to `augmented()` or `super.dispose()`, depending on if// there already is an existing body to call.//// If there was an existing body, it is responsible for calling// `super.dispose()`.var disposeMethod = (await builder.methodsOf(clazz)).firstWhere((method) => method.identifier.name == 'dispose');var disposeBuilder = await builder.buildMethod(disposeMethod.identifier);disposeBuilder.augment(FunctionBodyCode.fromParts(['{\n',if (disposeMethod.hasExternal || !disposeMethod.hasBody)'super.dispose();'else'augmented();',...disposeCalls,'}',]));}
}到这里大家应该可以直观感受到宏编程的魅力,上述 Demo 来自 dart-language 的 macros/example/auto_dispose_main ,其中 bin/ 目录下的代码是运行的脚本示例,lib/ 目录下的代码是宏编程实现的示例:
https://github.com/dart-lang/language/tree/main/working/macros/example
当然,因为现在是实验性阶段,API 和稳定性还有待商榷,所以想运行这些 Demo 还需要一些额外的处理,比如版本强关联,例如上述的 auto_dispose_main 例子:
-
需要 dart sdk 3.4.0-97.0.dev ,目前你可以通过 master 分支下载这个 dark-sdk https://storage.googleapis.com/dart-archive/channels/main/raw/latest/sdk/dartsdk-macos-arm64-release.zip
-
将 sdk 配置到环境变量,或者进入到 dart sdk 的 bin 目录执行 ./dart --version 检查版本
-
进入上诉的 example 下执行 dart pub get,过程可能会有点长

-
最后,执行
dart --enable-experiment=macros bin/auto_dispose_main.dart,记得这个 dart 是你指定版本的 dart 。
另外,还有一个第三方例子是来自 millsteed 的 macros ,这是一个简单的 JSON 序列化实现 Demo ,并且可以直接不用额外下载 dark-sdk,通过某个 flutter 内置 dart-sdk 版本就可以满足条件:3.19.0-12.0.pre :
在本地 Flutter 目录下,切换到
git checkout 3.19.0-12.0.pre,然后执行 flutter doctor 初始化 dark sdk 即可。
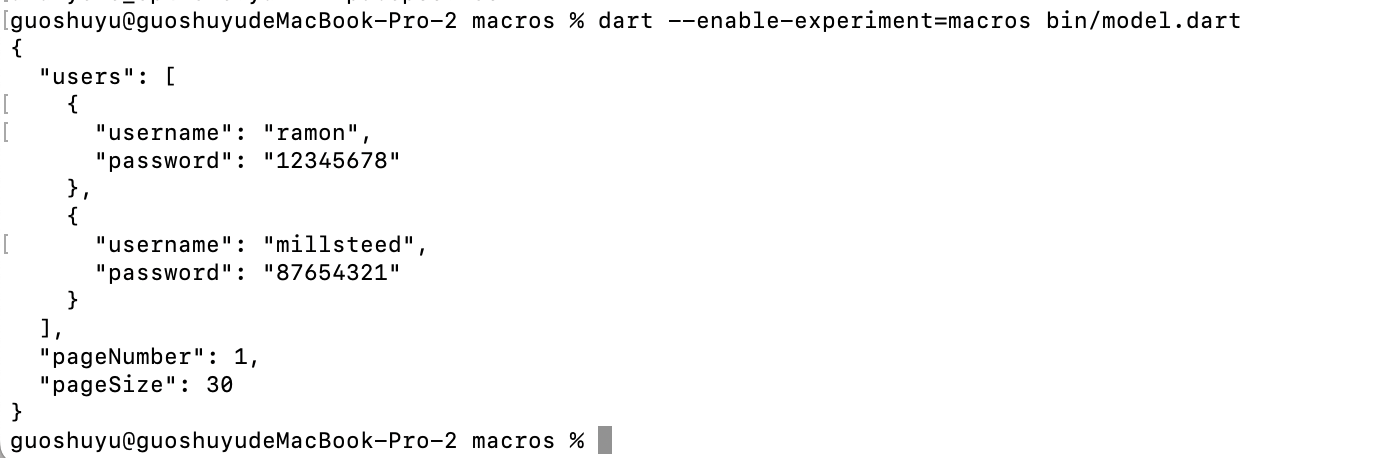
代码的实现很简单,首先看 bin 下的示例,通过 @Model() 将 GetUsersResponse 和 User 声明为 JSON 对象,然后在运行时,宏编程会自动添加 fromJson 和 toJson 方式。
import 'dart:convert';import 'package:macros/model.dart';()
class User {User({required this.username,required this.password,});final String username;final String password;
}()
class GetUsersResponse {GetUsersResponse({required this.users,required this.pageNumber,required this.pageSize,});final List<User> users;final int pageNumber;final int pageSize;
}void main() {const body = '''{"users": [{"username": "ramon","password": "12345678"}],"pageNumber": 1,"pageSize": 30}''';final json = jsonDecode(body) as Map<String, dynamic>;final response = GetUsersResponse.fromJson(json);final ramon = response.users.first;final millsteed = ramon.copyWith(username: 'millsteed', password: '87654321');final newResponse = response.copyWith(users: [...response.users, millsteed]);print(const JsonEncoder.withIndent(' ').convert(newResponse));
}
而 Model 的宏实现就相对复杂一些,但是实际上就是将类似 freezed/ json_serializable 是实现调整到宏实现了,而最终效果就是,开发者使用起来更加优雅了。
// ignore_for_file: depend_on_referenced_packages, implementation_importsimport 'dart:async';import 'package:_fe_analyzer_shared/src/macros/api.dart';macro class Model implements ClassDeclarationsMacro {const Model();static const _baseTypes = ['bool', 'double', 'int', 'num', 'String'];static const _collectionTypes = ['List'];Future<void> buildDeclarationsForClass(ClassDeclaration classDeclaration,MemberDeclarationBuilder builder,) async {final className = classDeclaration.identifier.name;final fields = await builder.fieldsOf(classDeclaration);final fieldNames = <String>[];final fieldTypes = <String, String>{};final fieldGenerics = <String, List<String>>{};for (final field in fields) {final fieldName = field.identifier.name;fieldNames.add(fieldName);final fieldType = (field.type.code as NamedTypeAnnotationCode).name.name;fieldTypes[fieldName] = fieldType;if (_collectionTypes.contains(fieldType)) {final generics = (field.type.code as NamedTypeAnnotationCode).typeArguments.map((e) => (e as NamedTypeAnnotationCode).name.name).toList();fieldGenerics[fieldName] = generics;}}final fieldTypesWithGenerics = fieldTypes.map((name, type) {final generics = fieldGenerics[name];return MapEntry(name,generics == null ? type : '$type<${generics.join(', ')}>',);},);_buildFromJson(builder, className, fieldNames, fieldTypes, fieldGenerics);_buildToJson(builder, fieldNames, fieldTypes);_buildCopyWith(builder, className, fieldNames, fieldTypesWithGenerics);_buildToString(builder, className, fieldNames);_buildEquals(builder, className, fieldNames);_buildHashCode(builder, fieldNames);}void _buildFromJson(MemberDeclarationBuilder builder,String className,List<String> fieldNames,Map<String, String> fieldTypes,Map<String, List<String>> fieldGenerics,) {final code = ['factory $className.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) {'.indent(2),'return $className('.indent(4),for (final fieldName in fieldNames) ...[if (_baseTypes.contains(fieldTypes[fieldName])) ...["$fieldName: json['$fieldName'] as ${fieldTypes[fieldName]},".indent(6),] else if (_collectionTypes.contains(fieldTypes[fieldName])) ...["$fieldName: (json['$fieldName'] as List<dynamic>)".indent(6),'.whereType<Map<String, dynamic>>()'.indent(10),'.map(${fieldGenerics[fieldName]?.first}.fromJson)'.indent(10),'.toList(),'.indent(10),] else ...['$fieldName: ${fieldTypes[fieldName]}'".fromJson(json['$fieldName'] "'as Map<String, dynamic>),'.indent(6),],],');'.indent(4),'}'.indent(2),].join('\n');builder.declareInType(DeclarationCode.fromString(code));}void _buildToJson(MemberDeclarationBuilder builder,List<String> fieldNames,Map<String, String> fieldTypes,) {final code = ['Map<String, dynamic> toJson() {'.indent(2),'return {'.indent(4),for (final fieldName in fieldNames) ...[if (_baseTypes.contains(fieldTypes[fieldName])) ...["'$fieldName': $fieldName,".indent(6),] else if (_collectionTypes.contains(fieldTypes[fieldName])) ...["'$fieldName': $fieldName.map((e) => e.toJson()).toList(),".indent(6),] else ...["'$fieldName': $fieldName.toJson(),".indent(6),],],'};'.indent(4),'}'.indent(2),].join('\n');builder.declareInType(DeclarationCode.fromString(code));}void _buildCopyWith(MemberDeclarationBuilder builder,String className,List<String> fieldNames,Map<String, String> fieldTypes,) {final code = ['$className copyWith({'.indent(2),for (final fieldName in fieldNames) ...['${fieldTypes[fieldName]}? $fieldName,'.indent(4),],'}) {'.indent(2),'return $className('.indent(4),for (final fieldName in fieldNames) ...['$fieldName: $fieldName ?? this.$fieldName,'.indent(6),],');'.indent(4),'}'.indent(2),].join('\n');builder.declareInType(DeclarationCode.fromString(code));}void _buildToString(MemberDeclarationBuilder builder,String className,List<String> fieldNames,) {final code = ['@override'.indent(2),'String toString() {'.indent(2),"return '$className('".indent(4),for (final fieldName in fieldNames) ...[if (fieldName != fieldNames.last) ...["'$fieldName: \$$fieldName, '".indent(8),] else ...["'$fieldName: \$$fieldName'".indent(8),],],"')';".indent(8),'}'.indent(2),].join('\n');builder.declareInType(DeclarationCode.fromString(code));}void _buildEquals(MemberDeclarationBuilder builder,String className,List<String> fieldNames,) {final code = ['@override'.indent(2),'bool operator ==(Object other) {'.indent(2),'return other is $className &&'.indent(4),'runtimeType == other.runtimeType &&'.indent(8),for (final fieldName in fieldNames) ...[if (fieldName != fieldNames.last) ...['$fieldName == other.$fieldName &&'.indent(8),] else ...['$fieldName == other.$fieldName;'.indent(8),],],'}'.indent(2),].join('\n');builder.declareInType(DeclarationCode.fromString(code));}void _buildHashCode(MemberDeclarationBuilder builder,List<String> fieldNames,) {final code = ['@override'.indent(2),'int get hashCode {'.indent(2),'return Object.hash('.indent(4),'runtimeType,'.indent(6),for (final fieldName in fieldNames) ...['$fieldName,'.indent(6),],');'.indent(4),'}'.indent(2),].join('\n');builder.declareInType(DeclarationCode.fromString(code));}
}extension on String {String indent(int length) {final space = StringBuffer();for (var i = 0; i < length; i++) {space.write(' ');}return '$space$this';}
}
目前宏还处于试验性质的阶段,所以 API 还在调整,这也是为什么上面的例子需要指定 dart 版本的原因,另外宏目前规划里还有一些要求,例如
- 所有宏构造函数都必须标记为
const - 所有宏必须至少实现其中一个
Macro接口 - 宏不能是抽象对象
- 宏 class 不能由其他宏生成
- 宏 class 不能包含泛型类型参数
- 每个宏接口都需要声明宏类必须实现的方法,例如,在声明阶段应用的
ClassDeclarationsMacro及其buildDeclarationsForClass方法。
未来规划里,宏 API 可能会作为 Pub 包提供,通过库 dart:_macros 来提供支持 ,具体还要等正式发布时 dart 团队的决策。
总的来说,这对于 dart 和 flutter 是一个重大的厉害消息,虽然宏编程并不是什么新鲜概念,该是 dart 终于可以优雅地实现 JSON 序列化,并且还是用 dart 来实现,这对于 flutter 开发者来说,无疑是最好的新年礼物。
所以,新年快乐~我们节后再见~
这篇关于2024 Flutter 重大更新,Dart 宏(Macros)编程开始支持,JSON 序列化有救的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





