本文主要是介绍PCL Kdtree 使用示例,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
PCL Kdtree 使用示例
文章目录
- PCL Kdtree 使用示例
- 一、关于 KDTree
- 二、关于最近邻搜索
- 三、复杂度分析
- 四、C++代码示例
- 五、关键函数说明
- nearestKSearch 函数说明
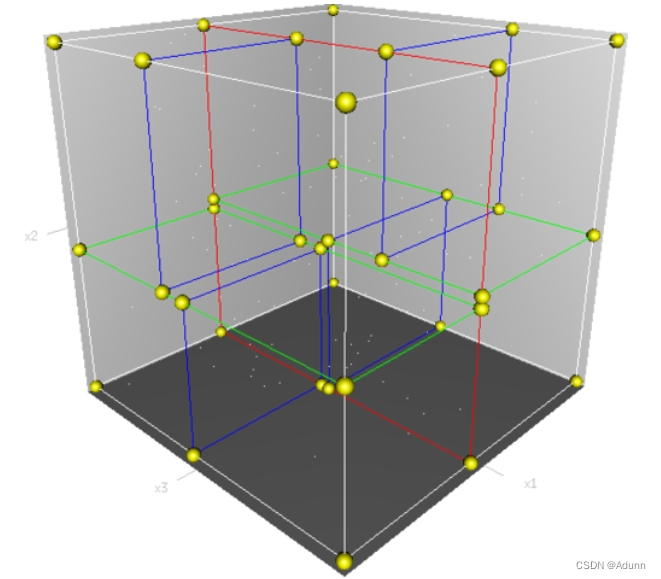
一、关于 KDTree
- 点云数据主要是, 表征 目标表面 的海量点集合, 并不具备传统实体网格数据的几何拓扑结构。
- 点云数据处理中最为核心的问题就是, 建立离散点间的拓扑关系, 实现基于邻域关系的快速查找。
- KDTree,即k-dimensional tree,是一种高维索引树形数据结构,常用于在大规模的高维数据空间进行最近邻查找(Nearest Neighbor)和近似最近邻查找(Approximate Nearest Neighbor),例如图像检索和识别中的高维图像特征向量的K近邻查找与匹配。
- KDTree的每一级(level)在指定维度上分开所有的子节点。在树的根部,所有的子节点在第一个维度上被分开(第一维坐标小于根节点的点将被分在左边的子树中,大于根节点的点将被分在右边的子树中)。树的每一级都在下一个维度上分开,所有其他的维度用完之后就回到第一个维度,直到你准备分类的最后一个树仅仅由有一个元素组成。
二、关于最近邻搜索
给定点p,查询数据集中与其距离最近点的过程即为最近邻搜索。
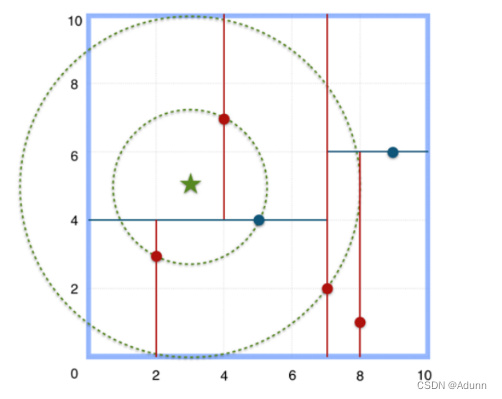
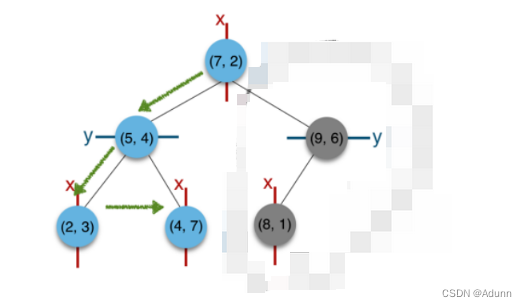
如在构建好的k-d tree上搜索(3,5)的最近邻时:
(1)首先从根节点(7,2)出发,将当前最近邻设为(7,2),对该k-d tree作深度优先遍历。以(3,5)为圆心,其到(7,2)的距离为半径画圆(多维空间为超球面),可以看出(8,1)右侧的区域与该圆不相交,所以(8,1)的右子树全部忽略。
(2) 接着走到(7,2)左子树根节点(5,4),与原最近邻对比距离后,更新当前最近邻为(5,4)。以(3,5)为圆心,其到(5,4)的距离为半径画圆,发现(7,2)右侧的区域与该圆不相交,忽略该侧所有节点,这样(7,2)的整个右子树被标记为已忽略。
(3) 遍历完(5,4)的左右叶子节点,发现与当前最优距离相等,不更新最近邻。所以(3,5)的最近邻为(5,4)。
三、复杂度分析
- 新增节点:平均复杂度为O(logn),最坏复杂度O(n);
- 删除节点:平均复杂度为O(logn),最坏复杂度O(n);
- 最近邻搜索: 平均复杂度为O(logn) ,最坏复杂度O(n);
四、C++代码示例
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree_flann.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <ctime>int main (int argc, char**argv)
{srand (time (NULL));pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>); // 创建一个PointCloud<PointXYZ> boost共享指针,并进行实例化为cloud// 随机生成一个1000个点的无序点云cloud->width =1000; // 注意因为cloud是指针,所以这里用->cloud->height =1;cloud->points.resize (cloud->width * cloud->height);for (size_t i=0; i< cloud->points.size (); ++i){cloud->points[i].x =1024.0f * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);cloud->points[i].y =1024.0f * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);cloud->points[i].z =1024.0f * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);}pcl::KdTreeFLANN<pcl::PointXYZ>kdtree; // 创建k-d tree对象kdtree.setInputCloud (cloud); // 将cloud设为k-d tree是搜索空间// 随机生成查询点pcl::PointXYZ searchPoint;searchPoint.x=1024.0f * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);searchPoint.y=1024.0f * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);searchPoint.z=1024.0f * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);int K =10;std::vector<int>pointIdxNKNSearch(K); // 设置一个整型的<vector>,用于存放第几近邻的索引std::vector<float>pointNKNSquaredDistance(K); // 设置一个浮点型的<vector>, 用于存放第几近邻与查询点的平方距离std::cout<<"K nearest neighbor search at ("<< searchPoint.x <<" "<< searchPoint.y <<" "<< searchPoint.z <<") with K="<< K <<std::endl;if ( kdtree.nearestKSearch (searchPoint, K, pointIdxNKNSearch, pointNKNSquaredDistance) >0 ) // 如果找到了近邻点{for (size_t i=0; i<pointIdxNKNSearch.size (); ++i){std::cout<<" "<< cloud->points[ pointIdxNKNSearch[i] ].x <<" "<< cloud->points[pointIdxNKNSearch[i] ].y <<" "<< cloud->points[pointIdxNKNSearch[i] ].z <<" (squared distance: "<<pointNKNSquaredDistance[i] <<")"<<std::endl;}}std::vector<int> pointIdxRadiusSearch;std::vector<float> pointRadiusSquaredDistance;float radius =256.0f * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f); // 设置半径阈值std::cout<<"Neighbors within radius search at ("<<searchPoint.x <<" "<<searchPoint.y<<" "<<searchPoint.z<<") with radius="<< radius <<std::endl;if ( kdtree.radiusSearch (searchPoint, radius, pointIdxRadiusSearch, pointRadiusSquaredDistance) >0 ){for (size_t i=0; i<pointIdxRadiusSearch.size (); ++i)std::cout<<" "<< cloud->points[ pointIdxRadiusSearch[i] ].x <<" "<< cloud->points[pointIdxRadiusSearch[i] ].y <<" "<< cloud->points[pointIdxRadiusSearch[i] ].z <<" (squared distance: "<<pointRadiusSquaredDistance[i] <<")"<<std::endl;}return 0;
}五、关键函数说明
nearestKSearch 函数说明
/** \brief Search for k-nearest neighbors for the given query point.* * \attention This method does not do any bounds checking for the input index* (i.e., index >= cloud.points.size () || index < 0), and assumes valid (i.e., finite) data.* * \param[in] point a given \a valid (i.e., finite) query point* \param[in] k the number of neighbors to search for* \param[out] k_indices the resultant indices of the neighboring points (must be resized to \a k a priori!)* \param[out] k_sqr_distances the resultant squared distances to the neighboring points (must be resized to \a k * a priori!)* \return number of neighbors found* * \exception asserts in debug mode if the index is not between 0 and the maximum number of points*/
int
nearestKSearch (const PointT &point, int k,std::vector<int> &k_indices, std::vector<float> &k_sqr_distances) const override;-
第一个参数:要查询的点
-
第二个参数:找top几最近邻
-
第三个参数:一个vector,执行后这里面存放找到的top几最近邻的索引(也就是指点云数据集中的第几个点)
-
第四个参数:一个vector,执行后这里面存放找到的top几最近邻到查询点的平方距离 这个函数返回找到的近邻点的数量
radiusSearch 函数说明
/** \brief Search for all the nearest neighbors of the query point in a given radius.* * \attention This method does not do any bounds checking for the input index* (i.e., index >= cloud.points.size () || index < 0), and assumes valid (i.e., finite) data.* * \param[in] point a given \a valid (i.e., finite) query point* \param[in] radius the radius of the sphere bounding all of p_q's neighbors* \param[out] k_indices the resultant indices of the neighboring points* \param[out] k_sqr_distances the resultant squared distances to the neighboring points* \param[in] max_nn if given, bounds the maximum returned neighbors to this value. If \a max_nn is set to* 0 or to a number higher than the number of points in the input cloud, all neighbors in \a radius will be* returned.* \return number of neighbors found in radius** \exception asserts in debug mode if the index is not between 0 and the maximum number of points*/
int
radiusSearch (const PointT &point, double radius, std::vector<int> &k_indices,std::vector<float> &k_sqr_distances, unsigned int max_nn = 0) const override;- 第一个参数:要查询的点
- 第二个参数:搜索半径阈值
- 第三个参数:一个vector,执行后这里面存放找到的top几最近邻的索引(也就是指点云数据集中的第几个点)
- 第四个参数:一个vector,执行后这里面存放找到的top几最近邻到查询点的平方距离
- 第五个参数:最多找几个近邻。如果设置为0或者大于点云数据中的数据数量,则返回满足阈值的所偶近邻
- 这个函数返回找到的近邻点的数量
这篇关于PCL Kdtree 使用示例的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






