本文主要是介绍RISC Zero的Babybear域 及其 扩域,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1. 引言
前序博客见:
- 有限域的Fast Multiplication和Modular Reduction算法实现
代码实现见:
- https://github.com/risc0/risc0/blob/main/risc0/core/src/field/baby_bear.rs
- https://github.com/risc0/risc0/tree/main/risc0/circuit/rv32im-sys/cxx
- https://github.com/risc0/risc0/blob/main/risc0/circuit/recursion-sys/cxx
- https://github.com/risc0/risc0/tree/main/risc0/build_kernel/kernels/cuda(Babybear域 及其 扩域 的CUDA代码实现)
- https://github.com/risc0/risc0/tree/main/risc0/build_kernel/kernels/metal(Babybear域 及其 扩域 的Metal代码实现)
Babybear域 F p \mathbb{F}_p Fp,其中 p = 2 31 − 2 17 + 1 = 15 ∗ 2 17 + 1 p=2^{31}-2^{17}+1=15*2^{17}+1 p=231−217+1=15∗217+1,取其4-th 扩域 F p 4 \mathbb{F}_{p^4} Fp4的不可约多项式为 x 4 − 11 x^4-11 x4−11。对应的sagemath验证脚本为:
sage: p=2**31-2**27+1
....: R.<x> = GF(p)[]
....: (x^4 - 11).is_irreducible()
True
对应的域定义为:
/// The BabyBear class is an element of the finite field F_p, where P is the
/// prime number 15*2^27 + 1. Put another way, Fp is basically integer
/// arithmetic modulo P.
///
/// The `Fp` datatype is the core type of all of the operations done within the
/// zero knowledge proofs, and is the smallest 'addressable' datatype, and the
/// base type of which all composite types are built. In many ways, one can
/// imagine it as the word size of a very strange architecture.
///
/// This specific prime P was chosen to:
/// - Be less than 2^31 so that it fits within a 32 bit word and doesn't
/// overflow on addition.
/// - Otherwise have as large a power of 2 in the factors of P-1 as possible.
///
/// This last property is useful for number theoretical transforms (the fast
/// fourier transform equivelant on finite fields). See NTT.h for details.
///
/// The Fp class wraps all the standard arithmetic operations to make the finite
/// field elements look basically like ordinary numbers (which they mostly are).
#[derive(Eq, Clone, Copy, Pod, Zeroable)]
#[repr(transparent)]
pub struct Elem(u32); //F_p
/// Alias for the Baby Bear [Elem]
pub type BabyBearElem = Elem;/// The size of the extension field in elements, 4 in this case.
const EXT_SIZE: usize = 4;/// Instances of `ExtElem` are elements of a finite field `F_p^4`. They are
/// represented as elements of `F_p[X] / (X^4 - 11)`. This large
/// finite field (about `2^128` elements) is used when the security of
/// operations depends on the size of the field. The field extension `ExtElem`
/// has `Elem` as a subfield, so operations on elements of each are compatible.
/// The irreducible polynomial `x^4 - 11` was chosen because `11` is
/// the smallest choice of `B` for `x^4 - B` that makes this polynomial
/// irreducible.
#[derive(Eq, Clone, Copy, Pod, Zeroable)]
#[repr(transparent)]
pub struct ExtElem([Elem; EXT_SIZE]); //F_{p^4}扩域/* struct Fp4 {/// The elements of Fp4, elems[0] + elems[1]*X + elems[2]*X^2 + elems[3]*x^4Fp elems[4];....} */
根据 有限域的Fast Multiplication和Modular Reduction算法实现,BabyBear域运算采用Montgomery形式:
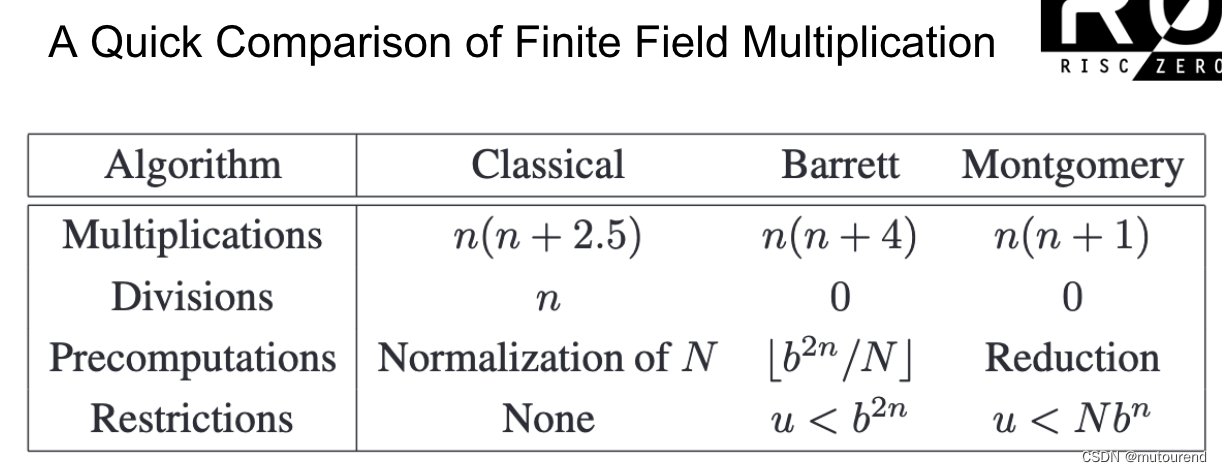
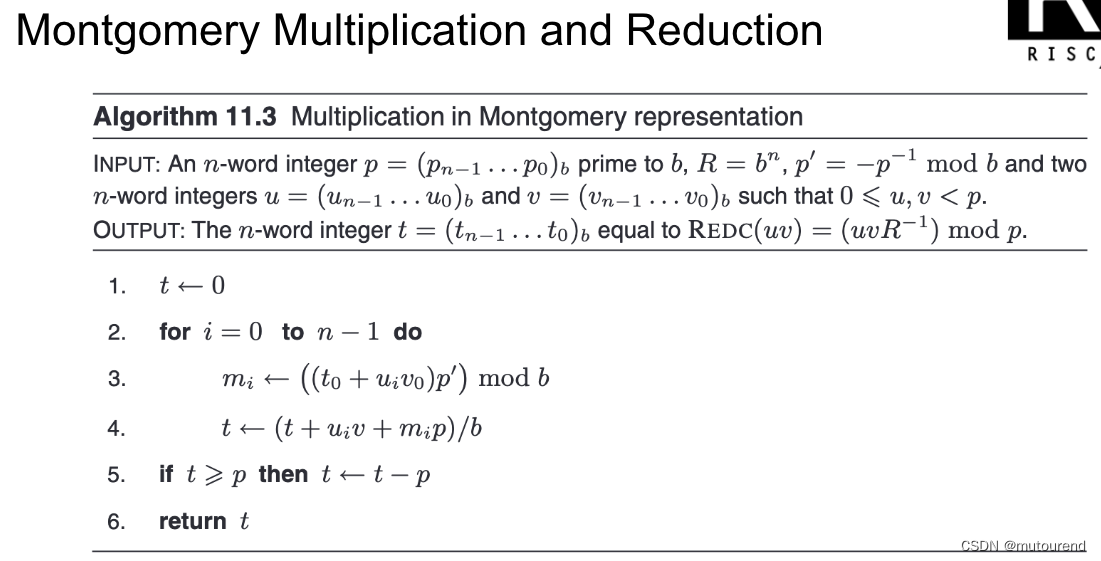
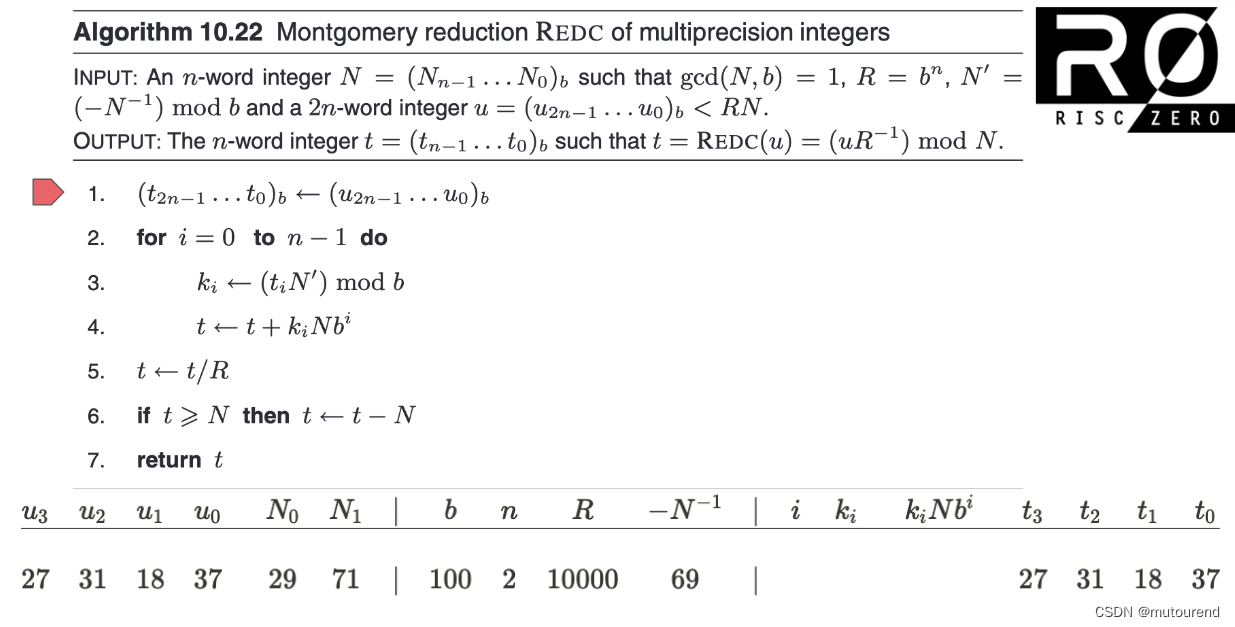
鉴于单个Babybear域元素可 以32位整数表示,2个Babybear域元素 0 ≤ u , v < p 0\leq u,v <p 0≤u,v<p 乘积可 以64位整数表示,且无需考虑进位情况。对应为:
- b = 2 32 b=2^{32} b=232
- n = 1 n=1 n=1
- R = b n = 2 32 R=b^n=2^{32} R=bn=232
- 实际代码实现时,由于 n = 1 n=1 n=1,可预计算出相应的R2值为
mod(r^2, p),相应的M值为mod(1/p,r)。
sage: p=2**31-2**27+1
sage: r=2**32
sage: mod(r^2, p)
1172168163
sage: mod(1/p,r)
2281701377
sage: hex(2281701377)
'0x88000001'
/// Wrapping multiplication of [Elem] using Baby Bear field modulus
// Copied from the C++ implementation (fp.h)
const fn mul(lhs: u32, rhs: u32) -> u32 {// uint64_t o64 = uint64_t(a) * uint64_t(b);let mut o64: u64 = (lhs as u64).wrapping_mul(rhs as u64);// uint32_t low = -uint32_t(o64);let low: u32 = 0u32.wrapping_sub(o64 as u32);// uint32_t red = M * low;let red = M.wrapping_mul(low);// o64 += uint64_t(red) * uint64_t(P);o64 += (red as u64).wrapping_mul(P_U64);// uint32_t ret = o64 >> 32;let ret = (o64 >> 32) as u32;// return (ret >= P ? ret - P : ret);if ret >= P {ret - P} else {ret}
}/// Encode to Montgomery form from direct form.
const fn encode(a: u32) -> u32 {mul(R2, a)
}/// Decode from Montgomery form from direct form.
const fn decode(a: u32) -> u32 {mul(1, a)
}
RISC Zero系列博客
- RISC0:Towards a Unified Compilation Framework for Zero Knowledge
- Risc Zero ZKVM:zk-STARKs + RISC-V
- 2023年 ZK Hack以及ZK Summit 9 亮点记
- RISC Zero zkVM 白皮书
- Risc0:使用Continunations来证明任意EVM交易
- Zeth:首个Type 0 zkEVM
- RISC Zero项目简介
- RISC Zero zkVM性能指标
- Continuations:扩展RISC Zero zkVM支持(无限)大计算
- A summary on the FRI low degree test前2页导读
- Reed-Solomon Codes及其与RISC Zero zkVM的关系
- RISC Zero zkVM架构
- RISC-V与RISC Zero zkVM的关系
- 有限域的Fast Multiplication和Modular Reduction算法实现
- RISC Zero的Bonsai证明服务
- RISC Zero ZKP协议中的商多项式
- FRI的Commit、Query以及FRI Batching内部机制
- RISC Zero的手撕STARK
- RISC Zero zkVM guest程序优化技巧 及其 与物理CPU的关键差异
- ZK*FM:RISC Zero zkVM的形式化验证
- Zirgen MLIR:RISC-Zero的ZK-circuits形式化验证
- 以RISC Zero ZK Fraud Proof赋能Optimistic Rollups
- zkSummit10 亮点记
- 技术探秘:在RISC Zero中验证FHE——由隐藏到证明:FHE验证的ZK路径(1)
- 技术探秘:在RISC Zero中验证FHE——RISC Zero应用的DevOps(2)
- RISC Zero STARK证明系统时序图及规范
- RISC Zero zkVM Host & Guest 101
- RISC Zero zk-STARK证明系统代码解析
这篇关于RISC Zero的Babybear域 及其 扩域的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








