本文主要是介绍对@SpringBootApplication注解的一些简单理解,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
@SpringBootApplication
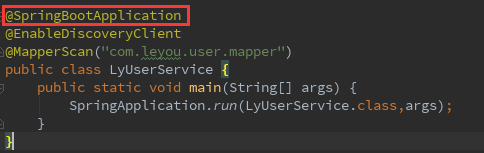
点进去这个注解看它的源码,如下:
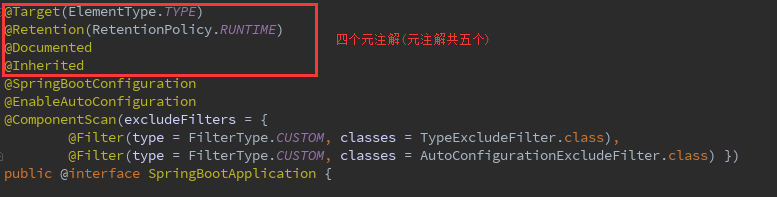
接下来先分析这四个元注解:
- @Target:限定注解运用的场景
- 此处是
@Target(ElementType.TYPE):限定给一个类型进行注解,比如类、接口、枚举 - 除此以外还有:
ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE 可以给一个注解进行注解
ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR 可以给构造方法进行注解
ElementType.FIELD 可以给属性进行注解
ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE 可以给局部变量进行注解
ElementType.METHOD 可以给方法进行注解
ElementType.PACKAGE 可以给一个包进行注解
ElementType.PARAMETER 可以给一个方法内的参数进行注解
- 此处是
- @Retention:该注解定义了这个注解存活的时间
- 此处是
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME),表明该注解可以保留到程序运行时,会被加载进JVM,运行时可以获得到他们,因此@SpringBootApplication可以在程序运行时被获取到,它的生存周期很长。常见的@Autowired注解就是运行期注解 - RetentionPolicy.SOURCE 注解只在源码阶段保留,在编译器进行编译时它将被丢弃忽视。
RetentionPolicy.CLASS 注解只被保留到编译进行的时候,它并不会被加载到 JVM 中。常见的编译期注解:@Override
- 此处是
- @Documented:注解信息会被包含到Javadoc文档中
- @Inherited:如果一个超类被 【【@Inherited 注解过】的注解】 进行注解的话,那么如果它的子类没有被任何注解应用的话,那么这个子类就继承了超类的注解
综上:@SpringBootApplication是一个被限定给类、接口进行注解的运行期注解,并且被@SpringBootApplication注解的类的子类没有被注解的话,子类可以继承该注解
除了上述四个注解,还有一个元注解:@Repeatable,JDK1.8新加入进来的,算是一个新特性,通常是注解的值可以同时取多个(比如一个Person身兼数职,既是学生又是兼职家教老师)
除去上面四个元注解,还有三个关键性的注解:
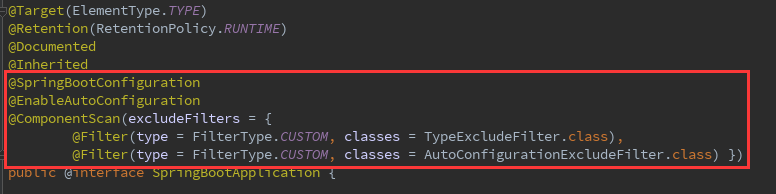
1.@SpringBootConfiguration:Spring Boot项目的配置注解
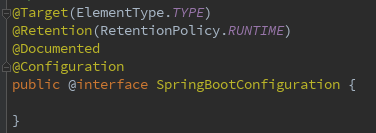
可以看到,@SpringBootConfiguration也是一个复合注解,但是前三个我们一句熟悉了,只有最后一个 @Configuration:它的作用是声明了这是一个配置类
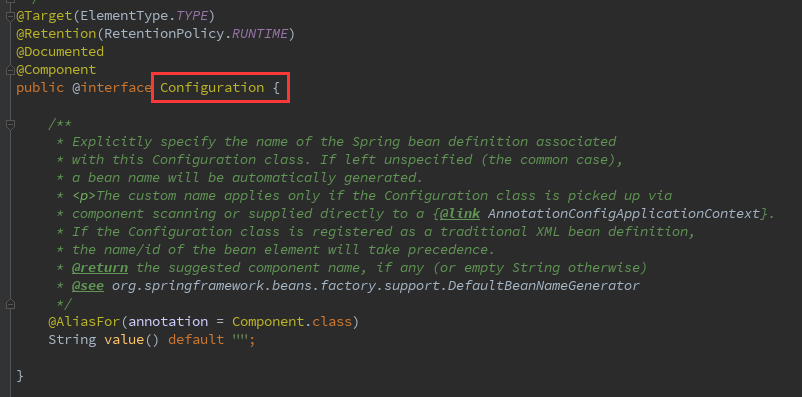
2.@EnableAutoConfiguration:完成自动配置,该注解会使Spring Boot根据项目中依赖的jar包自动配置项目的配置项
* Enable auto-configuration of the Spring Application Context, attempting to guess and* configure beans that you are likely to need. Auto-configuration classes are usually* applied based on your classpath and what beans you have defined. For example, if you* have {@code tomcat-embedded.jar} on your classpath you are likely to want a* {@link TomcatServletWebServerFactory} (unless you have defined your own* {@link ServletWebServerFactory} bean).* <p>* When using {@link SpringBootApplication}, the auto-configuration of the context is* automatically enabled and adding this annotation has therefore no additional effect.* <p>* Auto-configuration tries to be as intelligent as possible and will back-away as you* define more of your own configuration. You can always manually {@link #exclude()} any* configuration that you never want to apply (use {@link #excludeName()} if you don't* have access to them). You can also exclude them via the* {@code spring.autoconfigure.exclude} property. Auto-configuration is always applied* after user-defined beans have been registered.* <p>* The package of the class that is annotated with {@code @EnableAutoConfiguration},* usually via {@code @SpringBootApplication}, has specific significance and is often used* as a 'default'. For example, it will be used when scanning for {@code @Entity} classes.* It is generally recommended that you place {@code @EnableAutoConfiguration} (if you're* not using {@code @SpringBootApplication}) in a root package so that all sub-packages* and classes can be searched.* <p>* Auto-configuration classes are regular Spring {@link Configuration} beans. They are* located using the {@link SpringFactoriesLoader} mechanism (keyed against this class).* Generally auto-configuration beans are {@link Conditional @Conditional} beans (most* often using {@link ConditionalOnClass @ConditionalOnClass} and* {@link ConditionalOnMissingBean @ConditionalOnMissingBean} annotations).
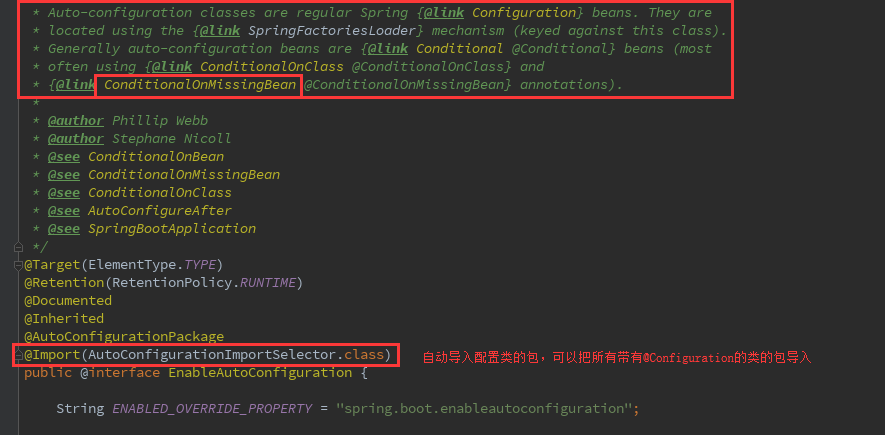
public @interface ConditionalOnMissingBean{…}
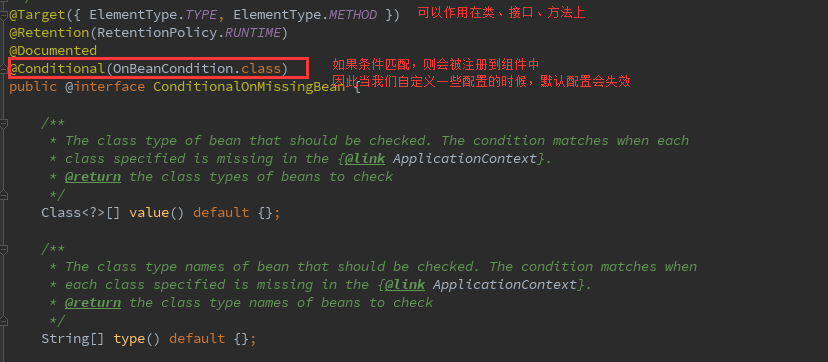
@Inherited注解会超类来找依赖中的类,完成自动初始化类加载
3.@ComponentScan:用注解配置实现自动扫描,默认会扫描当前包和所有子包,和xml配置自动扫描效果一样,@Filter是排除了两个类
* Configures component scanning directives for use with @{@link Configuration} classes.* Provides support parallel with Spring XML's {@code <context:component-scan>} element.** <p>Either {@link #basePackageClasses} or {@link #basePackages} (or its alias* {@link #value}) may be specified to define specific packages to scan. If specific* packages are not defined, scanning will occur from the package of the* class that declares this annotation.** <p>Note that the {@code <context:component-scan>} element has an* {@code annotation-config} attribute; however, this annotation does not. This is because* in almost all cases when using {@code @ComponentScan}, default annotation config* processing (e.g. processing {@code @Autowired} and friends) is assumed. Furthermore,* when using {@link AnnotationConfigApplicationContext}, annotation config processors are* always registered, meaning that any attempt to disable them at the* {@code @ComponentScan} level would be ignored.** <p>See {@link Configuration @Configuration}'s Javadoc for usage examples.
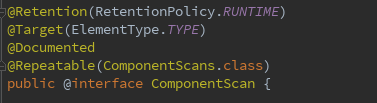
@ComponentScan 注解会自动扫描指定包下的全部标有 @Component注解 的类包括 @Component 下的子注解@Service、@Repository、@Controller等,并注册成bean
这篇关于对@SpringBootApplication注解的一些简单理解的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





