本文主要是介绍获取网络接口信息——ioctl()函数与结构体struct ifreq、 struct ifconf,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
http://blog.csdn.net/windeal3203/article/details/39320605
Linux 下 可以使用ioctl()函数 以及 结构体 struct ifreq 结构体struct ifconf来获取网络接口的各种信息。
ioctl
首先看ioctl()用法
ioctl()原型如下:
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
int ioctl(int fd, int request, ...);
参数:
fd : 文件描述符
request: 表示要请求的信息。如IP地址、网络掩码等
... : 后面的可变参数根据request而定
比如我们请求所有网络接口的清单:
- struct ifconf IoCtlReq;
- ...
- ioctl( Sock, SIOCGIFCONF, &IoCtlReq )
其中 IoCtlReq 是一个
与接口相关的request如下表所示( 来源: < http://baike.baidu.com/view/1081282.htm?fr=aladdin > ):
| 接 口 | SIOCGIFCONF SIOCSIFADDR SIOCGIFADDR SIOCSIFFLAGS SIOCGIFFLAGS SIOCSIFDSTADDR SIOCGIFDSTADDR SIOCGIFBRDADDR SIOCSIFBRDADDR SIOCGIFNETMASK SIOCSIFNETMASK SIOCGIFMETRIC SIOCSIFMETRIC SIOCGIFMTU SIOCxxx | 获取所有接口的清单 设置接口地址 获取接口地址 设置接口标志 获取接口标志 设置点到点地址 获取点到点地址 获取广播地址 设置广播地址 获取子网掩码 设置子网掩码 获取接口的测度 设置接口的测度 获取接口MTU (还有很多取决于系统的实现) | struct ifconf struct ifreq struct ifreq struct ifreq struct ifreq struct ifreq struct ifreq struct ifreq struct ifreq struct ifreq struct ifreq struct ifreq struct ifreq struct ifreq
|
关于ioctl的详细解释清查阅本博其它博文
结构体 struct ifreq用来保存某个接口的信息。
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- struct ifreq {
- #define IFHWADDRLEN 6
- union
- {
- char ifrn_name[IFNAMSIZ];
- } ifr_ifrn;
-
- union {
- struct sockaddr ifru_addr;
- struct sockaddr ifru_dstaddr;
- struct sockaddr ifru_broadaddr;
- struct sockaddr ifru_netmask;
- struct sockaddr ifru_hwaddr;
- short ifru_flags;
- int ifru_ivalue;
- int ifru_mtu;
- struct ifmap ifru_map;
- char ifru_slave[IFNAMSIZ];
- char ifru_newname[IFNAMSIZ];
- void __user * ifru_data;
- struct if_settings ifru_settings;
- } ifr_ifru;
- };
- #define ifr_name ifr_ifrn.ifrn_name /* interface name */
- #define ifr_hwaddr ifr_ifru.ifru_hwaddr /* MAC address */
- #define ifr_addr ifr_ifru.ifru_addr /* address */
- #define ifr_dstaddr ifr_ifru.ifru_dstaddr /* other end of p-p lnk */
- #define ifr_broadaddr ifr_ifru.ifru_broadaddr /* broadcast address */
- #define ifr_netmask ifr_ifru.ifru_netmask /* interface net mask */
- #define ifr_flags ifr_ifru.ifru_flags /* flags */
- #define ifr_metric ifr_ifru.ifru_ivalue /* metric */
- #define ifr_mtu ifr_ifru.ifru_mtu /* mtu */
- #define ifr_map ifr_ifru.ifru_map /* device map */
- #define ifr_slave ifr_ifru.ifru_slave /* slave device */
- #define ifr_data ifr_ifru.ifru_data /* for use by interface */
- #define ifr_ifindex ifr_ifru.ifru_ivalue /* interface index */
- #define ifr_bandwidth ifr_ifru.ifru_ivalue /* link bandwidth */
- #define ifr_qlen ifr_ifru.ifru_ivalue /* Queue length */
- #define ifr_newname ifr_ifru.ifru_newname /* New name */
- #define ifr_settings ifr_ifru.ifru_settings /* Device/proto settings*/
ifr_name 标识了某一接口。
可以通过ioctl获取该接口的信息。如:
ioctl(Sock, SIOCGIFNETMASK, &IfReq);//获取网络接口地址掩码
该代码需要先对IfReq->ifr_name赋值,然后获取与 IfReq->ifr_name向匹配的网络接口 的地址掩码
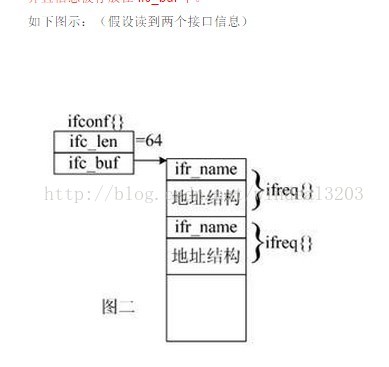
struct ifconf
结构体struct ifconf通常用来保存所有接口信息
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- struct ifconf {
- int ifc_len;
- union {
- char __user *ifcu_buf;
- struct ifreq __user *ifcu_req;
- } ifc_ifcu;
- };
- #define ifc_buf ifc_ifcu.ifcu_buf /* buffer address */
- #define ifc_req ifc_ifcu.ifcu_req /* array of structures */
该结构体可以用来获取所哟网络接口的名字和信息(不是全部信息,是ip地址)
(图片来自: http://tech.sunplusedu.com/space/post-4064.aspx )
Example:
- #include <sys/types.h>
- #include <sys/ioctl.h>
- #include <sys/socket.h>
- #include <net/if.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <netdb.h>
- #include <string.h>
- #include <fcntl.h>
- #include <string.h>
- #include <errno.h>
- typedef uint32_t uint32;
- #define MAX_IF 10
- int
- main()
- {
- struct ifreq ifVec[MAX_IF];
-
- int sock = -1;
- if ( (sock = socket( AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0 )) < 0 )
- fprintf(stderr, "Error:%d, cannot open RAM;\n");
-
-
- struct ifconf ioIfConf;
- ioIfConf.ifc_buf = (void *)ifVec;
- ioIfConf.ifc_len = sizeof(ifVec);
- printf("Len:%d\n", ioIfConf.ifc_len);
-
- if (ioctl(sock, SIOCGIFCONF, &ioIfConf) < 0 )
- fprintf(stderr, "Error:%d ioctl IFCONF\n");
-
- printf("Len:%d\n", ioIfConf.ifc_len);
-
- {
- struct ifreq *ifPt;
- struct ifreq *ifEndPt;
- ifPt = ifVec;
- ifEndPt = (void *)((char *)ifVec + ioIfConf.ifc_len);
- for (ifPt = ifVec; ifPt < ifEndPt; ifPt++)
- {
- struct ifreq ifReq;
- if ( ifPt->ifr_addr.sa_family != AF_INET ) {
- continue;
- }
-
-
- uint32 u32_addr, u32_mask;
-
-
- char ipDotBuf[16], subnetDotBuf[16], maskDotBuf[16];
- u32_addr = ((struct sockaddr_in *)&ifPt->ifr_addr)->sin_addr.s_addr;
- inet_ntop(AF_INET, &u32_addr, ipDotBuf, (socklen_t )sizeof(ipDotBuf));
- printf("IP Address: %s\n", ipDotBuf);
-
-
- bzero(&ifReq,sizeof(struct ifreq));
- memcpy(ifReq.ifr_name, ifPt->ifr_name, sizeof(ifReq.ifr_name));
- if (ioctl(sock, SIOCGIFNETMASK, &ifReq ) < 0){
- fprintf(stderr, "Error: %d, cannot get mask\n", errno);
- }
- else{
- u32_mask = ((struct sockaddr_in *)&ifReq.ifr_addr)->sin_addr.s_addr;
- inet_ntop(AF_INET, &u32_mask, maskDotBuf, (socklen_t )sizeof(maskDotBuf));
- printf("Mask: %s\n", maskDotBuf);
- }
-
- bzero(&ifReq,sizeof(struct ifreq));
- memcpy(ifReq.ifr_name, ifPt->ifr_name, sizeof(ifReq.ifr_name));
- if (ioctl(sock, SIOCGIFMTU, &ifReq ) < 0){
- fprintf(stderr, "Error: %d, cannot get MTU\n", errno);
- }
- else{
- printf("SIOCGIFMTU:%d\n", ifReq.ifr_mtu);
- }
-
- }
- }
-
-
-
- }
运行结果:
- windeal@ubuntu:~/Windeal/apue$ ./exe
- Len:320
- Len:64
- IP Address: 127.0.0.1
- Mask: 255.0.0.0
- SIOCGIFMTU:16436
- IP Address: 172.17.92.198
- Mask: 255.255.254.0
- SIOCGIFMTU:1500
- windeal@ubuntu:~/Windeal/apue$
这篇关于获取网络接口信息——ioctl()函数与结构体struct ifreq、 struct ifconf的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!