本文主要是介绍Java并发工具类---ForkJoin、countDownlatch、CyclicBarrier、Semaphore,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、Fork Join
fork join是JDK7引入的一种并发框架,采用分而治之的思想来处理并发任务
ForkJoin框架底层实现了工作窃取,当一个线程完成任务处于空闲状态时,会窃取其他工作线程的任务来做,这样可以充分利用线程来进行并行计算,减少线程竞争。但是在某些情况下也会存在竞争。
Fork Join框架局限性:
1.拆分任务中不应该去执行IO操作
2.任务不能检查抛出异常,必须通过必要的代码来抛出异常。这个在源码中就可以体现,很多地方都是通过代码主动抛出异常。
3.任务只能使用Fork和Join操作来进行同步机制,如果使用了其他同步机制,则在同步操作时,工作线程就不能执行其他任务了。比如,在Fork/Join框架中,使任务进行了睡眠,那么,在睡眠期间内,正在执行这个任务的工作线程将不会执行其他任务了。
Demo:
ForkJoin进行累加计算
public class MakeArray {public static final int ARRAY_LENGTH=4000;//获取一个随机数的数组public static int[] makeArray(){Random r=new Random();int[] res=new int[ARRAY_LENGTH];for(int i=0;i<ARRAY_LENGTH;i++){res[i]=r.nextInt(ARRAY_LENGTH*3);}return res;}
}public class SumArray {private static class SumTask extends RecursiveTask<Integer>{private final static int THRESHOLD=MakeArray.ARRAY_LENGTH/10;private int[] src;private int fromIndex;private int toIndex;public SumTask(int[] src, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {this.src = src;this.fromIndex = fromIndex;this.toIndex = toIndex;}@Overrideprotected Integer compute() {if(toIndex-fromIndex<THRESHOLD){//无需再拆分int count=0;for(int i=fromIndex;i<=toIndex;i++){try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1);count+=src[i];} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}return count;}else{int mid=(fromIndex+toIndex)/2;SumTask left=new SumTask(src,fromIndex,mid);SumTask right=new SumTask(src,mid+1,toIndex);invokeAll(left,right); //执行任务,把任务添加到队列,该方法中执行了forkreturn left.join()+right.join(); //合并结果}}}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] src=MakeArray.makeArray();ForkJoinPool pool=new ForkJoinPool();SumTask innerFind=new SumTask(src,0,src.length-1);long start=System.currentTimeMillis();pool.invoke(innerFind);System.out.println("The count is "+innerFind.join()+" spend time:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start)+" ms");}
}
运行结果:

采用单线程进行对比:
public class SumNormal {public static void main(String[] args) {int count=0;int[] src=MakeArray.makeArray();long start=System.currentTimeMillis();for(int i=0;i<src.length;i++){try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1);count+=src[i];} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}System.out.println("The count is "+count+" spend time:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start)+"ms");}
}
二、countDownlatch
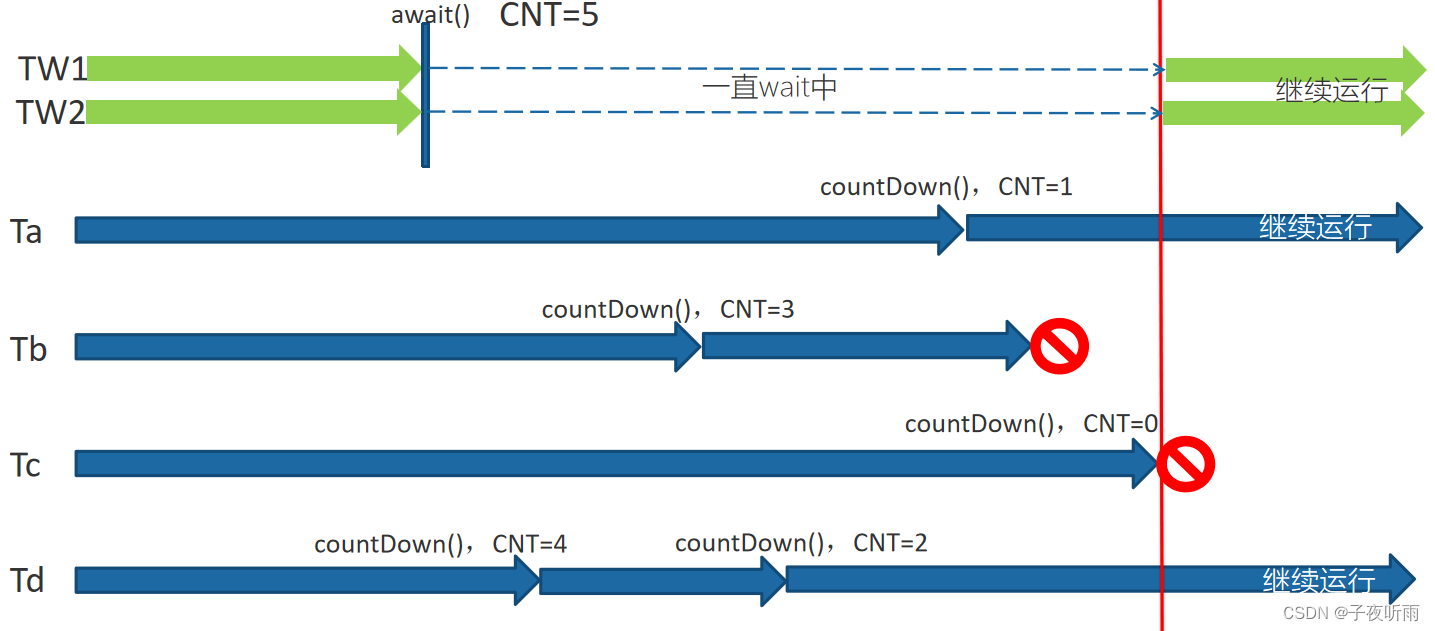
countDownlatch也是一个java的同步工具类,它通过计数器来控制线程的执行顺序。初始化时需要初始化计数器的值,一般都是线程数量。每当一个线程执行完任务,计数器减一,当计数器为0,等待的线程就可以恢复执行任务。
需注意: 计数器的值不一定就是线程数量,线程中可以多次调用countDown来使计数器减一。
执行减一操作后,线程不一定要终止,也可以继续执行任务(如上图Ta,Td)。
Demo:
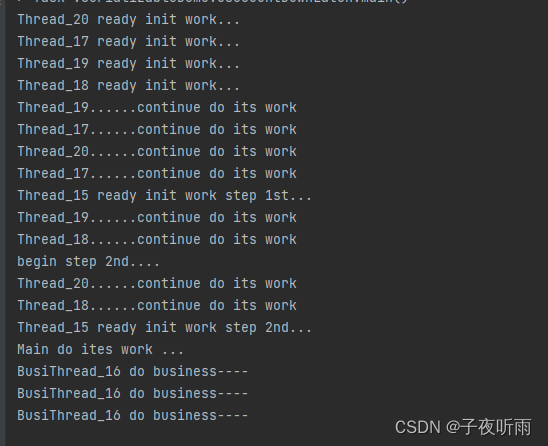
public class UseCountDownLatch {//计数器设置为6static CountDownLatch latch=new CountDownLatch(6);private static class InitThread implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("Thread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+" ready init work...");//计数器减1latch.countDown();for(int i=0;i<2;i++){System.out.println("Thread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+"......continue do its work");}}}private static class BusiThread implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {try {//在此处会阻塞,当计数器扣减为0时会被唤醒latch.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}for(int i=0;i<3;i++){System.out.println("BusiThread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+" do business----");}}}public static void main(String[] args) {new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1);System.out.println("Thread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+" ready init work step 1st...");latch.countDown();System.out.println("begin step 2nd....");TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1);System.out.println("Thread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+" ready init work step 2nd...");latch.countDown();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}).start();new Thread(new BusiThread()).start();for(int i=0;i<=3;i++){new Thread(new InitThread()).start();}try {latch.await();System.out.println("Main do ites work ...");} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}运行结果:
三、CyclicBarrier
CyclicBarrier可以实现让一组线程达到一个屏障(Barrier)时被阻塞,当所有线程都到达屏障时,被阻塞的线程才会继续执行
Demo:
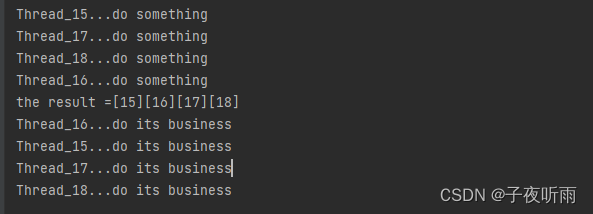
public class UseCyclicBarrier {//屏障拦截四个线程,当屏障放开时,会执行传入的CollectThreadprivate static CyclicBarrier barrier=new CyclicBarrier(4,new CollectThread());//存储子线程的工作结果private static ConcurrentHashMap<String,Long> resultmap=new ConcurrentHashMap<>();public static void main(String[] args) {for(int i=0;i<=3;i++){new Thread(new SubThread()).start();}}private static class CollectThread implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {StringBuilder res=new StringBuilder();for(Map.Entry<String,Long> r:resultmap.entrySet()){res.append("["+r.getValue()+"]");}System.out.println("the result ="+res);}}private static class SubThread implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {long id=Thread.currentThread().getId();resultmap.put(Thread.currentThread().getId()+"",id);System.out.println("Thread_"+id+"...do something");try {//在此处被屏障拦截,当屏障放开后才会继续执行barrier.await();System.out.println("Thread_"+id+"...do its business");} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}}
结果:
四、Semaphore
Semaphore的中文翻译就是信号量,是用来进行流量控制的,可以协调各个线程合理的使用资源。
new Semaphore(10) 来创建一个信号量,值为10,这里会创建一个非公平的锁的同步阻塞队列。
acquire方法信号量-1 release方法信号量+1 信号量为0时再执行acquire就会阻塞,直到信号量不为0时(其他线程执行了release)才会继续运行
1.Semaphore实现连接池
注意,实现连接池时需要用两个Semaphore,因为通过release归还时,信号量会超出10个的限制
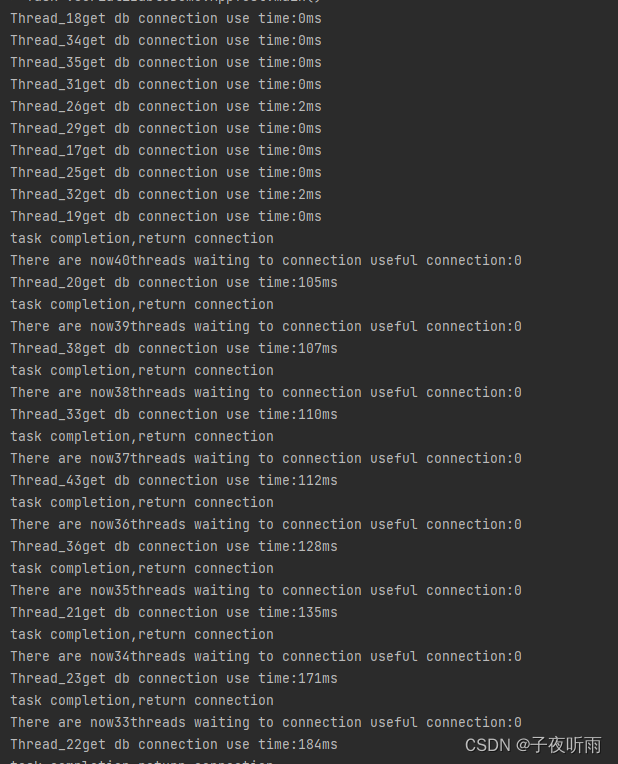
public class DBPoolSemaphore {private final static int POOL_SIZE=10;//可用连接和已用连接private final Semaphore useful,useless;//存放数据库连接的容器private static LinkedList<Connection> pool=new LinkedList<>();public DBPoolSemaphore() {this.useful=new Semaphore(10);this.useless=new Semaphore(0);for(int i=0;i<POOL_SIZE;i++){pool.addLast(SqlConnectImpl.fetchConnection());}}//归还连接public void returnConnect(Connection connection) throws InterruptedException {if(connection!=null){System.out.println("There are now"+useful.getQueueLength()+"threads waiting to connection "+"useful connection:"+ useful.availablePermits());useless.acquire();synchronized (pool){pool.addLast(connection);}useful.release();}}//获取连接public Connection getConnect() throws InterruptedException {useful.acquire();Connection connection;synchronized (pool){connection=pool.removeFirst();}useless.release();return connection;}
}public class AppTest {private static DBPoolSemaphore dbPool=new DBPoolSemaphore();private static class BusiThread extends Thread{@Overridepublic void run() {Random r=new Random();long start=System.currentTimeMillis();try {Connection connection= dbPool.getConnect();System.out.println("Thread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+"get db connection use time:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start)+"ms");TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100+r.nextInt(100)); //模拟业务操作System.out.println("task completion,return connection");dbPool.returnConnect(connection);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}public static void main(String[] args) {for(int i=0;i<50;i++){Thread thread=new BusiThread();thread.start();}}
}
运行结果:
2.思考
使用双信号量是为了防止信号量会超过10个的限制,如果按如下的方法调用连接池:
public class AppTest {private static DBPoolSemaphore dbPool=new DBPoolSemaphore();private static class BusiThread extends Thread{@Overridepublic void run() {Random r=new Random();long start=System.currentTimeMillis();try {
// Connection connection= dbPool.getConnect();
// System.out.println("Thread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+
// "get db connection use time:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start)+"ms");
// TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100+r.nextInt(100)); //模拟业务操作
// System.out.println("task completion,return connection");dbPool.returnConnect(new SqlConnectImpl());} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}public static void main(String[] args) {for(int i=0;i<50;i++){Thread thread=new BusiThread();thread.start();}}
}
在线程中,只归还连接,归还的是自己new出来的连接。如果此时是单信号量只有useful,那么useful会变成60个:
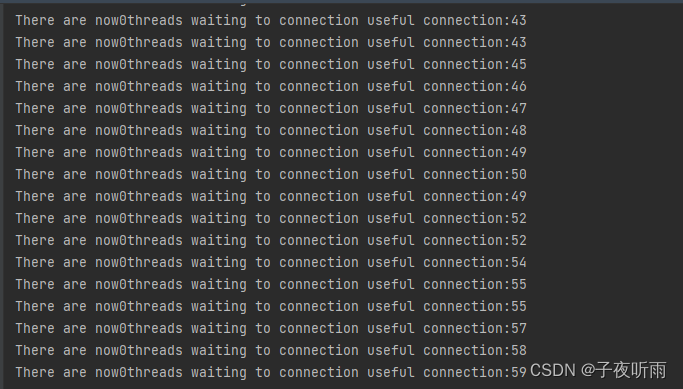
//单信号量public void returnConnect(Connection connection) throws InterruptedException {if(connection!=null) {System.out.println("There are now"+useful.getQueueLength()+"threads waiting to connection "+"useful connection:"+ useful.availablePermits());synchronized (pool) {pool.addLast(connection);}useful.release();}}
如果采用两个信号量,因为useless一开始为0,所以没有get连接直接归还连接时,会在useless.acquire那里阻塞住,可以有效的防止上面情况的发生。
//双信号量public void returnConnect(Connection connection) throws InterruptedException {if(connection!=null){System.out.println("There are now"+useful.getQueueLength()+"threads waiting to connection "+"useful connection:"+ useful.availablePermits());System.out.println("1");useless.acquire(); //useless一开始为0.直接调用returnConnect会在这里阻塞住System.out.println("2");synchronized (pool){pool.addLast(connection);}useful.release();}}

log中并没有2,归还连接时被阻塞在useless.acquire
总之,双信号量可以有效的防止可用连接溢出的情况发生。个人感觉,如果是实现一个线程池,线程池中的连接不能让用户通过new SqlConnectImpl()这种形式new出来,SqlConnectImpl应该是对用户不可见的。对于用户来说,应该只能通过getConnect来从线程池获取连接,这样或许也能够避免这种问题出现。
这篇关于Java并发工具类---ForkJoin、countDownlatch、CyclicBarrier、Semaphore的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







