本文主要是介绍2022年智能算法之凌日搜索算法(TS),原理公式详解,附matlab代码,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!

凌日搜索算法(Transit Search,TS)是一种新型元启发式优化算法,该算法基于著名的系外行星探测方法,具有寻优能力强、进化能力强、搜索速度快的特点。该成果于2022年发表在知名SCI期刊Results in Control and Optimization上。目前在谷歌学术上有着很高的被引量,共被引32次。
通过太空望远镜的数据库,使用凌日技术已经发现了3800多颗行星,由于凌日法在天体物理学中的高效率和它的能力,它已被用于制定一种优化技术。在凌日算法中,通过研究恒星在一定时间间隔内接收到的光,检测其光度的变化,如果接收到的光量减少,则表明有一颗行星从恒星前方经过。
在凌日搜索算法结构中,定义了两个参数:主星数(ns)和信噪比(SN)。根据经纬仪模型确定经纬仪的经纬仪参数。此外,噪声是利用在凌日外获得的观测值的标准差估计的。凌日搜索算法的实施分为五个阶段,即星系阶段、凌日阶段、行星阶段、邻居阶段和开发阶段。
算法原理
(1)星系阶段
在此阶段,算法首先选择一个星系。为此,在搜索空间中随机选择一个位置作为星系中心。一旦确定了这个位置,就有必要确定银河系的可居住区。为了做到这一点,先评估ns*SN随机区域LR,最后,选择其中具有最佳适应度的20%。ns选定的区域有可能成为生命的宿主,算法的下一步开始就从这些区域开始,数学公式如下:
在上面提到的公式中, 代表星系的中心位置。此外,Lr是搜索空间中的一个随机位置。在0到1之间有两个系数,分别表示一个随机数(c1)和一个随机向量(c2),表示优化问题的变量数量大小。
(2)凌日阶段
为了探测凌日,有必要重新测量从星星接收到的光量,以探测其可能减少的接收光信号。算法中LS及其对应的适应度(fs)有M1和M2两种含义。如果目标是使用恒星的位置来确定和更新行星的位置,则使用M1。如果目标是确定从恒星接收到的亮度并对其进行更新,则使用M2。相应地,在M2的情况下,LS的变化意味着一个新的规格的光信号,而在M1的情况下,LS的变化意味着星星的位置的变化。根据观测者接收到的光谱(和观测者与恒星之间的距离,可以估计出恒星的光度,小的距离导致接收到更多的光子。恒星的光度数学公式如下:
其中,Li、Ri为星号i的光度和阶数,公式表达了望远镜到星号i的距离。望远镜的位置LT在算法开始时随机选取,优化时不改变。
(3)行星阶段
如果观测到凌日,则在算法中实现行星阶段。在这一阶段,首先确定被探测行星的初始位置。考虑到观察者接收到的光来自恒星,所以当行星经过恒星和望远镜之间时,这种光的数量就会减少。可以确定被探测行星(LZ)的初始位置,数学公式如下:
其中参数RL表示亮度比。系数c8也有一个0到1之间的随机值。利用恒星和望远镜两个相对位置的平均值,确定当前位置在恒星和望远镜之间的行星的位置。
(4)邻居阶段
如果当前观测的恒星没有凌日现象,则将研究该恒星之前探测到的行星附近的行星。如果它的邻居比当前的行星有更好的条件,它将被该恒星当前的行星所取代。首先,利用计算邻域(Lz)的初始位置,同时考虑其宿主星(LS,new)和随机位置(LR)。然后,由方程式确定相邻行星(LN)的最终位置。
其中区域参数z的值是随机数1、2或3,系数c11和c12处理0和1之间的随机数。同样,c13和c14分别是一个随机数和一个介于-1和1之间的向量。
(5)开发阶段
在之前的阶段,为每颗恒星确定最佳的行星。正如前面提到的,发现一颗行星本身并不重要。事实上,有必要研究这颗行星的特性和适合生命生存的条件。在此阶段,将表示LP的新定义。换句话说,LP在当前阶段(LE)指的是行星的特征(如密度、物质、大气等)。然后,通过添加新的知识(K),将行星的最终特征修改SN次(j= 1,…,SN)使用方程式。在这个阶段,每颗恒星的最佳行星是LE。
其中,c15为0~2之间的随机数,c16为0~1之间的随机数,c17是一个介于0和1之间的随机向量。参数P表示1到(ns*SN)之间的随机幂。在这个方程中,ck是一个随机数(1、2、3或4),表示知识索引。
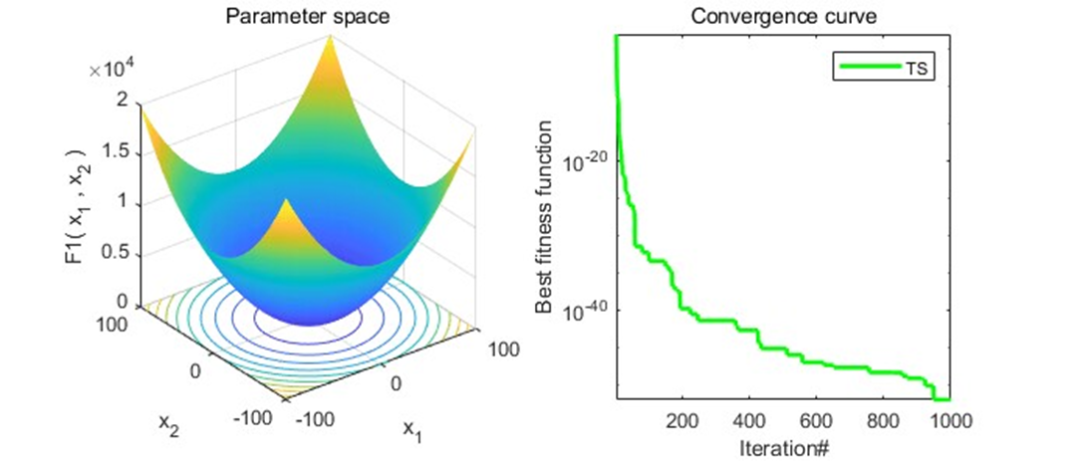
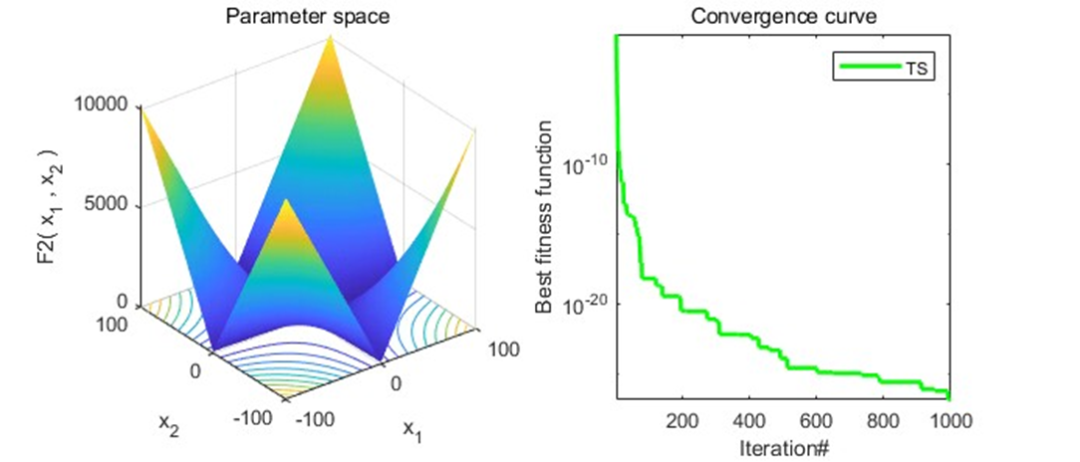
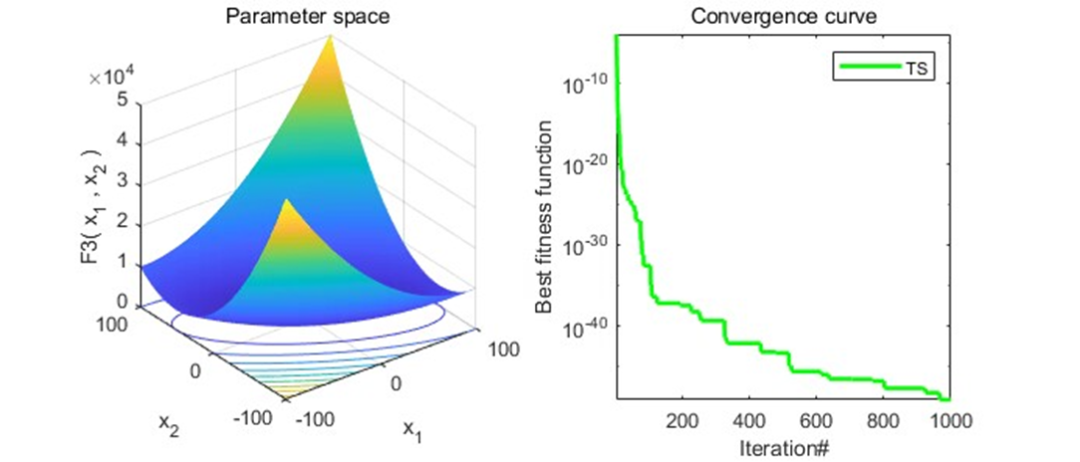
结果展示
以为CEC2005函数集为例,进行结果展示:
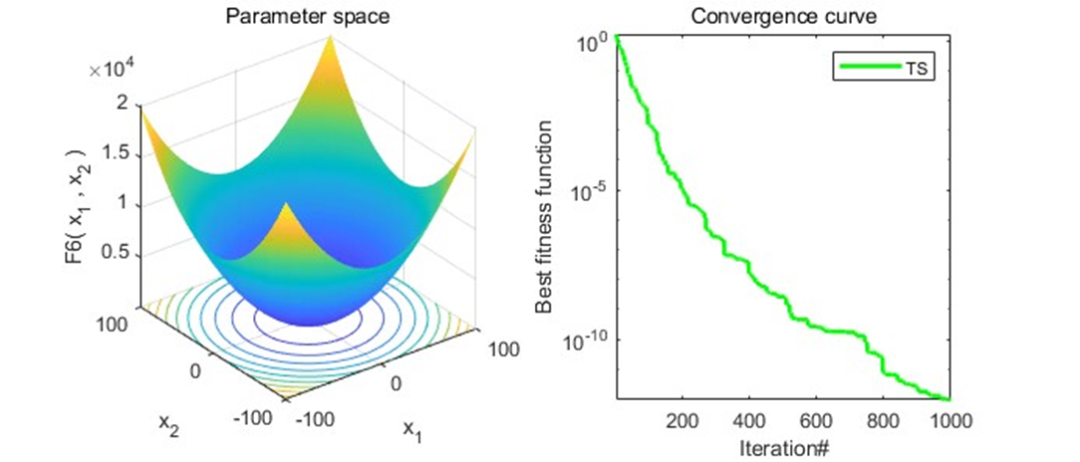
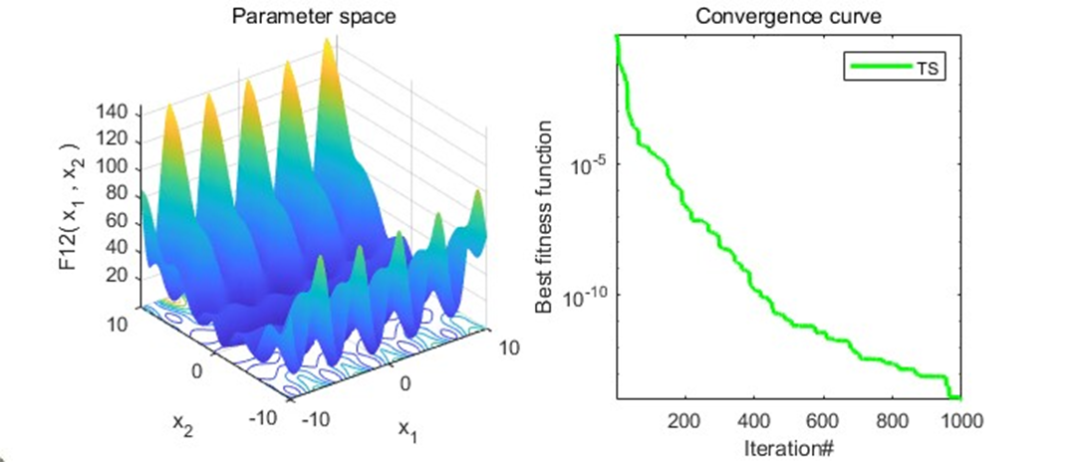
MATLAB核心代码
function [Bests] = TransitSearch (CostFunction,Vmin,Vmax,nV,ns,SN,maxcycle)
%% Initialization
Empty.Location = [];
Empty.Cost = inf;
Galaxy_Center = repmat (Empty, 1, 1);
region = repmat (Empty, ns*SN, 1);
selected_regions = repmat (Empty, ns, 1);
Stars = repmat (Empty, ns, 1);
Stars_sorted = zeros(ns,1);
Ranks = 1:1:ns;
Stars_Ranks = zeros(ns,1);
Luminosity = zeros(ns,1);
Star_RanksNormal = zeros(ns,1);
Distance = zeros(ns,1);
Transit0 = zeros(ns,1);
SN_P = repmat (Empty, SN, 1);
Bests=region;
if length(Vmin) ~= nVVmin=Vmin*ones(1,nV);Vmax=Vmax*ones(1,nV);
end
%% Galaxy Phase
% Initial Location of The Center of the Galaxy
Galaxy_Center.Location = unifrnd(Vmin,Vmax,1,nV);
Galaxy_Center.Cost = CostFunction(Galaxy_Center.Location);
% Galactic Habitate Zone of the Galaxy
for l = 1:(ns*SN)zone = randi(2);if zone ==1difference = rand().*(Galaxy_Center.Location)-(unifrnd(Vmin,Vmax,1,nV));elsedifference = rand().*(Galaxy_Center.Location)+(unifrnd(Vmin,Vmax,1,nV));endNoise = ((rand(1,nV)).^3).*(unifrnd(Vmin,Vmax,1,nV));region(l).Location = Galaxy_Center.Location + difference - Noise;region(l).Location = max(region(l).Location, Vmin);region(l).Location = min(region(l).Location, Vmax);region(l).Cost = CostFunction(region(l).Location);
end
% Selection of Stars from the Galactic Habitate Zone of the Galaxy
[Sort,index]=sort([region.Cost]);
for i = 1:nsselected_regions(i) = region(index(1,i));for k = 1:SNzone = randi(2);if zone ==1difference = rand().*(selected_regions(i).Location)-rand().*(unifrnd(Vmin,Vmax,1,nV));elsedifference = rand().*(selected_regions(i).Location)+rand().*(unifrnd(Vmin,Vmax,1,nV));endNoise = ((rand(1,nV)).^3).*(unifrnd(Vmin,Vmax,1,nV));new.Location = selected_regions(i).Location + difference - Noise;new.Location = max(new.Location, Vmin);new.Location = min(new.Location, Vmax);new.Cost = CostFunction(new.Location);if new.Cost < Stars(i).CostStars(i) = new;endend
end
% Initial Location of the Best Planets (Start Point: Its Star)
Best_Planets = Stars;
% Specification of the Best Planet
[Sort,index]=sort([Best_Planets.Cost]);
Best_Planet = Best_Planets(index(1,1));
% Telescope Location
Telescope.Location = unifrnd(Vmin,Vmax,1,nV);
% Determination of the Luminosity of the Stars
for i = 1:nsStars_sorted(i,1) = Stars(i).Cost;
end
Stars_sorted = sort (Stars_sorted);
for i = 1:nsfor ii = 1:nsif Stars(i).Cost == Stars_sorted(ii,1)Stars_Ranks(i,1) = Ranks(1,ii);Star_RanksNormal(i,1) = (Stars_Ranks(i,1))./ns;endendDistance(i,1) = sum((Stars(i).Location-Telescope.Location).^2).^0.5;Luminosity(i,1) = Star_RanksNormal(i,1)/((Distance(i,1))^2);
end
Luminosity_new = Luminosity;
Stars2 = Stars;
%% Loops of the TS Algorithm
for it = 1:maxcycle%% Transit PhaseTransit = Transit0;Luminosity = Luminosity_new;for i = 1:nsdifference = (2*rand()-1).*(Stars(i).Location);Noise = ((rand(1,nV)).^3).*(unifrnd(Vmin,Vmax,1,nV));Stars2(i).Location = Stars(i).Location + difference - Noise;Stars2(i).Location = max(Stars2(i).Location, Vmin);Stars2(i).Location = min(Stars2(i).Location, Vmax);Stars2(i).Cost = CostFunction(Stars2(i).Location);endfor i = 1:nsStars_sorted(i,1) = Stars2(i).Cost;endStars_sorted = sort (Stars_sorted);for i = 1:nsfor ii = 1:nsif Stars2(i).Cost == Stars_sorted(ii,1)Stars_Ranks(i,1) = Ranks(1,ii);Star_RanksNormal(i,1) = (Stars_Ranks(i,1))./ns;endendDistance(i,1) = sum((Stars2(i).Location-Telescope.Location).^2).^0.5;Luminosity_new(i,1) = Star_RanksNormal(i,1)/((Distance(i,1))^2);if Luminosity_new(i,1) < Luminosity(i,1)Transit (i,1) = 1; % Has transit been observed? 0 = No; 1 = YesendendStars = Stars2;%% Location Phase (Exploration)for i = 1:nsif Transit (i,1) == 1% Determination of the Location of the PlanetLuminosity_Ratio = Luminosity_new(i,1)/Luminosity(i,1);Planet.Location = (rand().*Telescope.Location + Luminosity_Ratio.*Stars(i).Location)./2;for k = 1:SNzone = randi(3);if zone ==1new.Location = Planet.Location - (2*rand()-1).*(unifrnd(Vmin,Vmax,1,nV));elseif zone ==2new.Location = Planet.Location + (2*rand()-1).*(unifrnd(Vmin,Vmax,1,nV));elsenew.Location = Planet.Location + (2.*rand(1,nV)-1).*(unifrnd(Vmin,Vmax,1,nV));endnew.Location = max(new.Location, Vmin);new.Location = min(new.Location, Vmax);% new.Cost = CostFunction(new.Location);SN_P(k) = new;endSUM = 0;for k = 1:SNSUM = SUM+SN_P(k).Location;endnew.Location = SUM./SN;new.Cost = CostFunction(new.Location);if new.Cost < Best_Planets(i).CostBest_Planets(i) = new;endelse % No Transit observed: Neighbouring planetsNeighbor.Location = (rand().*Stars(i).Location + rand().*(unifrnd(Vmin,Vmax,1,nV)))./2;for k = 1:SNzone = randi(3);if zone ==1Neighbor.Location = Neighbor.Location - (2*rand()-1).*(unifrnd(Vmin,Vmax,1,nV));elseif zone ==2Neighbor.Location = Neighbor.Location + (2*rand()-1).*(unifrnd(Vmin,Vmax,1,nV));elseNeighbor.Location = Neighbor.Location + (2.*rand(1,nV)-1).*(unifrnd(Vmin,Vmax,1,nV));endNeighbor.Location = max(Neighbor.Location, Vmin);Neighbor.Location = min(Neighbor.Location, Vmax);Neighbor.Cost = CostFunction (Neighbor.Location);SN_P(k) = Neighbor;endSUM = 0;for k = 1:SNSUM = SUM+SN_P(k).Location;endNeighbor.Location = SUM./SN;Neighbor.Cost = CostFunction (Neighbor.Location);if Neighbor.Cost < Best_Planets(i).CostBest_Planets(i) = Neighbor;endend
end
%% Signal Amplification of the Best Planets (Exploitation)for i = 1:nsfor k = 1:SNRAND = randi(2 );if RAND ==1Power = randi(SN*ns);Coefficient = 2*rand();Noise = ((rand(1,nV)).^Power).*(unifrnd(Vmin,Vmax,1,nV));elsePower = randi(SN*ns);Coefficient = 2*rand();Noise = -((rand(1,nV)).^Power).*(unifrnd(Vmin,Vmax,1,nV));end% new.Location = (rand().*Best_Planets(i).Location) - Coefficient.*Noise;chance = randi(2);if chance ==1new.Location = Best_Planets(i).Location - Coefficient.*Noise;elsenew.Location = (rand().*Best_Planets(i).Location) - Coefficient.*Noise;endnew.Location = max(new.Location, Vmin);new.Location = min(new.Location, Vmax);new.Cost = CostFunction(new.Location);% new.Cost = CostFunction(new.Location);if new.Cost < Best_Planets(i).CostBest_Planets(i) = new;endendif Best_Planets(i).Cost < Best_Planet.CostBest_Planet = Best_Planets(i);endend% ResultsBests(it)=Best_Planet;
end
end参考文献
[1] Mirrashid M, Naderpour H. Transit search: An optimization algorithm based on exoplanet exploration[J]. Results in Control and Optimization, 2022, 7: 100127.
完整代码获取方式:后台回复关键字:
TGDM101
这篇关于2022年智能算法之凌日搜索算法(TS),原理公式详解,附matlab代码的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





