本文主要是介绍cuda lib 线程安全的要义,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1, 概述
cuda lib 线程安全的几个多线程的情景:
单卡多线程;
多卡多线程-每卡单线程;
多卡多线程-每卡多线程;
需要考虑的问题:
每个 cublasHandle_t 只能有一个stream么?
每个cusolverHandle_t 只能有一个 stream么?
每个cusolverHandle_t只能有要给cublasHandle_t么?
多个线程同时跑在多个或一个gpu上,需要使用多个stream么?都是NULL 默认stream的话,不会影响效率吧?
2, 多线程示例
从如下代码思考开去,这个多线程场景是使用了openmp自动划分任务,也可以使用pthread来七分任务,这里对这个示例进行了注释:
https://github.com/NVIDIA/cuda-samples/blob/v11.4/Samples/cudaOpenMP/cudaOpenMP.cu
/** Multi-GPU sample using OpenMP for threading on the CPU side* needs a compiler that supports OpenMP 2.0*/
//使用openmp时包含其头文件
#include <omp.h>
#include <stdio.h> // stdio functions are used since C++ streams aren't necessarily thread safe
//#include <helper_cuda.h>#define checkCudaErrors(val) valusing namespace std;// a simple kernel that simply increments each array element by b
__global__ void kernelAddConstant(int *g_a, const int b)
{int idx = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;g_a[idx] += b;
}// a predicate that checks whether each array element is set to its index plus b
int correctResult(int *data, const int n, const int b)
{for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)if (data[i] != i + b)return 0;return 1;
}int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{int num_gpus = 0; // number of CUDA GPUsprintf("%s Starting...\n\n", argv[0]);/// determine the number of CUDA capable GPUs//cudaGetDeviceCount(&num_gpus);if (num_gpus < 1){printf("no CUDA capable devices were detected\n");return 1;}/// display CPU and GPU configuration//printf("number of host CPUs:\t%d\n", omp_get_num_procs());printf("number of CUDA devices:\t%d\n", num_gpus);for (int i = 0; i < num_gpus; i++){cudaDeviceProp dprop;cudaGetDeviceProperties(&dprop, i);printf(" %d: %s\n", i, dprop.name);}printf("---------------------------\n");/// initialize data//unsigned int n = num_gpus * 8192;unsigned int nbytes = n * sizeof(int);// nbytes = num_gpus * [8192*sizeof(int)]printf("nbytes=%u\n", nbytes);int *a = 0; // pointer to data on the CPUint b = 3; // value by which the array is incrementeda = (int *)malloc(nbytes);if (0 == a){printf("couldn't allocate CPU memory\n");return 1;}
//这里如果使用 #pragma omp parallel for 的话,会不会影响下面的线程数?for (unsigned int i = 0; i < n; i++)a[i] = i;// run as many CPU threads as there are CUDA devices// each CPU thread controls a different device, processing its// portion of the data. It's possible to use more CPU threads// than there are CUDA devices, in which case several CPU// threads will be allocating resources and launching kernels// on the same device. For example, try omp_set_num_threads(2*num_gpus);// Recall that all variables declared inside an "omp parallel" scope are// local to each CPU thread//// 通过获知GPU的数量来设定下面参与工作的线程数量omp_set_num_threads(num_gpus); // create as many CPU threads as there are CUDA devices//omp_set_num_threads(2*num_gpus);// create twice as many CPU threads as there are CUDA devices//自动创建 num_gpus 个线程#pragma omp parallel{//每个线程获得自己的线程号,从0开始计数unsigned int cpu_thread_id = omp_get_thread_num();//获取 openmp 自动创建的总的线程数unsigned int num_cpu_threads = omp_get_num_threads();printf("cpu_thread_id=%u num_cpu_threads=%u\n", cpu_thread_id, num_cpu_threads);// set and check the CUDA device for this CPU threadint gpu_id = -1;//两个或以上的线程,可以同时使用同一个 gpu 设备;cudaSetDevice(id) 会使得本线程锁定这个 id-th gpu 设备,接下来发生的cudaXXX,都是在这个gpu上发生的。checkCudaErrors(cudaSetDevice(cpu_thread_id % num_gpus)); // "% num_gpus" allows more CPU threads than GPU devicescheckCudaErrors(cudaGetDevice(&gpu_id));//这个函数仅仅返回本线程锁定的gpu的id。printf("CPU thread %d (of %d) uses CUDA device %d, set id=%d, get id = %d\n", cpu_thread_id, num_cpu_threads, gpu_id, cpu_thread_id%num_gpus, gpu_id);int *d_a = 0; // pointer to memory on the device associated with this CPU thread//下面找到本线程需要处理的数据起始地址int *sub_a = a + cpu_thread_id * n / num_cpu_threads; // pointer to this CPU thread's portion of dataunsigned int nbytes_per_kernel = nbytes / num_cpu_threads;//其中的 nbytes = num_gpus * [8192*sizeof(int)], 是整除关系;得到每个线程需要分配的显存字节数dim3 gpu_threads(128); // 128 threads per blockdim3 gpu_blocks(n / (gpu_threads.x * num_cpu_threads));// n = num_gpus * 8192; 其中 8192 是128的整数倍, num_cpu_threads 是 num_gpus 的小小的整数倍; // 这样每个block含128个线程; 每个线程需要几个block呢 = n/(gpu_threads.x * num_cpu_threads)checkCudaErrors(cudaMalloc((void **)&d_a, nbytes_per_kernel));//在本线程所setDevice的gpu上cudaMalloc显存空间;checkCudaErrors(cudaMemset(d_a, 0, nbytes_per_kernel));//将分的的空间刷0// 将本线程需要处理的数据块拷贝的本线程所cudaMalloc的显存中;checkCudaErrors(cudaMemcpy(d_a, sub_a, nbytes_per_kernel, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice));//本线程启动kernel,处理自己的显存的数据;kernelAddConstant<<<gpu_blocks, gpu_threads>>>(d_a, b);// 本线程将处理好的数据拷贝到本线程负责的系统内存块中checkCudaErrors(cudaMemcpy(sub_a, d_a, nbytes_per_kernel, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost));//释放显存checkCudaErrors(cudaFree(d_a));}printf("---------------------------\n");if (cudaSuccess != cudaGetLastError())printf("%s\n", cudaGetErrorString(cudaGetLastError()));// check the result//对计算结果进行对比bool bResult = correctResult(a, n, b);if (a)free(a); // free CPU memoryexit(bResult ? EXIT_SUCCESS : EXIT_FAILURE);
}
运行效果:
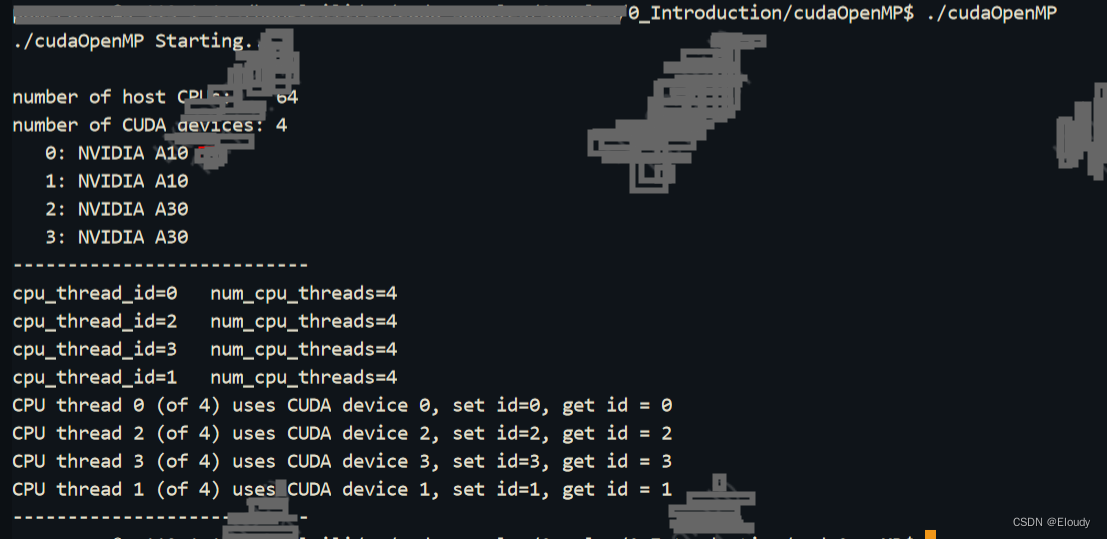
要保证cuda lib的线程安全,首先确定cuda driver cuda runtime 都是线程安全的,这个其实是没有问题的,也就是说多个线程多块显卡同时运行的场景是不会引发cuda runtime的线程安全问题的,这点可以放心;
3, 多线程安全分析
这篇关于cuda lib 线程安全的要义的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








