本文主要是介绍CppCheck静态代码检查工具教程【Windows和Linux端】,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
1、背景
2、特性介绍
2.1、检查结果
2.2、检查范围
2.3、支持的检查规则(列举一些):
2.4、自定义规则
3、linux 端
4、windows 端
1、背景
最近调研了几款 c/c++ 代码静态检查工具,包括 cppcheck、cpplint、cppdepend、splint、tscancode、sonaqube 等,对比后认为 cppcheck 使用起来最方便,检查内容相对全面,支持多平台应用(linux 和 windows),且免费,因此选用 cppcheck 作为 c/c++ 代码静态检查的第一选择。本文对该工具的使用方法进行一个总结介绍。
2、特性介绍
cppceck 是一个 C/C++ 代码分析工具。与 C/C++ 编译器和许多其他分析工具不同,它不检测语法错误。cppcheck 仅检测编译器通常无法检测到的错误类型。目标是没有误报。
2.1、检查结果
- error:出现的错误
- warning:为了预防bug防御性编程建议信息越
- style:编码格式问题(没有使用的函数、多余的代码等)
- portablity:移植性警告。该部分如果移植到其他平台上,可能出现兼容性问题
- performance:建议优化该部分代码的性能
- information:一些有趣的信息,可以忽略
2.2、检查范围
- 自动变量检查;
- 数组的边界检查;
- class类检查;
- 过期的函数,废弃函数调用检查;
- 异常内存使用,释放检查;
- 内存泄漏检查,主要是通过内存引用指针;
- 操作系统资源释放检查,中断,文件描述符等;
- 异常STL 函数使用检查;
- 代码格式错误,以及性能因素检查。
2.3、支持的检查规则(列举一些):
- 禁止在头文件前有可执行代码。
- 引起二义性理解的逻辑表达式,必须使用括号显式说明优先级顺序。
- 逻辑判别表达式中的运算项必须要使用括号。
- 禁止对参数指针进行赋值。
- 动态分配的指针变量定义时如未被分配空间必须初始化为NULL
- 动态分配的指针变量第一次使用前必须进行是否为NULL的判别。
- 数组禁止越界使用。
- 数组下标必须是大于等于零的整型数。
- 禁止使用已被释放了的内存空间。
- 被free的指针必须指向最初malloc、calloc分配的地址。
- 建议用宏或const定义常数。
- 动态申请的内存空间用完后及时释放。
- 建议变量在声明的同时进行初始化。
- 函数中固定长度数组变量的传递必须使用引用方式。
- 定义为const的成员函数禁止返回非const的指针或引用。
- 禁止可导致非资源性对象数据被外部修改的成员函数返回。
- 捕获的顺序必须按由派生类到基类的次序排序。
- 每个指定的抛出必须有与之匹配的捕获。
- 异常抛出的对象必须使用引用方式捕获。
- 缺省捕获必须放在所有指定捕获之后。
- 禁止显式直接抛出
2.4、自定义规则
1. 使用 --suppress 选项过滤特定的警告:
如果你想要忽略某些警告,可以在命令行中使用 --suppress 选项。例如,如果你想要忽略所有的“缺少头文件”的警告,可以使用以下命令:
cppcheck --suppress=missingInclude ./# 这里,“missingInclude” 是要忽略的警告类型。将其替换为您希望过滤掉的警告类型。2 . 编写自定义脚本:
在 CppCheck 运行结束后,使用自定义脚本对输出结果进行过滤。例如,您可以使用 Python 编写一个脚本,读取 CppCheck 的输出,然后根据自定义规则筛选警告信息。以下是一个简单的示例:import subprocess import sysdef main():cppcheck_command = "cppcheck --enable=all --xml --xml-version=2 ./"result = subprocess.run(cppcheck_command.split(), capture_output=True, text=True)# 在这里添加自定义规则def custom_filter(error):# 示例规则:过滤所有包含特定文件名的警告return "my_special_file.cpp" not in errorfiltered_errors = list(filter(custom_filter, result.stderr.splitlines()))for error in filtered_errors:print(error)if __name__ == "__main__":main()这个示例脚本使用 subprocess.run 来运行 CppCheck,并捕获输出。然后,它根据自定义规则(在这里是忽略包含特定文件名的警告)对输出进行过滤。您可以在 custom_filter 函数中编写自己的过滤规则。
3.可以使用--rule和--rule-file选项添加此类规则。 也可以使用正则表达式,例如:
\sget[A-Za-z]+\(\)\s+{\s+return这取决于代码库。
如果可以编写正则表达式,那么这是创建自定义规则的最直接,最简单的方法。
有关更多信息,请在此处阅读"写作规则"文章:cppcheck - Browse /Articles at SourceForge.net
但是也许想编写更复杂的规则,可以使用Cppcheck SymbolDatabase,tokenlist和语法树来搜索此类getter方法。 则不能使用--rule和--rule-file。 然后,有以下选择:
- 使用--dump并编写自己的自定义脚本,以读取输出数据(xml)。
- 编写C ++代码并将其编译为Cppcheck。
cppcheck 官方手册
https://cppcheck.sourceforge.io/manual.html
cppcheck 支持的检查内容列表如下
cppcheck / Wiki / ListOfChecks
3、linux 端
安装方法很简单,直接通过 apt 即可安装
sudo apt-ge install cppcheck使用 help 指令查看使用方法,重要的部分标红处理
$ cppcheck --help
Cppcheck - A tool for static C/C++ code analysisSyntax:
cppcheck [OPTIONS] [files or paths]If a directory is given instead of a filename, *.cpp, *.cxx, *.cc, *.c++, *.c,
*.tpp, and *.txx files are checked recursively from the given directory.Options:
--cppcheck-build-dir=<dir>
Analysis output directory. Useful for various data.
Some possible usages are; whole program analysis,
incremental analysis, distributed analysis.
--check-config Check cppcheck configuration. The normal code
analysis is disabled by this flag.
--check-library Show information messages when library files have
incomplete info.
--config-exclude=<dir>
Path (prefix) to be excluded from configuration
checking. Preprocessor configurations defined in
headers (but not sources) matching the prefix will not
be considered for evaluation.
--config-excludes-file=<file>
A file that contains a list of config-excludes
--dump Dump xml data for each translation unit. The dump
files have the extension .dump and contain ast,
tokenlist, symboldatabase, valueflow.
-D<ID> Define preprocessor symbol. Unless --max-configs or
--force is used, Cppcheck will only check the given
configuration when -D is used.
Example: '-DDEBUG=1 -D__cplusplus'.
-U<ID> Undefine preprocessor symbol. Use -U to explicitly
hide certain #ifdef <ID> code paths from checking.
Example: '-UDEBUG'
-E Print preprocessor output on stdout and don't do any
further processing.
--enable=<id> Enable additional checks. The available ids are:
* all
Enable all checks. It is recommended to only
use --enable=all when the whole program is
scanned, because this enables unusedFunction.
* warning
Enable warning messages
* style
Enable all coding style checks. All messages
with the severities 'style', 'performance' and
'portability' are enabled.
* performance
Enable performance messages
* portability
Enable portability messages
* information
Enable information messages
* unusedFunction
Check for unused functions. It is recommend
to only enable this when the whole program is
scanned.
* missingInclude
Warn if there are missing includes. For
detailed information, use '--check-config'.
Several ids can be given if you separate them with
commas. See also --std
--error-exitcode=<n> If errors are found, integer [n] is returned instead of
the default '0'. '1' is returned
if arguments are not valid or if no input files are
provided. Note that your operating system can modify
this value, e.g. '256' can become '0'.
--errorlist Print a list of all the error messages in XML format.
--doc Print a list of all available checks.
--exitcode-suppressions=<file>
Used when certain messages should be displayed but
should not cause a non-zero exitcode.
--file-list=<file> Specify the files to check in a text file. Add one
filename per line. When file is '-,' the file list will
be read from standard input.
-f, --force Force checking of all configurations in files. If used
together with '--max-configs=', the last option is the
one that is effective.
-h, --help Print this help.
-I <dir> Give path to search for include files. Give several -I
parameters to give several paths. First given path is
searched for contained header files first. If paths are
relative to source files, this is not needed.
--includes-file=<file>
Specify directory paths to search for included header
files in a text file. Add one include path per line.
First given path is searched for contained header
files first. If paths are relative to source files,
this is not needed.
--include=<file>
Force inclusion of a file before the checked file. Can
be used for example when checking the Linux kernel,
where autoconf.h needs to be included for every file
compiled. Works the same way as the GCC -include
option.
-i <dir or file> Give a source file or source file directory to exclude
from the check. This applies only to source files so
header files included by source files are not matched.
Directory name is matched to all parts of the path.
--inconclusive Allow that Cppcheck reports even though the analysis is
inconclusive.
There are false positives with this option. Each result
must be carefully investigated before you know if it is
good or bad.
--inline-suppr Enable inline suppressions. Use them by placing one or
more comments, like: '// cppcheck-suppress warningId'
on the lines before the warning to suppress.
-j <jobs> Start <jobs> threads to do the checking simultaneously.
-l <load> Specifies that no new threads should be started if
there are other threads running and the load average is
at least <load>.
--language=<language>, -x <language>
Forces cppcheck to check all files as the given
language. Valid values are: c, c++
--library=<cfg> Load file <cfg> that contains information about types
and functions. With such information Cppcheck
understands your code better and therefore you
get better results. The std.cfg file that is
distributed with Cppcheck is loaded automatically.
For more information about library files, read the
manual.
--output-file=<file> Write results to file, rather than standard error.
--project=<file> Run Cppcheck on project. The <file> can be a Visual
Studio Solution (*.sln), Visual Studio Project
(*.vcxproj), or compile database
(compile_commands.json). The files to analyse,
include paths, defines, platform and undefines in
the specified file will be used.
--max-configs=<limit>
Maximum number of configurations to check in a file
before skipping it. Default is '12'. If used together
with '--force', the last option is the one that is
effective.
--platform=<type>, --platform=<file>
Specifies platform specific types and sizes. The
available builtin platforms are:
* unix32
32 bit unix variant
* unix64
64 bit unix variant
* win32A
32 bit Windows ASCII character encoding
* win32W
32 bit Windows UNICODE character encoding
* win64
64 bit Windows
* avr8
8 bit AVR microcontrollers
* native
Type sizes of host system are assumed, but no
further assumptions.
* unspecified
Unknown type sizes
--plist-output=<path>
Generate Clang-plist output files in folder.
-q, --quiet Do not show progress reports.
-rp, --relative-paths
-rp=<paths>, --relative-paths=<paths>
Use relative paths in output. When given, <paths> are
used as base. You can separate multiple paths by ';'.
Otherwise path where source files are searched is used.
We use string comparison to create relative paths, so
using e.g. ~ for home folder does not work. It is
currently only possible to apply the base paths to
files that are on a lower level in the directory tree.
--report-progress Report progress messages while checking a file.
--rule=<rule> Match regular expression.
--rule-file=<file> Use given rule file. For more information, see:
http://sourceforge.net/projects/cppcheck/files/Articles/
--std=<id> Set standard.
The available options are:
* posix
POSIX compatible code
* c89
C code is C89 compatible
* c99
C code is C99 compatible
* c11
C code is C11 compatible (default)
* c++03
C++ code is C++03 compatible
* c++11
C++ code is C++11 compatible
* c++14
C++ code is C++14 compatible (default)
More than one --std can be used:
'cppcheck --std=c99 --std=posix file.c'
--suppress=<spec> Suppress warnings that match <spec>. The format of
<spec> is:
[error id]:[filename]:[line]
The [filename] and [line] are optional. If [error id]
is a wildcard '*', all error ids match.
--suppressions-list=<file>
Suppress warnings listed in the file. Each suppression
is in the same format as <spec> above.
--template='<text>' Format the error messages. E.g.
'{file}:{line},{severity},{id},{message}' or
'{file}({line}):({severity}) {message}' or
'{callstack} {message}'
Pre-defined templates: gcc, vs, edit.
-v, --verbose Output more detailed error information.
--version Print out version number.
--xml Write results in xml format to error stream (stderr).
--xml-version=<version>
Select the XML file version. Currently only versions 2 is available.
使用示例
(1)检查当前路径下的代码,并输出到 txt 文件
cppcheck . --output-file=err.txt(2)检查某个路径,不输出过程日志
cppcheck --quiet ../myproject/(3)启用所有检查规则,检查某个文件
cppcheck --enable=all --inconclusive --std=posix test.cpp(4)输出 xml 格式的日志文件
cppcheck src --enable=all --output-file=log.xml --xml4、windows 端
在官网下载安装包,双击安装即可

打开 cppcheck 后新建一个扫描项目,导入代码路径
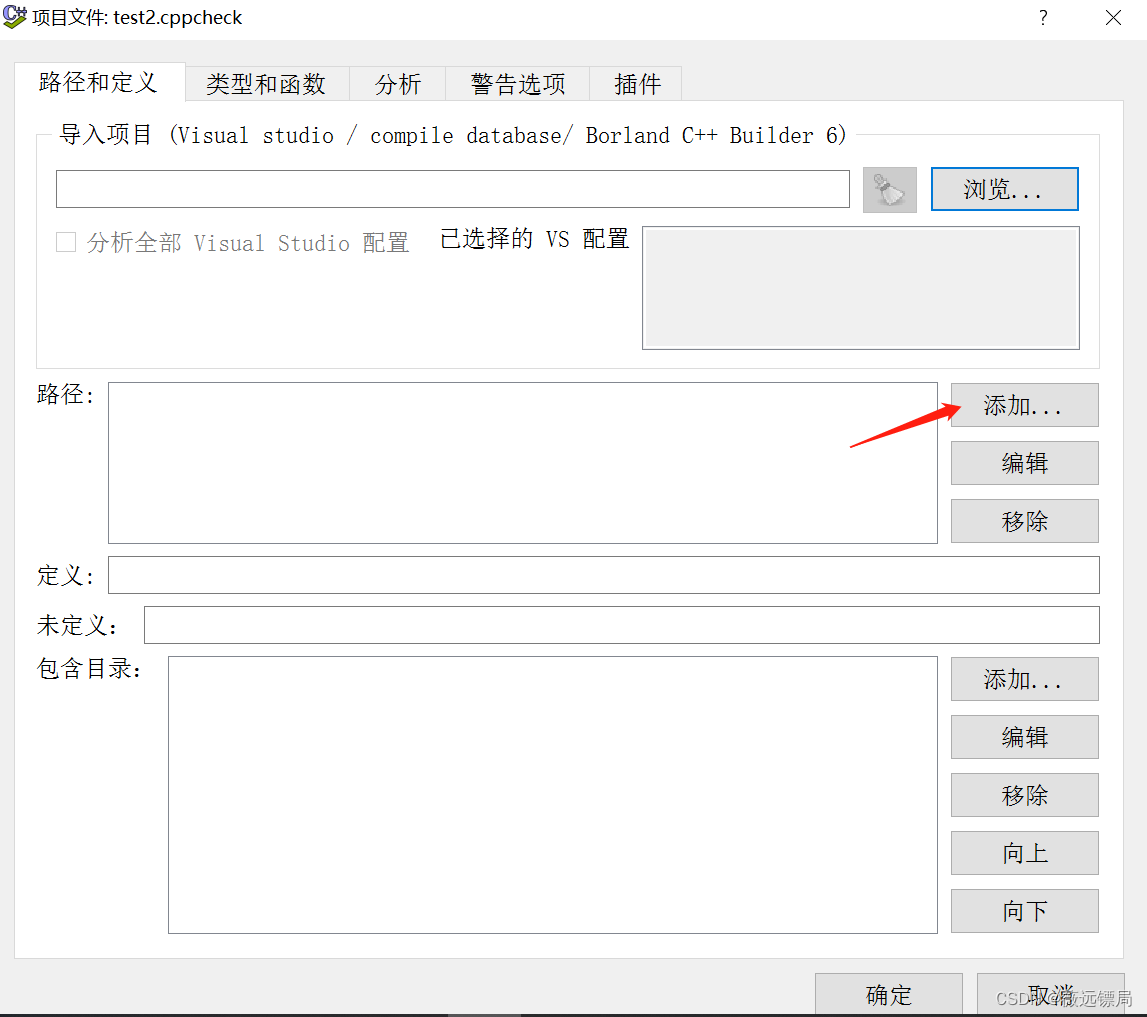
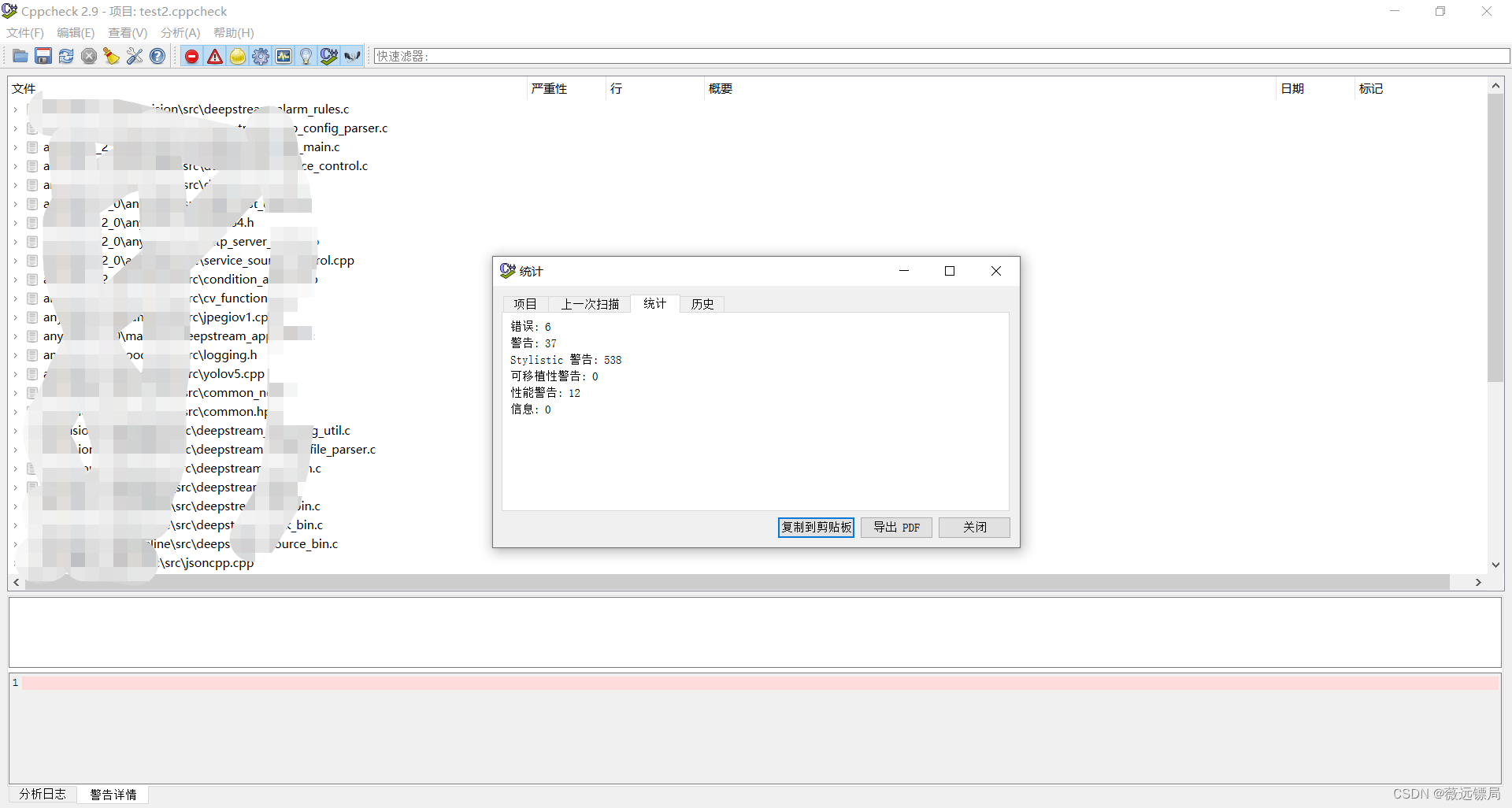
即可开始分析,分析完后可以在 查看--统计--统计 中查看总的扫描结果
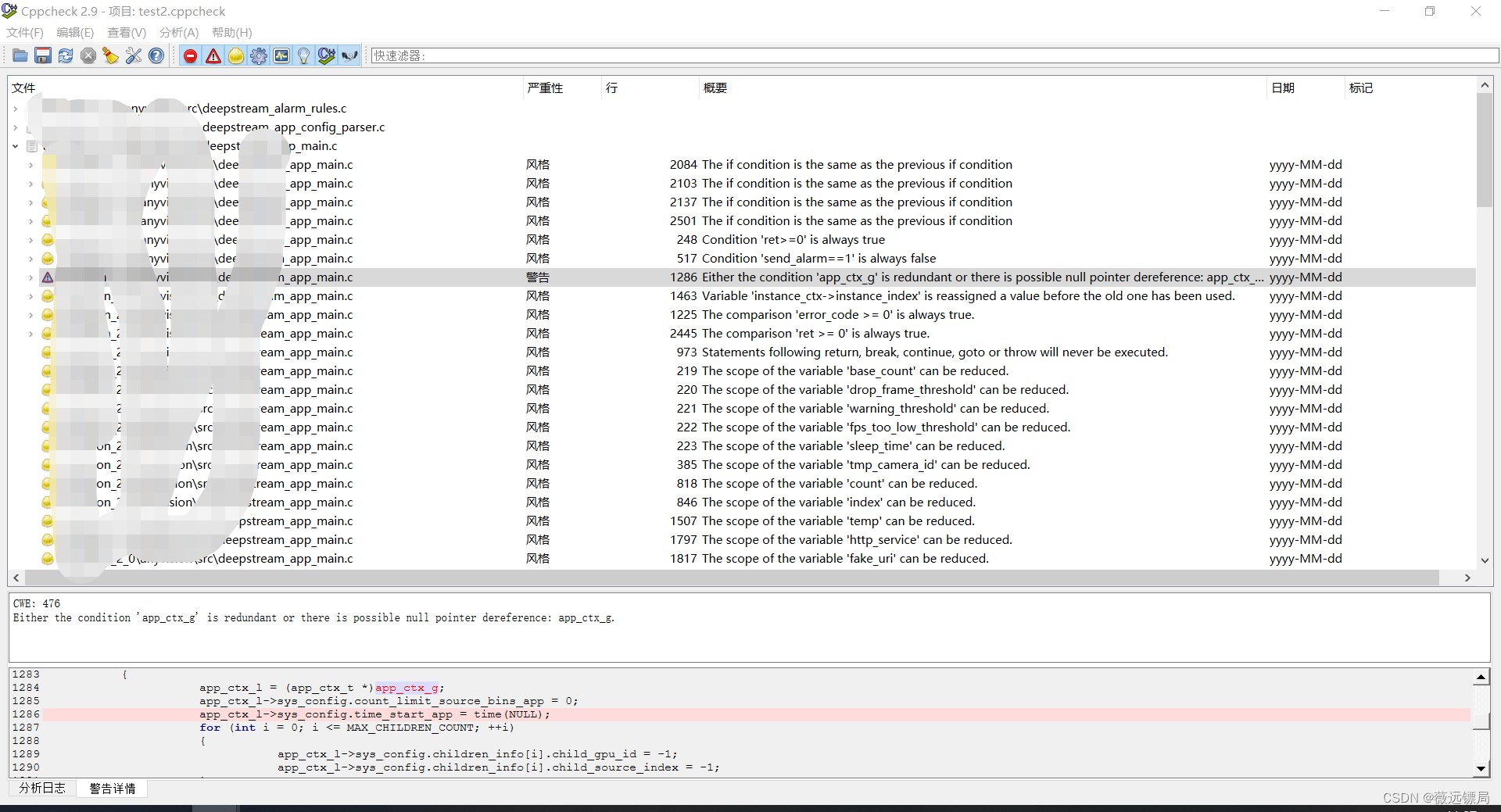
同时可以实时查看每一个告警及错误的内容及对应的代码
在工具栏可以根据严重性进行过滤,比如之关注错误内容
这篇关于CppCheck静态代码检查工具教程【Windows和Linux端】的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





