本文主要是介绍空间金字塔池化(SPP,Spatial Pyramid Pooling)系列,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
空间金字塔池化的作用是解决输入图片大小不一造成的缺陷,同时在目标识别中增加了精度。空间金字塔池化可以使得任意大小的特征图都能够转换成固定大小的特征向量,下面针对一些典型的空间金字塔进行盘点。
部分图片来自blog:空间金字塔池化改进 SPP / SPPF / SimSPPF / ASPP / RFB / SPPCSPC / SPPFCSPC_金字塔池化模块-CSDN博客, 侵删
(1)SPP, Spatial Pyramid Pooling
paper:Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep ConvolutionalNetworks for Visual Recognition
paper link: https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.4729
repo link: https://github.com/yifanjiang19/sppnet-pytorch
核心思想
把经典的金字塔池化结构Spatial Pyramid Pooling引入CNN中,从而使CNN可以处理任意尺寸的图片
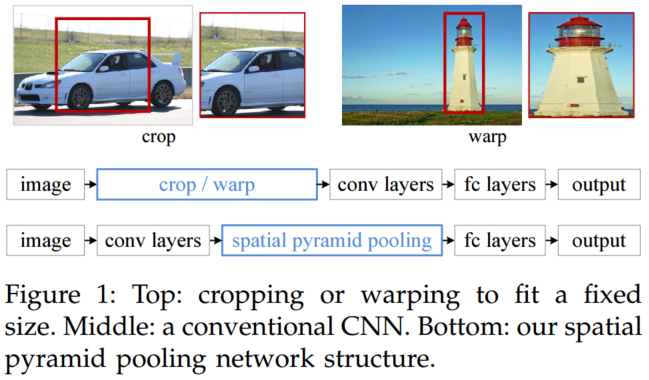
框架
具有空间金字塔池化层的网络结构。这里256是conv5层的卷积核个数,conv5是最后一个卷积层。
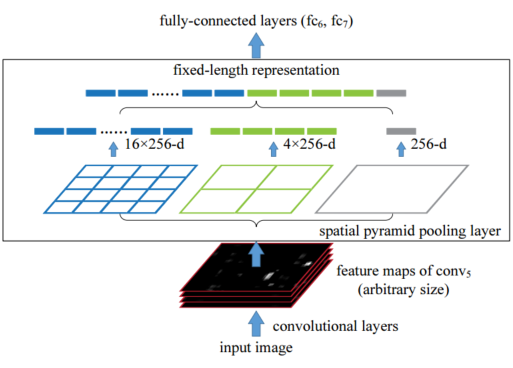
code_pytorch
import math
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.nn import init
import functools
from torch.autograd import Variable
import numpy as np
import torch.nn.functional as F
class SPP_NET(nn.Module):'''A CNN model which adds spp layer so that we can input multi-size tensor'''def __init__(self, opt, input_nc, ndf=64, gpu_ids=[]):super(SPP_NET, self).__init__()self.gpu_ids = gpu_idsself.output_num = [4,2,1]self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(input_nc, ndf, 4, 2, 1, bias=False)self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(ndf, ndf * 2, 4, 1, 1, bias=False)self.BN1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 2)self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(ndf * 2, ndf * 4, 4, 1, 1, bias=False)self.BN2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 4)self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(ndf * 4, ndf * 8, 4, 1, 1, bias=False)self.BN3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 8)self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(ndf * 8, 64, 4, 1, 0, bias=False)self.fc1 = nn.Linear(10752,4096)self.fc2 = nn.Linear(4096,1000)def forward(self,x):x = self.conv1(x)x = self.LReLU1(x)x = self.conv2(x)x = F.leaky_relu(self.BN1(x))x = self.conv3(x)x = F.leaky_relu(self.BN2(x))x = self.conv4(x)# x = F.leaky_relu(self.BN3(x))# x = self.conv5(x)spp = spatial_pyramid_pool(x,1,[int(x.size(2)),int(x.size(3))],self.output_num)# print(spp.size())fc1 = self.fc1(spp)fc2 = self.fc2(fc1)s = nn.Sigmoid()output = s(fc2)return output
def spatial_pyramid_pool(self,previous_conv, num_sample, previous_conv_size, out_pool_size):'''previous_conv: a tensor vector of previous convolution layernum_sample: an int number of image in the batchprevious_conv_size: an int vector [height, width] of the matrix features size of previous convolution layerout_pool_size: a int vector of expected output size of max pooling layerreturns: a tensor vector with shape [1 x n] is the concentration of multi-level pooling''' # print(previous_conv.size())for i in range(len(out_pool_size)):# print(previous_conv_size)h_wid = int(math.ceil(previous_conv_size[0] / out_pool_size[i]))w_wid = int(math.ceil(previous_conv_size[1] / out_pool_size[i]))h_pad = (h_wid*out_pool_size[i] - previous_conv_size[0] + 1)/2w_pad = (w_wid*out_pool_size[i] - previous_conv_size[1] + 1)/2maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d((h_wid, w_wid), stride=(h_wid, w_wid), padding=(h_pad, w_pad))x = maxpool(previous_conv)if(i == 0):spp = x.view(num_sample,-1)# print("spp size:",spp.size())else:# print("size:",spp.size())spp = torch.cat((spp,x.view(num_sample,-1)), 1)return spp(2)SPPF(Spatial Pyramid Pooling -Fast)
paper: 由于SPPF是yolov5作者基于SPP提出的,所以没有论文出处
yolov5 link: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
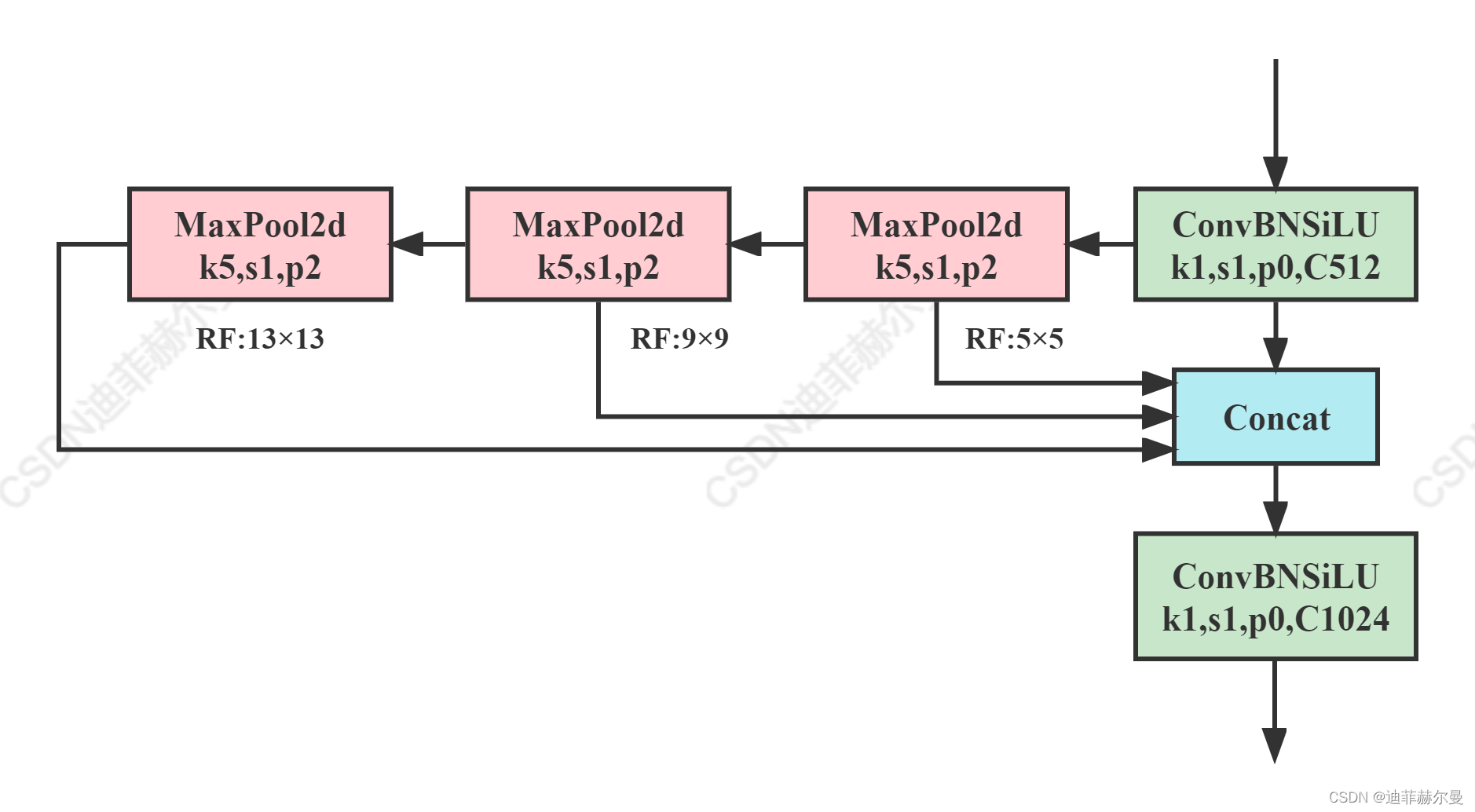
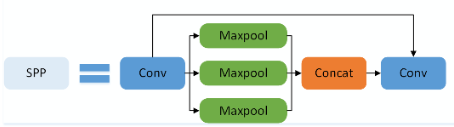

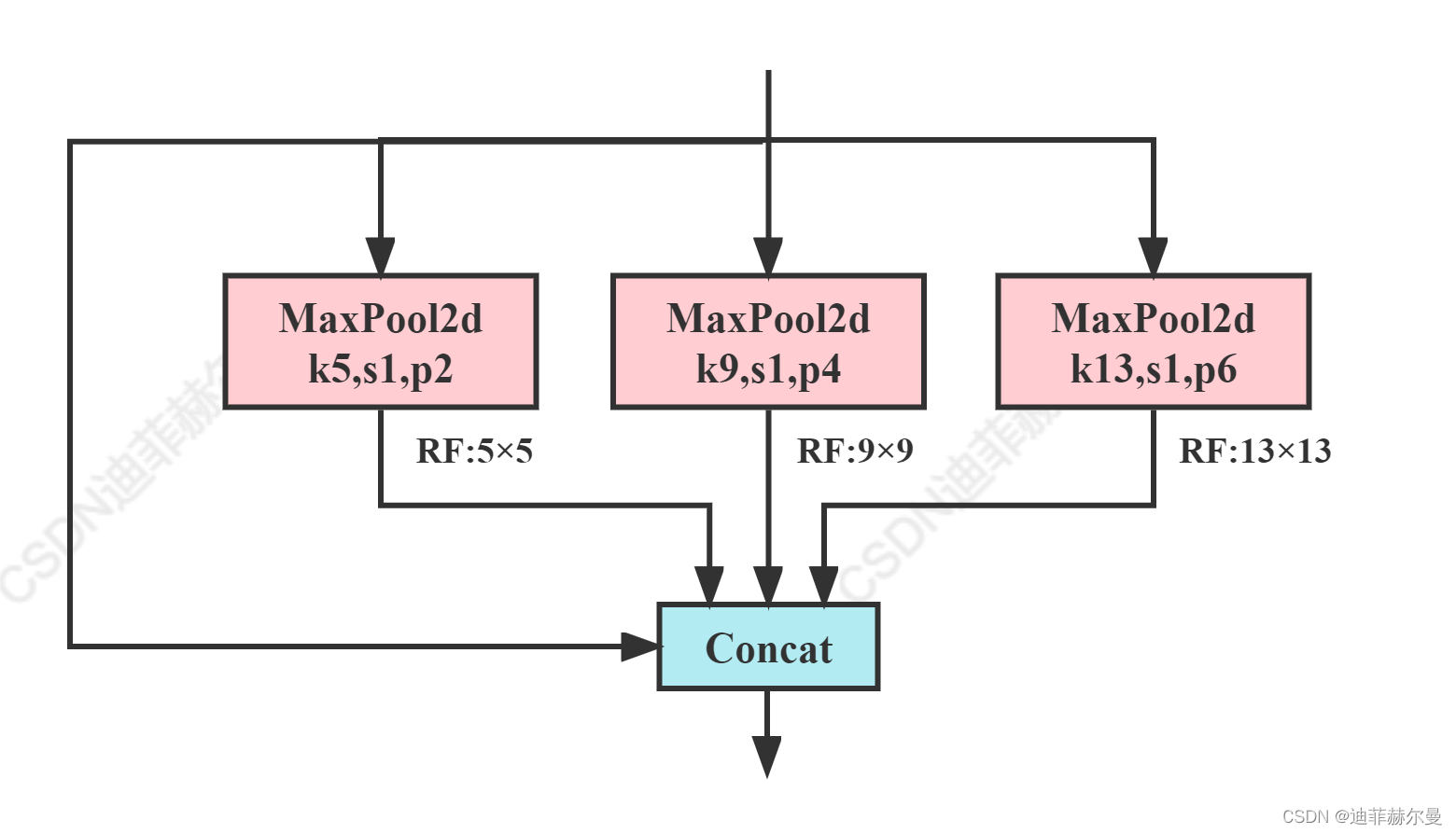
code_pytorch
class SPPF(nn.Module):# Spatial Pyramid Pooling - Fast (SPPF) layer for YOLOv5 by Glenn Jocherdef __init__(self, c1, c2, k=5): # equivalent to SPP(k=(5, 9, 13))super().__init__()c_ = c1 // 2 # hidden channelsself.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)self.cv2 = Conv(c_ * 4, c2, 1, 1)self.m = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=k, stride=1, padding=k // 2)def forward(self, x):x = self.cv1(x)with warnings.catch_warnings():warnings.simplefilter('ignore') # suppress torch 1.9.0 max_pool2d() warningy1 = self.m(x)y2 = self.m(y1)return self.cv2(torch.cat((x, y1, y2, self.m(y2)), 1))(3)ASPP(Simplified SPPF)
paper: DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs
paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1606.00915.pdf
repo link: https://github.com/kazuto1011/deeplab-pytorch
核心思想
提出了不对称空间金字塔池(ASPP)来在多个尺度上稳健地分割对象。ASPP在多个采样率和有效视场下使用滤波器探测传入的卷积特征层,从而在多个尺度上捕获对象和图像上下文。
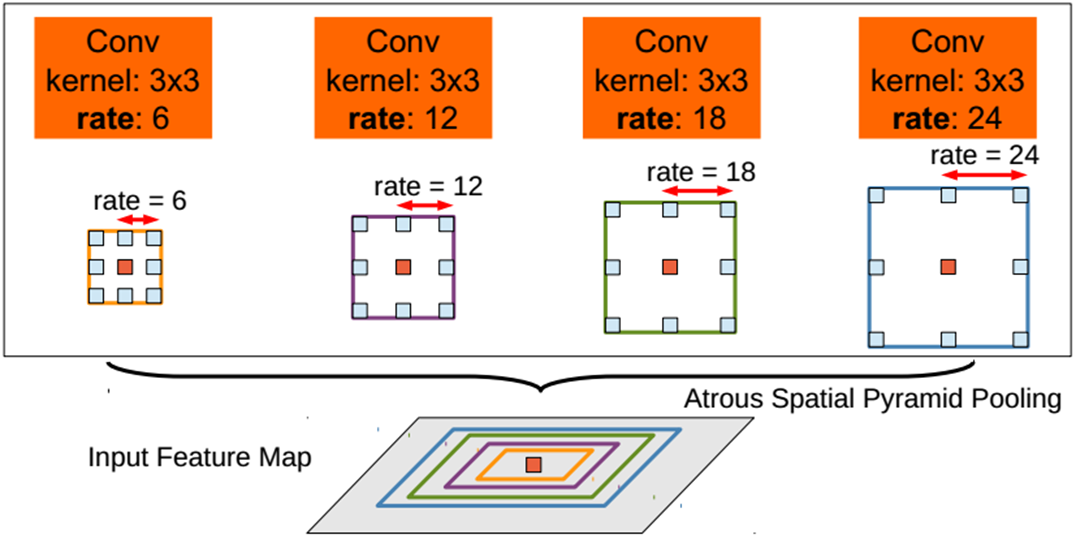
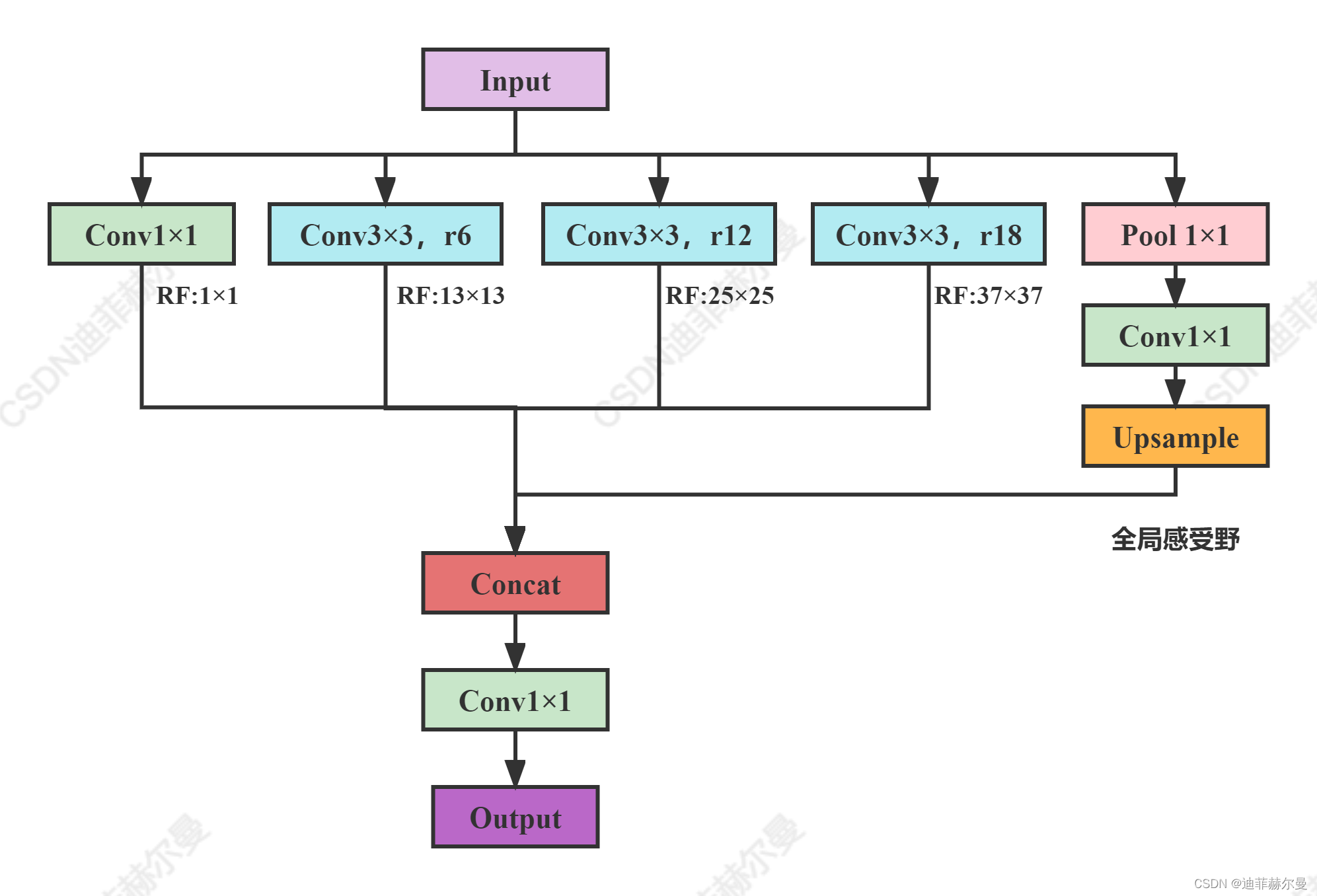
code_pytorch
class _ASPP(nn.Module):"""Atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP)"""def __init__(self, in_ch, out_ch, rates):super(_ASPP, self).__init__()for i, rate in enumerate(rates):self.add_module("c{}".format(i),nn.Conv2d(in_ch, out_ch, 3, 1, padding=rate, dilation=rate, bias=True),)for m in self.children():nn.init.normal_(m.weight, mean=0, std=0.01)nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)def forward(self, x):return sum([stage(x) for stage in self.children()])(4)RFB
paper: Receptive Field Block Net for Accurate and Fast Object Detection
paper link: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ECCV_2018/papers/Songtao_Liu_Receptive_Field_Block_ECCV_2018_paper.pdf
repo link: GitHub - GOATmessi7/RFBNet: Receptive Field Block Net for Accurate and Fast Object Detection, ECCV 2018
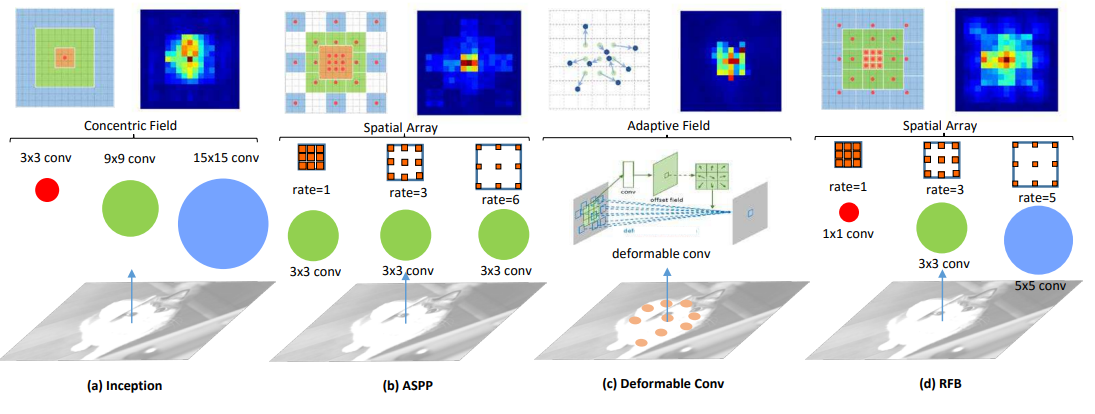
核心思想
受感受野(RF)结构的启发,我们提出了一种新的RF Block(RFB)模块,该模块考虑了RF的大小和偏心率之间的关系,以增强特征的可分辨性和鲁棒性。
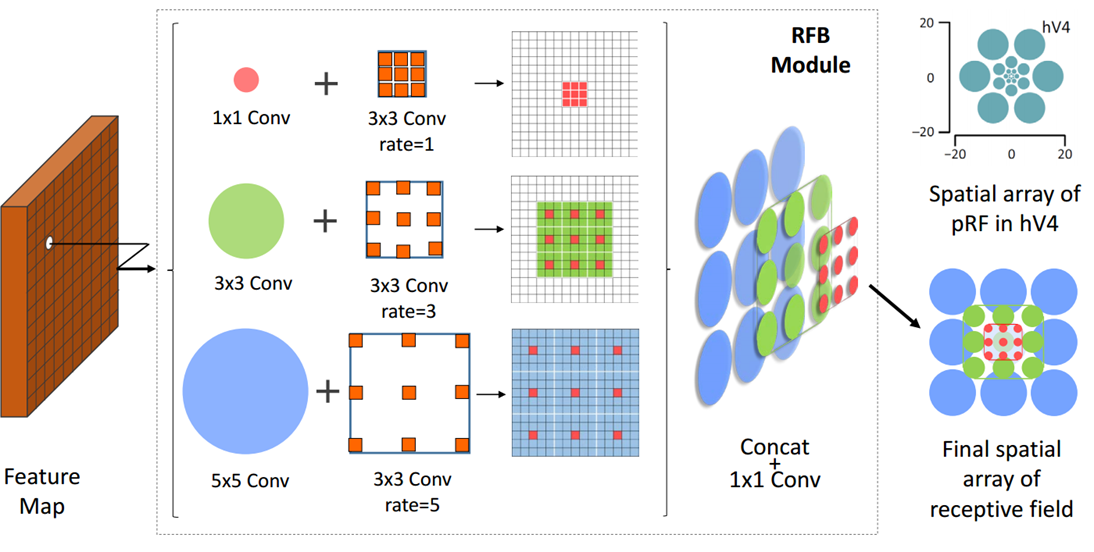

Code_Pytorch
class BasicRFB(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, stride=1, scale = 0.1, visual = 1):super(BasicRFB, self).__init__()self.scale = scaleself.out_channels = out_planesinter_planes = in_planes // 8self.branch0 = nn.Sequential(BasicConv(in_planes, 2*inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride),BasicConv(2*inter_planes, 2*inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=visual, dilation=visual, relu=False))self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(BasicConv(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1),BasicConv(inter_planes, 2*inter_planes, kernel_size=(3,3), stride=stride, padding=(1,1)),BasicConv(2*inter_planes, 2*inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=visual+1, dilation=visual+1, relu=False))self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(BasicConv(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1),BasicConv(inter_planes, (inter_planes//2)*3, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),BasicConv((inter_planes//2)*3, 2*inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1),BasicConv(2*inter_planes, 2*inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=2*visual+1, dilation=2*visual+1, relu=False))self.ConvLinear = BasicConv(6*inter_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1, relu=False)self.shortcut = BasicConv(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, relu=False)self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=False)def forward(self,x):x0 = self.branch0(x)x1 = self.branch1(x)x2 = self.branch2(x)out = torch.cat((x0,x1,x2),1)out = self.ConvLinear(out)short = self.shortcut(x)out = out*self.scale + shortout = self.relu(out)return outclass BasicRFB_a(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, stride=1, scale = 0.1):super(BasicRFB_a, self).__init__()self.scale = scaleself.out_channels = out_planesinter_planes = in_planes //4self.branch0 = nn.Sequential(BasicConv(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1),BasicConv(inter_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1,relu=False))self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(BasicConv(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1),BasicConv(inter_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=(3,1), stride=1, padding=(1,0)),BasicConv(inter_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=3, dilation=3, relu=False))self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(BasicConv(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1),BasicConv(inter_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=(1,3), stride=stride, padding=(0,1)),BasicConv(inter_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=3, dilation=3, relu=False))self.branch3 = nn.Sequential(BasicConv(in_planes, inter_planes//2, kernel_size=1, stride=1),BasicConv(inter_planes//2, (inter_planes//4)*3, kernel_size=(1,3), stride=1, padding=(0,1)),BasicConv((inter_planes//4)*3, inter_planes, kernel_size=(3,1), stride=stride, padding=(1,0)),BasicConv(inter_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=5, dilation=5, relu=False))self.ConvLinear = BasicConv(4*inter_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1, relu=False)self.shortcut = BasicConv(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, relu=False)self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=False)def forward(self,x):x0 = self.branch0(x)x1 = self.branch1(x)x2 = self.branch2(x)x3 = self.branch3(x)out = torch.cat((x0,x1,x2,x3),1)out = self.ConvLinear(out)short = self.shortcut(x)out = out*self.scale + shortout = self.relu(out)return outclass RFBNet(nn.Module):"""RFB Net for object detectionThe network is based on the SSD architecture.Each multibox layer branches into1) conv2d for class conf scores2) conv2d for localization predictions3) associated priorbox layer to produce default boundingboxes specific to the layer's feature map size.See: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1711.07767.pdf for more details on RFB Net.Args:phase: (string) Can be "test" or "train"base: VGG16 layers for input, size of either 300 or 512extras: extra layers that feed to multibox loc and conf layershead: "multibox head" consists of loc and conf conv layers"""def __init__(self, phase, size, base, extras, head, num_classes):super(RFBNet, self).__init__()self.phase = phaseself.num_classes = num_classesself.size = sizeif size == 300:self.indicator = 3elif size == 512:self.indicator = 5else:print("Error: Sorry only SSD300 and SSD512 are supported!")return# vgg networkself.base = nn.ModuleList(base)# conv_4self.Norm = BasicRFB_a(512,512,stride = 1,scale=1.0)self.extras = nn.ModuleList(extras)self.loc = nn.ModuleList(head[0])self.conf = nn.ModuleList(head[1])if self.phase == 'test':self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)def forward(self, x):"""Applies network layers and ops on input image(s) x.Args:x: input image or batch of images. Shape: [batch,3*batch,300,300].Return:Depending on phase:test:list of concat outputs from:1: softmax layers, Shape: [batch*num_priors,num_classes]2: localization layers, Shape: [batch,num_priors*4]3: priorbox layers, Shape: [2,num_priors*4]train:list of concat outputs from:1: confidence layers, Shape: [batch*num_priors,num_classes]2: localization layers, Shape: [batch,num_priors*4]3: priorbox layers, Shape: [2,num_priors*4]"""sources = list()loc = list()conf = list()# apply vgg up to conv4_3 relufor k in range(23):x = self.base[k](x)s = self.Norm(x)sources.append(s)# apply vgg up to fc7for k in range(23, len(self.base)):x = self.base[k](x)# apply extra layers and cache source layer outputsfor k, v in enumerate(self.extras):x = v(x)if k < self.indicator or k%2 ==0:sources.append(x)# apply multibox head to source layersfor (x, l, c) in zip(sources, self.loc, self.conf):loc.append(l(x).permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous())conf.append(c(x).permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous())#print([o.size() for o in loc])loc = torch.cat([o.view(o.size(0), -1) for o in loc], 1)conf = torch.cat([o.view(o.size(0), -1) for o in conf], 1)if self.phase == "test":output = (loc.view(loc.size(0), -1, 4), # loc predsself.softmax(conf.view(-1, self.num_classes)), # conf preds)else:output = (loc.view(loc.size(0), -1, 4),conf.view(conf.size(0), -1, self.num_classes),)return outputdef load_weights(self, base_file):other, ext = os.path.splitext(base_file)if ext == '.pkl' or '.pth':print('Loading weights into state dict...')self.load_state_dict(torch.load(base_file))print('Finished!')else:print('Sorry only .pth and .pkl files supported.')# This function is derived from torchvision VGG make_layers()
# https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/master/torchvision/models/vgg.py(5)SPPCSPC
paper: YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors
paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2207.02696v1.pdf
repo link: YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors | Papers With Code
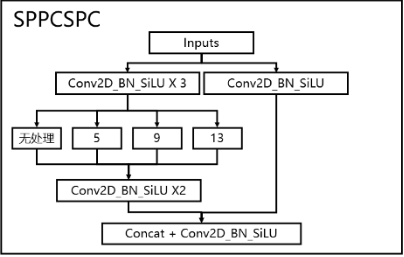
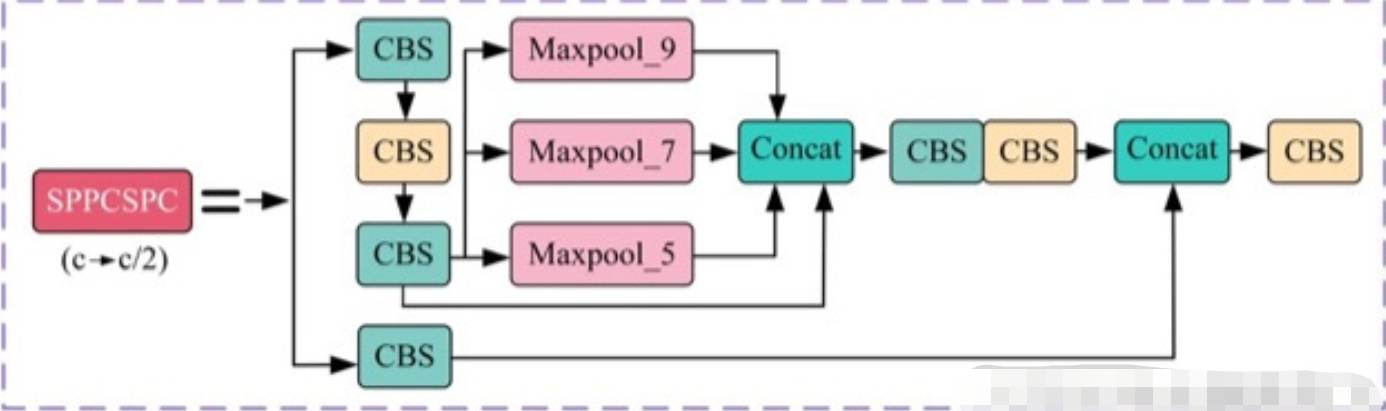
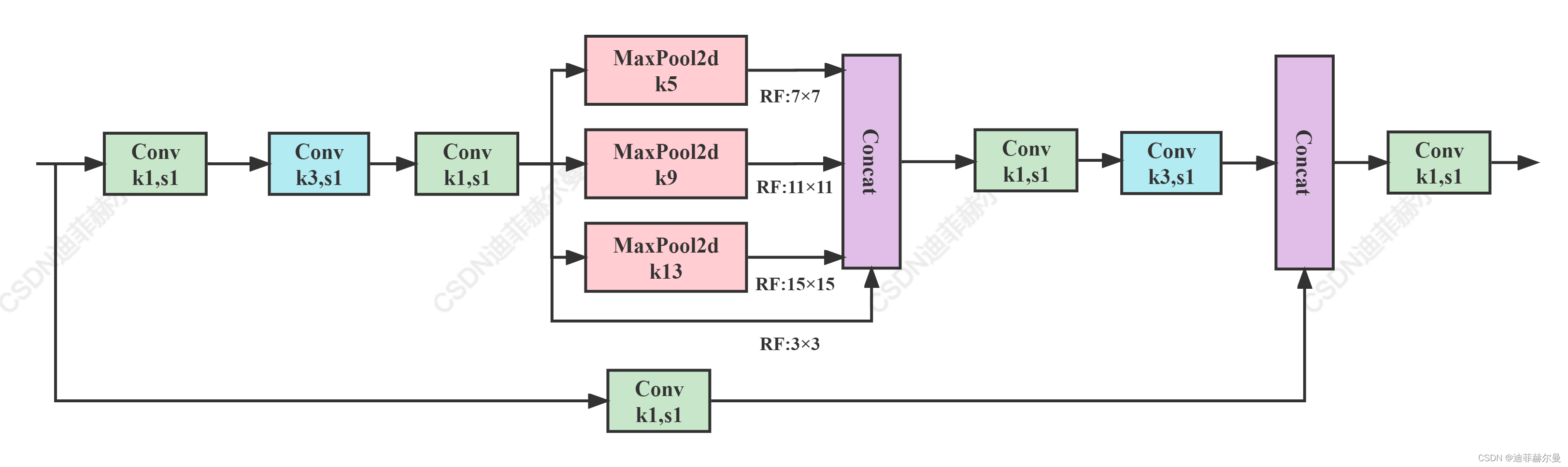
code_pytorch
class SPPCSPC(nn.Module):# CSP https://github.com/WongKinYiu/CrossStagePartialNetworksdef __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5, k=(5, 9, 13)):super(SPPCSPC, self).__init__()c_ = int(2 * c2 * e) # hidden channelsself.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)self.cv3 = Conv(c_, c_, 3, 1)self.cv4 = Conv(c_, c_, 1, 1)self.m = nn.ModuleList([nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=x, stride=1, padding=x // 2) for x in k])self.cv5 = Conv(4 * c_, c_, 1, 1)self.cv6 = Conv(c_, c_, 3, 1)self.cv7 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1, 1)def forward(self, x):x1 = self.cv4(self.cv3(self.cv1(x)))y1 = self.cv6(self.cv5(torch.cat([x1] + [m(x1) for m in self.m], 1)))y2 = self.cv2(x)return self.cv7(torch.cat((y1, y2), dim=1))(6) SimCSPSPPF
paper: YOLOv6 v3.0: A Full-Scale Reloading
paper link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.05586
repo link: GitHub - meituan/YOLOv6: YOLOv6: a single-stage object detection framework dedicated to industrial applications.
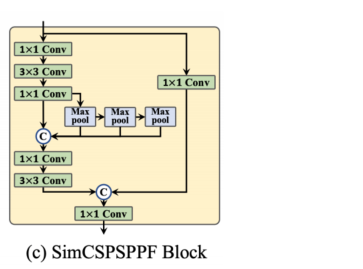
本文将SPPF简化为SimCSPSPF块,带来了性能增益,而速度退化可以忽略不计。
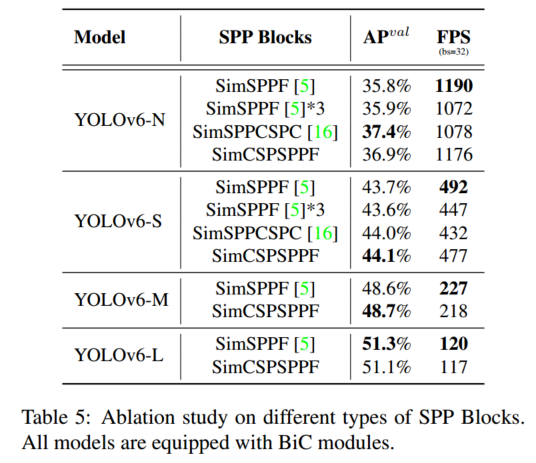
此外,探讨了不同类型的SPP块的影响,包括SPPF和SPPCSPC的简化变体(分别表示为SimSPPF和SimSPPCSPC)以及SimCSPSPF块,性能对比如下。
code_pytorch
class SPPFModule(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=5, block=ConvBNReLU):super().__init__()c_ = in_channels // 2 # hidden channelsself.cv1 = block(in_channels, c_, 1, 1)self.cv2 = block(c_ * 4, out_channels, 1, 1)self.m = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=1, padding=kernel_size // 2)def forward(self, x):x = self.cv1(x)with warnings.catch_warnings():warnings.simplefilter('ignore')y1 = self.m(x)y2 = self.m(y1)return self.cv2(torch.cat([x, y1, y2, self.m(y2)], 1))class SimSPPF(nn.Module):'''Simplified SPPF with ReLU activation'''def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=5, block=ConvBNReLU):super().__init__()self.sppf = SPPFModule(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, block)def forward(self, x):return self.sppf(x)class SPPF(nn.Module):'''SPPF with SiLU activation'''def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=5, block=ConvBNSiLU):super().__init__()self.sppf = SPPFModule(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, block)def forward(self, x):return self.sppf(x)class CSPSPPFModule(nn.Module):# CSP https://github.com/WongKinYiu/CrossStagePartialNetworksdef __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=5, e=0.5, block=ConvBNReLU):super().__init__()c_ = int(out_channels * e) # hidden channelsself.cv1 = block(in_channels, c_, 1, 1)self.cv2 = block(in_channels, c_, 1, 1)self.cv3 = block(c_, c_, 3, 1)self.cv4 = block(c_, c_, 1, 1)self.m = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=1, padding=kernel_size // 2)self.cv5 = block(4 * c_, c_, 1, 1)self.cv6 = block(c_, c_, 3, 1)self.cv7 = block(2 * c_, out_channels, 1, 1)def forward(self, x):x1 = self.cv4(self.cv3(self.cv1(x)))y0 = self.cv2(x)with warnings.catch_warnings():warnings.simplefilter('ignore')y1 = self.m(x1)y2 = self.m(y1)y3 = self.cv6(self.cv5(torch.cat([x1, y1, y2, self.m(y2)], 1)))return self.cv7(torch.cat((y0, y3), dim=1))class SimCSPSPPF(nn.Module):'''CSPSPPF with ReLU activation'''def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=5, e=0.5, block=ConvBNReLU):super().__init__()self.cspsppf = CSPSPPFModule(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, e, block)def forward(self, x):return self.cspsppf(x)class CSPSPPF(nn.Module):'''CSPSPPF with SiLU activation'''def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=5, e=0.5, block=ConvBNSiLU):super().__init__()self.cspsppf = CSPSPPFModule(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, e, block)def forward(self, x):return self.cspsppf(x)这篇关于空间金字塔池化(SPP,Spatial Pyramid Pooling)系列的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







