本文主要是介绍SpringBootApplication注解保姆级带你如何应对面试官,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
SpringBootApplication注解保姆级带你如何应对面试官
一介绍
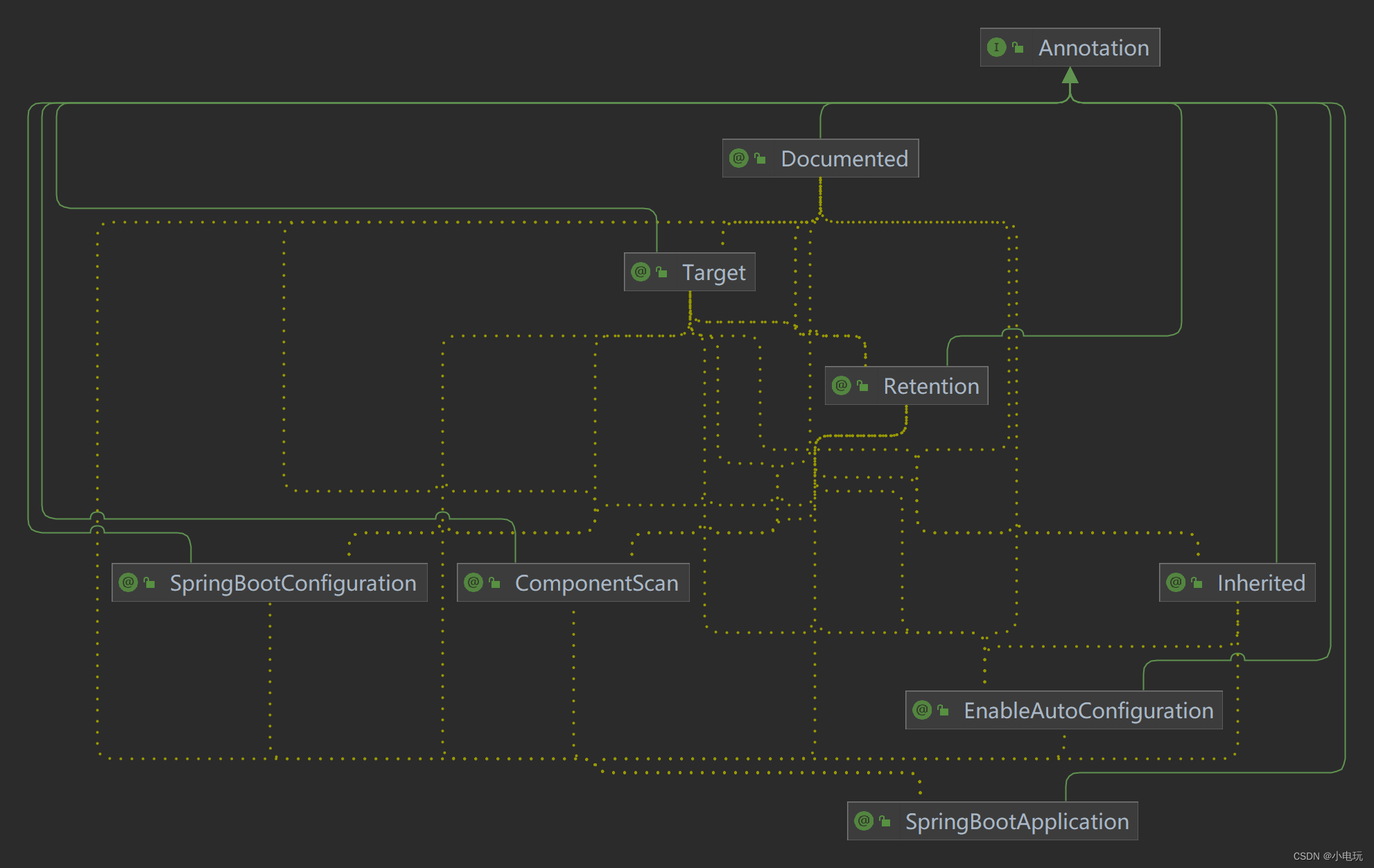
在Java Spring Boot框架中,@SpringBootApplication注解是一个组合注解,它由以下三个注解组成:@SpringBootConfiguration,@EnableAutoConfiguration和@ComponentScan。
这三个注解的加载顺序如下:
-
@SpringBootConfiguration:这个注解用于标识该类是Spring Boot应用的配置类,它会被自动扫描并加载。通常,这个注解会放在主类上(即包含main方法的类)。
-
@EnableAutoConfiguration:这个注解用于启用Spring Boot的自动配置机制。它会根据项目的依赖和配置来自动配置Spring应用上下文。这个注解通常会放在配置类上,以确保自动配置生效。
-
@ComponentScan:这个注解用于指定Spring应用程序上下文中要扫描的包。它会自动扫描并注册被@Component、@Service、@Controller等注解标记的Bean。通常,这个注解会放在配置类上,以扫描并加载所有需要的组件。
总结起来,@SpringBootApplication注解的加载顺序是先加载@SpringBootConfiguration,然后@EnableAutoConfiguration,最后@ComponentScan。这个加载顺序确保了正确的配置和自动装配,以及将需要的组件加载到Spring应用程序上下文中。
@SpringBootApplication 是 Spring Boot 中的一个组合注解,它包含了多个常用的注解,其中包括 @SpringBootConfiguration、@EnableAutoConfiguration 和 @ComponentScan 等。这些注解的加载顺序如下:
-
@Target(ElementType.TYPE):指定该注解只能用于类或接口上。 -
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME):指定该注解保留到运行时,并可以通过反射获取。 -
@Documented:指定该注解可以被 javadoc 工具记录。 -
@Inherited:指定该注解可以被继承。 -
@SpringBootConfiguration:该注解用于替换 Spring 的@Configuration注解,表明该类是 Spring Boot 应用的配置类。 -
@EnableAutoConfiguration:该注解用于自动配置 Spring Boot 应用程序,并根据 classpath 中的 jar 包依赖自动配置应用程序。 -
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class), @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) }):该注解用于扫描指定包中的 bean,并排除一些不需要的 bean。其中,excludeFilters属性用于指定排除哪些 bean,这里通过@Filter注解指定了两个自定义的过滤器。
总的来说,这些注解的加载顺序并没有具体的规定,因为这些注解之间并没有先后依赖关系。但是,如果你想要自定义 Spring Boot 应用程序的配置或者排除一些不需要的组件,你应该将这些注解应用在合适的位置,并根据需要进行合理的组合和配置。
二,源码注解以及翻译
@SpringBootApplication
Indicates a configuration class that declares one or more @Bean methods and also triggers auto-configuration and component scanning. This is a convenience annotation that is equivalent to declaring @Configuration, @EnableAutoConfiguration and @ComponentScan.
指示一个配置类,它声明一个或多个@Bean方法,并触发自动配置和组件扫描。这是一个方便的注释,相当于声明@Configuration, @EnableAutoConfiguration和@ComponentScan。
@SpringBootConfiguration
Indicates that a class provides Spring Boot application @Configuration. Can be used as an alternative to the Spring’s standard @Configuration annotation so that configuration can be found automatically (for example in tests). Application should only ever include one @SpringBootConfiguration and most idiomatic Spring Boot applications will inherit it from @SpringBootApplication.
指示一个类提供Spring Boot应用程序@Configuration。可以用作Spring的标准@Configuration注释的替代,以便可以自动找到配置(例如在测试中)。应用程序应该只包含一个@SpringBootConfiguration,大多数习惯的Spring引导应用程序将从@SpringBootApplication继承它。
@EnableAutoConfiguration
Enable auto-configuration of the Spring Application Context, attempting to guess and configure beans that you are likely to need. Auto-configuration classes are usually applied based on your classpath and what beans you have defined. For example, if you have tomcat-embedded.jar on your classpath you are likely to want a TomcatServletWebServerFactory (unless you have defined your own ServletWebServerFactory bean).
When using @SpringBootApplication, the auto-configuration of the context is automatically enabled and adding this annotation has therefore no additional effect.
Auto-configuration tries to be as intelligent as possible and will back-away as you define more of your own configuration. You can always manually exclude() any configuration that you never want to apply (use excludeName() if you don’t have access to them). You can also exclude them via the spring.autoconfigure.exclude property. Auto-configuration is always applied after user-defined beans have been registered.
The package of the class that is annotated with @EnableAutoConfiguration, usually via @SpringBootApplication, has specific significance and is often used as a ‘default’. For example, it will be used when scanning for @Entity classes. It is generally recommended that you place @EnableAutoConfiguration (if you’re not using @SpringBootApplication) in a root package so that all sub-packages and classes can be searched.
Auto-configuration classes are regular Spring @Configuration beans. They are located using the SpringFactoriesLoader mechanism (keyed against this class). Generally auto-configuration beans are @Conditional beans (most often using @ConditionalOnClass and @ConditionalOnMissingBean annotations).
启用Spring应用程序上下文的自动配置,尝试猜测和配置您可能需要的bean。自动配置类通常基于您的类路径和您定义的bean来应用。例如,如果您的类路径中有tomcat-embedded.jar,那么您可能需要一个TomcatServletWebServerFactory(除非您已经定义了自己的ServletWebServerFactory bean)。
当使用@SpringBootApplication时,上下文的自动配置是自动启用的,因此添加这个注释没有额外的效果。
自动配置试图尽可能地智能,并且会随着您定义更多自己的配置而后退。您始终可以手动排除()任何您不想应用的配置(如果您没有访问权限,请使用excludeName())。你也可以通过spring.autoconfigure.exclude属性排除它们。自动配置总是在用户定义bean注册之后应用。
用@EnableAutoConfiguration注释的类包,通常通过@SpringBootApplication,具有特定的意义,通常被用作“默认”。例如,它将在扫描@Entity类时使用。通常建议将@EnableAutoConfiguration(如果不使用@SpringBootApplication)放在根包中,以便可以搜索所有子包和类。
自动配置类是常规的Spring @Configuration bean。它们是使用springfactoresloader机制定位的(与这个类相关)。通常自动配置bean是@条件bean(最常使用@ConditionalOnClass和@ConditionalOnMissingBean注释)。
ComponentScan
Configures component scanning directives for use with @Configuration classes. Provides support parallel with Spring XML’s context:component-scan element.
Either basePackageClasses or basePackages (or its alias value) may be specified to define specific packages to scan. If specific packages are not defined, scanning will occur from the package of the class that declares this annotation.
Note that the context:component-scan element has an annotation-config attribute; however, this annotation does not. This is because in almost all cases when using @ComponentScan, default annotation config processing (e.g. processing @Autowired and friends) is assumed. Furthermore, when using AnnotationConfigApplicationContext, annotation config processors are always registered, meaning that any attempt to disable them at the @ComponentScan level would be ignored.
See @Configuration’s Javadoc for usage examples.
配置与@Configuration类一起使用的组件扫描指令。提供与Spring XML的context:component-scan元素并行的支持。
可以指定basepackageclass或basePackages(或其别名值)来定义要扫描的特定包。如果没有定义特定的包,则将从声明该注释的类的包中进行扫描。
注意,context:component-scan元素有一个annotation-config属性;但是,这个注释没有。这是因为在几乎所有使用@ComponentScan的情况下,默认的注释配置处理(例如处理@Autowired和friends)都是假设的。此外,当使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext时,注释配置处理器总是被注册的,这意味着任何在@ComponentScan级别禁用它们的尝试都会被忽略。
有关使用示例,请参阅@Configuration的Javadoc。
这篇关于SpringBootApplication注解保姆级带你如何应对面试官的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





