本文主要是介绍Redis ziplist源码解析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
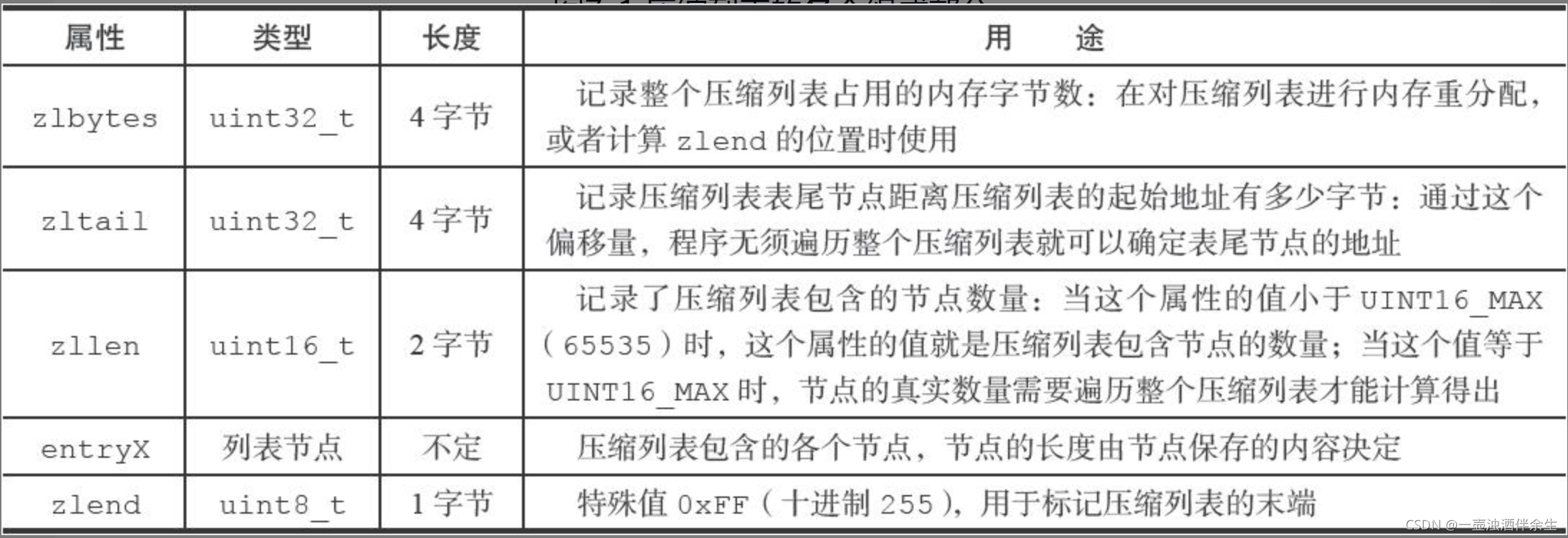
area |<---- ziplist header ---->|<----------- entries ------------->|<-end->|size 4 bytes 4 bytes 2 bytes ? ? ? ? 1 byte+---------+--------+-------+--------+--------+--------+--------+-------+ component | zlbytes | zltail | zllen | entry1 | entry2 | ... | entryN | zlend |+---------+--------+-------+--------+--------+--------+--------+-------+
+--------------+------------+---------------+ entry | prevlen | encoding | data | +--------------+------------+---------------+
|<-前一项长度 ->|<-当前编码->|<-存储的数据 ->|
编码过程:
entry存储的键值对会根据数据进行转码,尝试转化为整数编码,这样可以节省更多的空间。
各个版本差异比较大,这里参考的是redis3.0版本
/** 整数编码类型*/
#define ZIP_INT_16B (0xc0 | 0<<4)
#define ZIP_INT_32B (0xc0 | 1<<4)
#define ZIP_INT_64B (0xc0 | 2<<4)
#define ZIP_INT_24B (0xc0 | 3<<4)
#define ZIP_INT_8B 0xfe/* 4 bit integer immediate encoding ** 4 位整数编码的掩码和类型*/
#define ZIP_INT_IMM_MASK 0x0f
#define ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN 0xf1 /* 11110001 */
#define ZIP_INT_IMM_MAX 0xfd /* 11111101 */
#define ZIP_INT_IMM_VAL(v) (v & ZIP_INT_IMM_MASK)/* Check if string pointed to by 'entry' can be encoded as an integer.* Stores the integer value in 'v' and its encoding in 'encoding'. ** 检查 entry 中指向的字符串能否被编码为整数。** 如果可以的话,* 将编码后的整数保存在指针 v 的值中,并将编码的方式保存在指针 encoding 的值中。** 注意,这里的 entry 和前面代表节点的 entry 不是一个意思。** T = O(N)*/
static int zipTryEncoding(unsigned char *entry, unsigned int entrylen, long long *v, unsigned char *encoding) {long long value;// 忽略太长或太短的字符串if (entrylen >= 32 || entrylen == 0) return 0;// 尝试转换// T = O(N)if (string2ll((char*)entry,entrylen,&value)) {/* Great, the string can be encoded. Check what's the smallest* of our encoding types that can hold this value. */// 转换成功,以从小到大的顺序检查适合值 value 的编码方式if (value >= 0 && value <= 12) {*encoding = ZIP_INT_IMM_MIN+value;} else if (value >= INT8_MIN && value <= INT8_MAX) {*encoding = ZIP_INT_8B;} else if (value >= INT16_MIN && value <= INT16_MAX) {*encoding = ZIP_INT_16B;} else if (value >= INT24_MIN && value <= INT24_MAX) {*encoding = ZIP_INT_24B;} else if (value >= INT32_MIN && value <= INT32_MAX) {*encoding = ZIP_INT_32B;} else {*encoding = ZIP_INT_64B;}// 记录值到指针*v = value;// 返回转换成功标识return 1;}// 转换失败return 0;
}缺点:
查找性能差
查找一块连续内存区域,当储存的元素过多时,需要从头到尾去遍历,每一个entry都需要编码过程,十分耗时
/* Find pointer to the entry equal to the specified entry. * * 寻找节点值和 vstr 相等的列表节点,并返回该节点的指针。* * Skip 'skip' entries between every comparison. ** 每次比对之前都跳过 skip 个节点。** Returns NULL when the field could not be found. ** 如果找不到相应的节点,则返回 NULL 。** T = O(N^2)*/
unsigned char *ziplistFind(unsigned char *p, unsigned char *vstr, unsigned int vlen, unsigned int skip) {int skipcnt = 0;unsigned char vencoding = 0;long long vll = 0;// 只要未到达列表末端,就一直迭代// T = O(N^2)while (p[0] != ZIP_END) {unsigned int prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len;unsigned char *q;ZIP_DECODE_PREVLENSIZE(p, prevlensize);ZIP_DECODE_LENGTH(p + prevlensize, encoding, lensize, len);q = p + prevlensize + lensize;if (skipcnt == 0) {/* Compare current entry with specified entry */// 对比字符串值// T = O(N)if (ZIP_IS_STR(encoding)) {if (len == vlen && memcmp(q, vstr, vlen) == 0) {return p;}} else {/* Find out if the searched field can be encoded. Note that* we do it only the first time, once done vencoding is set* to non-zero and vll is set to the integer value. */// 因为传入值有可能被编码了,// 所以当第一次进行值对比时,程序会对传入值进行解码// 这个解码操作只会进行一次if (vencoding == 0) {if (!zipTryEncoding(vstr, vlen, &vll, &vencoding)) {/* If the entry can't be encoded we set it to* UCHAR_MAX so that we don't retry again the next* time. */vencoding = UCHAR_MAX;}/* Must be non-zero by now */assert(vencoding);}/* Compare current entry with specified entry, do it only* if vencoding != UCHAR_MAX because if there is no encoding* possible for the field it can't be a valid integer. */// 对比整数值if (vencoding != UCHAR_MAX) {// T = O(1)long long ll = zipLoadInteger(q, encoding);if (ll == vll) {return p;}}}/* Reset skip count */skipcnt = skip;} else {/* Skip entry */skipcnt--;}/* Move to next entry */// 后移指针,指向后置节点p = q + len;}// 没有找到指定的节点return NULL;
}连锁更新性能问题
更新或者删除某元素时,需要重新计算所需空间大小并且重新分配所需要的空间,性能肯定是不行的。详细请看下面ziplist增加元素的做法,一个 ziplist 元素包括了 prevlen(编码需要改变)、encoding 和实际数据 data 三个部分
/* Insert item at "p". */
/** 根据指针 p 所指定的位置,将长度为 slen 的字符串 s 插入到 zl 中。** 函数的返回值为完成插入操作之后的 ziplist** T = O(N^2)*/
static unsigned char *__ziplistInsert(unsigned char *zl, unsigned char *p, unsigned char *s, unsigned int slen) {// 记录当前 ziplist 的长度size_t curlen = intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_BYTES(zl)), reqlen, prevlen = 0;size_t offset;int nextdiff = 0;unsigned char encoding = 0;long long value = 123456789; /* initialized to avoid warning. Using a valuethat is easy to see if for some reasonwe use it uninitialized. */zlentry entry, tail;/* Find out prevlen for the entry that is inserted. */if (p[0] != ZIP_END) {// 如果 p[0] 不指向列表末端,说明列表非空,并且 p 正指向列表的其中一个节点// 那么取出 p 所指向节点的信息,并将它保存到 entry 结构中// 然后用 prevlen 变量记录前置节点的长度// (当插入新节点之后 p 所指向的节点就成了新节点的前置节点)// T = O(1)entry = zipEntry(p);prevlen = entry.prevrawlen;} else {// 如果 p 指向表尾末端,那么程序需要检查列表是否为:// 1)如果 ptail 也指向 ZIP_END ,那么列表为空;// 2)如果列表不为空,那么 ptail 将指向列表的最后一个节点。unsigned char *ptail = ZIPLIST_ENTRY_TAIL(zl);if (ptail[0] != ZIP_END) {// 表尾节点为新节点的前置节点// 取出表尾节点的长度// T = O(1)prevlen = zipRawEntryLength(ptail);}}/* See if the entry can be encoded */// 尝试看能否将输入字符串转换为整数,如果成功的话:// 1)value 将保存转换后的整数值// 2)encoding 则保存适用于 value 的编码方式// 无论使用什么编码, reqlen 都保存节点值的长度// T = O(N)if (zipTryEncoding(s,slen,&value,&encoding)) {/* 'encoding' is set to the appropriate integer encoding */reqlen = zipIntSize(encoding);} else {/* 'encoding' is untouched, however zipEncodeLength will use the* string length to figure out how to encode it. */reqlen = slen;}/* We need space for both the length of the previous entry and* the length of the payload. */// 计算编码前置节点的长度所需的大小// T = O(1)reqlen += zipPrevEncodeLength(NULL,prevlen);// 计算编码当前节点值所需的大小// T = O(1)reqlen += zipEncodeLength(NULL,encoding,slen);/* When the insert position is not equal to the tail, we need to* make sure that the next entry can hold this entry's length in* its prevlen field. */// 只要新节点不是被添加到列表末端,// 那么程序就需要检查看 p 所指向的节点(的 header)能否编码新节点的长度。// nextdiff 保存了新旧编码之间的字节大小差,如果这个值大于 0 // 那么说明需要对 p 所指向的节点(的 header )进行扩展// T = O(1)nextdiff = (p[0] != ZIP_END) ? zipPrevLenByteDiff(p,reqlen) : 0;/* Store offset because a realloc may change the address of zl. */// 因为重分配空间可能会改变 zl 的地址// 所以在分配之前,需要记录 zl 到 p 的偏移量,然后在分配之后依靠偏移量还原 p offset = p-zl;// curlen 是 ziplist 原来的长度// reqlen 是整个新节点的长度// nextdiff 是新节点的后继节点扩展 header 的长度(要么 0 字节,要么 4 个字节)// T = O(N)zl = ziplistResize(zl,curlen+reqlen+nextdiff);p = zl+offset;/* Apply memory move when necessary and update tail offset. */if (p[0] != ZIP_END) {// 新元素之后还有节点,因为新元素的加入,需要对这些原有节点进行调整/* Subtract one because of the ZIP_END bytes */// 移动现有元素,为新元素的插入空间腾出位置// T = O(N)memmove(p+reqlen,p-nextdiff,curlen-offset-1+nextdiff);/* Encode this entry's raw length in the next entry. */// 将新节点的长度编码至后置节点// p+reqlen 定位到后置节点// reqlen 是新节点的长度// T = O(1)zipPrevEncodeLength(p+reqlen,reqlen);/* Update offset for tail */// 更新到达表尾的偏移量,将新节点的长度也算上ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+reqlen);/* When the tail contains more than one entry, we need to take* "nextdiff" in account as well. Otherwise, a change in the* size of prevlen doesn't have an effect on the *tail* offset. */// 如果新节点的后面有多于一个节点// 那么程序需要将 nextdiff 记录的字节数也计算到表尾偏移量中// 这样才能让表尾偏移量正确对齐表尾节点// T = O(1)tail = zipEntry(p+reqlen);if (p[reqlen+tail.headersize+tail.len] != ZIP_END) {ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) =intrev32ifbe(intrev32ifbe(ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl))+nextdiff);}} else {/* This element will be the new tail. */// 新元素是新的表尾节点ZIPLIST_TAIL_OFFSET(zl) = intrev32ifbe(p-zl);}/* When nextdiff != 0, the raw length of the next entry has changed, so* we need to cascade the update throughout the ziplist */// 当 nextdiff != 0 时,新节点的后继节点的(header 部分)长度已经被改变,// 所以需要级联地更新后续的节点if (nextdiff != 0) {offset = p-zl;// T = O(N^2)zl = __ziplistCascadeUpdate(zl,p+reqlen);p = zl+offset;}/* Write the entry */// 一切搞定,将前置节点的长度写入新节点的 headerp += zipPrevEncodeLength(p,prevlen);// 将节点值的长度写入新节点的 headerp += zipEncodeLength(p,encoding,slen);// 写入节点值if (ZIP_IS_STR(encoding)) {// T = O(N)memcpy(p,s,slen);} else {// T = O(1)zipSaveInteger(p,value,encoding);}// 更新列表的节点数量计数器// T = O(1)ZIPLIST_INCR_LENGTH(zl,1);return zl;
}这篇关于Redis ziplist源码解析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





