本文主要是介绍FFMpeg分析:第一个函数avformat_open_input,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
在上篇文章中的demo中,main函数的流程里调用的第一个函数就是avformat_open_input()。直观看来,其最明显的功能就是制定了要播放的文件名了。但是除了问价名之外还有几个结构体作为了函数的参数。那么这个函数的功能是什么?又是怎么完成的?一起慢慢研究。
先贴代码:
int avformat_open_input(AVFormatContext **ps, const char *filename, AVInputFormat *fmt, AVDictionary **options)
{AVFormatContext *s = *ps;int ret = 0;AVDictionary *tmp = NULL;ID3v2ExtraMeta *id3v2_extra_meta = NULL;if (!s && !(s = avformat_alloc_context()))return AVERROR(ENOMEM);if (!s->av_class){av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Input context has not been properly allocated by avformat_alloc_context() and is not NULL either\n");return AVERROR(EINVAL);}if (fmt)s->iformat = fmt;if (options)av_dict_copy(&tmp, *options, 0);if ((ret = av_opt_set_dict(s, &tmp)) < 0)goto fail;if ((ret = init_input(s, filename, &tmp)) < 0)goto fail;s->probe_score = ret;avio_skip(s->pb, s->skip_initial_bytes);/* check filename in case an image number is expected */if (s->iformat->flags & AVFMT_NEEDNUMBER) {if (!av_filename_number_test(filename)) {ret = AVERROR(EINVAL);goto fail;}}s->duration = s->start_time = AV_NOPTS_VALUE;av_strlcpy(s->filename, filename ? filename : "", sizeof(s->filename));/* allocate private data */if (s->iformat->priv_data_size > 0) {if (!(s->priv_data = av_mallocz(s->iformat->priv_data_size))){ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);goto fail;}if (s->iformat->priv_class) {*(const AVClass**)s->priv_data = s->iformat->priv_class;av_opt_set_defaults(s->priv_data);if ((ret = av_opt_set_dict(s->priv_data, &tmp)) < 0)goto fail;}}/* e.g. AVFMT_NOFILE formats will not have a AVIOContext */if (s->pb)ff_id3v2_read(s, ID3v2_DEFAULT_MAGIC, &id3v2_extra_meta);if (!(s->flags&AVFMT_FLAG_PRIV_OPT) && s->iformat->read_header)if ((ret = s->iformat->read_header(s)) < 0)goto fail;if (id3v2_extra_meta){if (!strcmp(s->iformat->name, "mp3") || !strcmp(s->iformat->name, "aac") ||!strcmp(s->iformat->name, "tta")) {if((ret = ff_id3v2_parse_apic(s, &id3v2_extra_meta)) < 0)goto fail;} elseav_log(s, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "demuxer does not support additional id3 data, skipping\n");}ff_id3v2_free_extra_meta(&id3v2_extra_meta);if ((ret = avformat_queue_attached_pictures(s)) < 0)goto fail;if (!(s->flags&AVFMT_FLAG_PRIV_OPT) && s->pb && !s->data_offset)s->data_offset = avio_tell(s->pb);s->raw_packet_buffer_remaining_size = RAW_PACKET_BUFFER_SIZE;if (options) {av_dict_free(options);*options = tmp;}*ps = s;return 0;fail:ff_id3v2_free_extra_meta(&id3v2_extra_meta);av_dict_free(&tmp);if (s->pb && !(s->flags & AVFMT_FLAG_CUSTOM_IO))avio_close(s->pb);avformat_free_context(s);*ps = NULL;return ret;
}1、AVFormatContext **ps:指向用户提供的结构体,一般可以将这个参数定义指向空然后传递到函数中,这样avformat_open_input函数将会分配这个结构体的内存空间并初始化。
2、const char *filename:打开视频文件的文件名。
3、AVInputFormat *fmt:如果这个参数不为空,则指定固定的输入格式,否则自动检测输入格式;一般设为空即可。
4、AVDictionary **options:由AVFormatContext和demuxer-private options组成的字典结构,可设为空。
该函数中调用了init_input()函数实现打开目标文件和检测文件格式等操作,代码如下:
static int init_input(AVFormatContext *s, const char *filename, AVDictionary **options)
{int ret;AVProbeData pd = {filename, NULL, 0};int score = AVPROBE_SCORE_RETRY;if (s->pb) {s->flags |= AVFMT_FLAG_CUSTOM_IO;if (!s->iformat)return av_probe_input_buffer2(s->pb, &s->iformat, filename, s, 0, s->probesize);else if (s->iformat->flags & AVFMT_NOFILE)av_log(s, AV_LOG_WARNING, "Custom AVIOContext makes no sense and ""will be ignored with AVFMT_NOFILE format.\n");return 0;}if ( (s->iformat && s->iformat->flags & AVFMT_NOFILE) ||(!s->iformat && (s->iformat = av_probe_input_format2(&pd, 0, &score))))return score;if ((ret = avio_open2(&s->pb, filename, AVIO_FLAG_READ | s->avio_flags,&s->interrupt_callback, options)) < 0)return ret;if (s->iformat)return 0;return av_probe_input_buffer2(s->pb, &s->iformat, filename, s, 0, s->probesize);
}int av_probe_input_buffer2(AVIOContext *pb, AVInputFormat **fmt, const char *filename, void *logctx, unsigned int offset, unsigned int max_probe_size)
{AVProbeData pd = { filename ? filename : "", NULL, -offset };unsigned char *buf = NULL;uint8_t *mime_type;int ret = 0, probe_size, buf_offset = 0;int score = 0;if (!max_probe_size) {max_probe_size = PROBE_BUF_MAX;} else if (max_probe_size > PROBE_BUF_MAX) {max_probe_size = PROBE_BUF_MAX;} else if (max_probe_size < PROBE_BUF_MIN) {av_log(logctx, AV_LOG_ERROR,"Specified probe size value %u cannot be < %u\n", max_probe_size, PROBE_BUF_MIN);return AVERROR(EINVAL);}if (offset >= max_probe_size) {return AVERROR(EINVAL);}if (!*fmt && pb->av_class && av_opt_get(pb, "mime_type", AV_OPT_SEARCH_CHILDREN, &mime_type) >= 0 && mime_type) {if (!av_strcasecmp(mime_type, "audio/aacp")) {*fmt = av_find_input_format("aac");}av_freep(&mime_type);}for(probe_size= PROBE_BUF_MIN; probe_size<=max_probe_size && !*fmt;probe_size = FFMIN(probe_size<<1, FFMAX(max_probe_size, probe_size+1))) {if (probe_size < offset) {continue;}score = probe_size < max_probe_size ? AVPROBE_SCORE_RETRY : 0;/* read probe data */if ((ret = av_reallocp(&buf, probe_size + AVPROBE_PADDING_SIZE)) < 0)return ret;if ((ret = avio_read(pb, buf + buf_offset, probe_size - buf_offset)) < 0) {/* fail if error was not end of file, otherwise, lower score */if (ret != AVERROR_EOF) {av_free(buf);return ret;}score = 0;ret = 0; /* error was end of file, nothing read */}pd.buf_size = buf_offset += ret;pd.buf = &buf[offset];memset(pd.buf + pd.buf_size, 0, AVPROBE_PADDING_SIZE);/* guess file format */*fmt = av_probe_input_format2(&pd, 1, &score);if(*fmt){if(score <= AVPROBE_SCORE_RETRY){ //this can only be true in the last iterationav_log(logctx, AV_LOG_WARNING, "Format %s detected only with low score of %d, misdetection possible!\n", (*fmt)->name, score);}elseav_log(logctx, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "Format %s probed with size=%d and score=%d\n", (*fmt)->name, probe_size, score);}}if (!*fmt) {av_free(buf);return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;}/* rewind. reuse probe buffer to avoid seeking */ret = ffio_rewind_with_probe_data(pb, &buf, pd.buf_size);return ret < 0 ? ret : score;
}avio_open2()的代码如下:
int avio_open2(AVIOContext **s, const char *filename, int flags, const AVIOInterruptCB *int_cb, AVDictionary **options)
{URLContext *h;int err;err = ffurl_open(&h, filename, flags, int_cb, options);if (err < 0)return err;err = ffio_fdopen(s, h);if (err < 0) {ffurl_close(h);return err;}return 0;
}1、AVIOContext **s:用于指向返回的AVIOContext结构体的指针,调用时应设为NULL;
2、const char *url:指定资源的地址;考虑本地播放时,就是文件名的字符串的地址;
3、int flags:标志位,控制文件打开的方式;
4、const AVIOInterruptCB *int_cb:在协议层使用的中断回调指针;
5、AVDictionary **options:protocol-private options组成的字典元素,设为空即可。
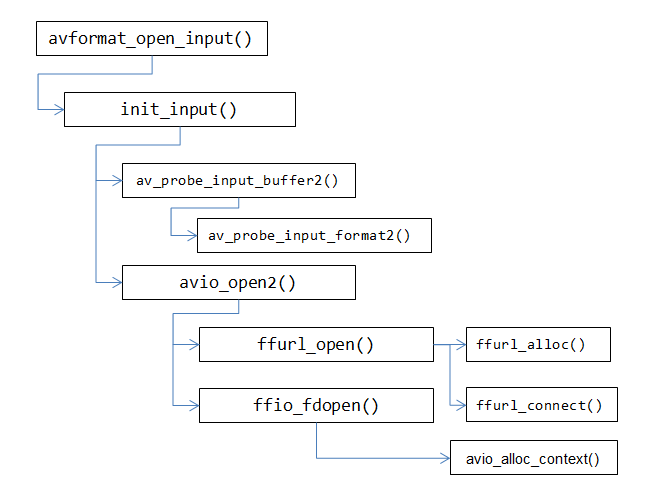
avio_open2()调用了ffurl_open()函数,创建一个URLContext结构体用于获取并打开url指向的资源(分别调用ffurl_alloc()和ffurl_connect()创建和链接URLContext结构体);调用ffio_fdopen()函数创建AVIOContext()结构体并获取URLContext结构体引用的资源(调用avio_alloc_context()实现);
整个函数的大致框图如下:
在实际运行的过程中,url_read、url_write等函数都由一个URLProtocal实现,代码如下:
typedef struct URLProtocol
{const char *name;int (*url_open)( URLContext *h, const char *url, int flags);/*** This callback is to be used by protocols which open further nested* protocols. options are then to be passed to ffurl_open()/ffurl_connect()* for those nested protocols.*/int (*url_open2)(URLContext *h, const char *url, int flags, AVDictionary **options);/*** Read data from the protocol.* If data is immediately available (even less than size), EOF is* reached or an error occurs (including EINTR), return immediately.* Otherwise:* In non-blocking mode, return AVERROR(EAGAIN) immediately.* In blocking mode, wait for data/EOF/error with a short timeout (0.1s),* and return AVERROR(EAGAIN) on timeout.* Checking interrupt_callback, looping on EINTR and EAGAIN and until* enough data has been read is left to the calling function; see* retry_transfer_wrapper in avio.c.*/int (*url_read)( URLContext *h, unsigned char *buf, int size);int (*url_write)(URLContext *h, const unsigned char *buf, int size);int64_t (*url_seek)( URLContext *h, int64_t pos, int whence);int (*url_close)(URLContext *h);struct URLProtocol *next;int (*url_read_pause)(URLContext *h, int pause);int64_t (*url_read_seek)(URLContext *h, int stream_index,int64_t timestamp, int flags);int (*url_get_file_handle)(URLContext *h);int (*url_get_multi_file_handle)(URLContext *h, int **handles,int *numhandles);int (*url_shutdown)(URLContext *h, int flags);int priv_data_size;const AVClass *priv_data_class;int flags;int (*url_check)(URLContext *h, int mask);
} URLProtocol;文件协议:
URLProtocol ff_pipe_protocol = {.name = "pipe",.url_open = pipe_open,.url_read = file_read,.url_write = file_write,.url_get_file_handle = file_get_handle,.url_check = file_check,.priv_data_size = sizeof(FileContext),.priv_data_class = &pipe_class,
};URLProtocol ff_ftp_protocol = {.name = "ftp",.url_open = ftp_open,.url_read = ftp_read,.url_write = ftp_write,.url_seek = ftp_seek,.url_close = ftp_close,.url_get_file_handle = ftp_get_file_handle,.url_shutdown = ftp_shutdown,.priv_data_size = sizeof(FTPContext),.priv_data_class = &ftp_context_class,.flags = URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NETWORK,
};URLProtocol ff_http_protocol = {.name = "http",.url_open2 = http_open,.url_read = http_read,.url_write = http_write,.url_seek = http_seek,.url_close = http_close,.url_get_file_handle = http_get_file_handle,.url_shutdown = http_shutdown,.priv_data_size = sizeof(HTTPContext),.priv_data_class = &http_context_class,.flags = URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NETWORK,
};URLProtocol ff_librtmp_protocol ={.name = "rtmp",.url_open = rtmp_open,.url_read = rtmp_read,.url_write = rtmp_write,.url_close = rtmp_close,.url_read_pause = rtmp_read_pause,.url_read_seek = rtmp_read_seek,.url_get_file_handle = rtmp_get_file_handle,.priv_data_size = sizeof(LibRTMPContext),.priv_data_class = &librtmp_class,.flags = URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NETWORK,
};
这篇关于FFMpeg分析:第一个函数avformat_open_input的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!