本文主要是介绍pytorch的使用:使用神经网络进行气温预测,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1.首先,我们查看一下数据的相关情况


数据表中
- year,moth,day,week分别表示的具体的时间
- temp_2:前天的最高温度值
- temp_1:昨天的最高温度值
- average:在历史中,每年这一天的平均最高温度值
- actual:这就是我们的标签值了,当天的真实最高温度
- friend:这一列可能是凑热闹的,你的朋友猜测的可能值,不管它就好了
年月日都是时间方面的特征,我们将它转换为时间类型的数据,方便我们的绘图展示
# 处理时间数据
import datetime# 分别得到年,月,日
years = features['year']
months = features['month']
days = features['day']# datetime格式
dates = [str(int(year)) + '-' + str(int(month)) + '-' + str(int(day)) for year, month, day in zip(years, months, days)]
dates = [datetime.datetime.strptime(date, '%Y-%m-%d') for date in dates]
我们再用图直观的将数据展示出来:
# 准备画图
# 指定默认风格
plt.style.use('fivethirtyeight')# 设置布局
fig, ((ax1, ax2), (ax3, ax4)) = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, figsize = (10,10))
fig.autofmt_xdate(rotation = 45)# 标签值
ax1.plot(dates, features['actual'])
ax1.set_xlabel(''); ax1.set_ylabel('Temperature'); ax1.set_title('Max Temp')# 昨天
ax2.plot(dates, features['temp_1'])
ax2.set_xlabel(''); ax2.set_ylabel('Temperature'); ax2.set_title('Previous Max Temp')# 前天
ax3.plot(dates, features['temp_2'])
ax3.set_xlabel('Date'); ax3.set_ylabel('Temperature'); ax3.set_title('Two Days Prior Max Temp')# 我的逗逼朋友
ax4.plot(dates, features['friend'])
ax4.set_xlabel('Date'); ax4.set_ylabel('Temperature'); ax4.set_title('Friend Estimate')plt.tight_layout(pad=2) 
将文本数据转换为独热编码:

在特征中去掉标签列:
# 标签
labels = np.array(features['actual'])# 在特征中去掉标签
features= features.drop('actual', axis = 1)# 名字单独保存一下,以备后患
feature_list = list(features.columns)# 转换成合适的格式
features = np.array(features)对数据进行标准化处理:

2.构建网络模型
包括:权重参数初始化、计算隐层、加入激活函数、预测结果、计算损失、返向传播计算、更新参数。另外,每次迭代都得记得清空梯度,否则梯度会累加
x = torch.tensor(input_features, dtype = float)y = torch.tensor(labels, dtype = float)# 权重参数初始化
weights = torch.randn((14, 128), dtype = float, requires_grad = True)
biases = torch.randn(128, dtype = float, requires_grad = True)
weights2 = torch.randn((128, 1), dtype = float, requires_grad = True)
biases2 = torch.randn(1, dtype = float, requires_grad = True) learning_rate = 0.001
losses = []for i in range(1000):# 计算隐层hidden = x.mm(weights) + biases# 加入激活函数hidden = torch.relu(hidden)# 预测结果predictions = hidden.mm(weights2) + biases2# 通计算损失loss = torch.mean((predictions - y) ** 2) losses.append(loss.data.numpy())# 打印损失值if i % 100 == 0:print('loss:', loss)#返向传播计算loss.backward()#更新参数weights.data.add_(- learning_rate * weights.grad.data) biases.data.add_(- learning_rate * biases.grad.data)weights2.data.add_(- learning_rate * weights2.grad.data)biases2.data.add_(- learning_rate * biases2.grad.data)# 每次迭代都得记得清空weights.grad.data.zero_()biases.grad.data.zero_()weights2.grad.data.zero_()biases2.grad.data.zero_()
3.更简单的网络模型
直接使用nn.Model
input_size = input_features.shape[1]
hidden_size = 128
output_size = 1
batch_size = 16
my_nn = torch.nn.Sequential(torch.nn.Linear(input_size, hidden_size),torch.nn.Sigmoid(),torch.nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size),
)
cost = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean')
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(my_nn.parameters(), lr = 0.001)训练网络:
# 训练网络
losses = []
for i in range(1000):batch_loss = []# MINI-Batch方法来进行训练for start in range(0, len(input_features), batch_size):end = start + batch_size if start + batch_size < len(input_features) else len(input_features)xx = torch.tensor(input_features[start:end], dtype = torch.float, requires_grad = True)yy = torch.tensor(labels[start:end], dtype = torch.float, requires_grad = True)prediction = my_nn(xx)loss = cost(prediction, yy)optimizer.zero_grad()loss.backward(retain_graph=True)optimizer.step()batch_loss.append(loss.data.numpy())# 打印损失if i % 100==0:losses.append(np.mean(batch_loss))print(i, np.mean(batch_loss))
4.预训练结果
x = torch.tensor(input_features, dtype = torch.float)
predict = my_nn(x).data.numpy() 转换日期格式
dates = [str(int(year)) + '-' + str(int(month)) + '-' + str(int(day)) for year, month, day in zip(years, months, days)]
dates = [datetime.datetime.strptime(date, '%Y-%m-%d') for date in dates]# 创建一个表格来存日期和其对应的标签数值
true_data = pd.DataFrame(data = {'date': dates, 'actual': labels})# 同理,再创建一个来存日期和其对应的模型预测值
months = features[:, feature_list.index('month')]
days = features[:, feature_list.index('day')]
years = features[:, feature_list.index('year')]test_dates = [str(int(year)) + '-' + str(int(month)) + '-' + str(int(day)) for year, month, day in zip(years, months, days)]test_dates = [datetime.datetime.strptime(date, '%Y-%m-%d') for date in test_dates]predictions_data = pd.DataFrame(data = {'date': test_dates, 'prediction': predict.reshape(-1)}) # 真实值
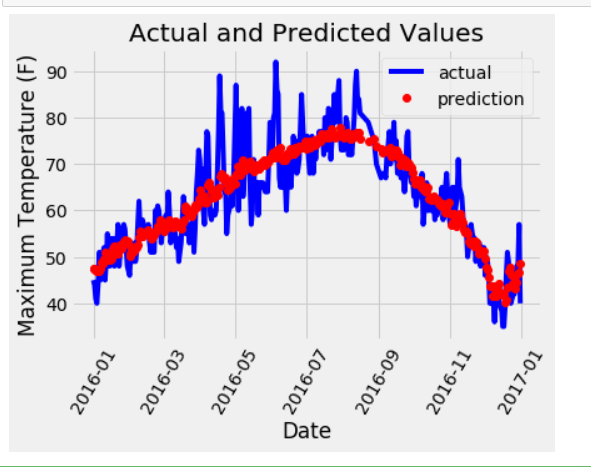
plt.plot(true_data['date'], true_data['actual'], 'b-', label = 'actual')# 预测值
plt.plot(predictions_data['date'], predictions_data['prediction'], 'ro', label = 'prediction')
plt.xticks(rotation = '60');
plt.legend()# 图名
plt.xlabel('Date'); plt.ylabel('Maximum Temperature (F)'); plt.title('Actual and Predicted Values');
这篇关于pytorch的使用:使用神经网络进行气温预测的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




