本文主要是介绍【6.824】分布式lab1 mapReduce,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Paper main idea
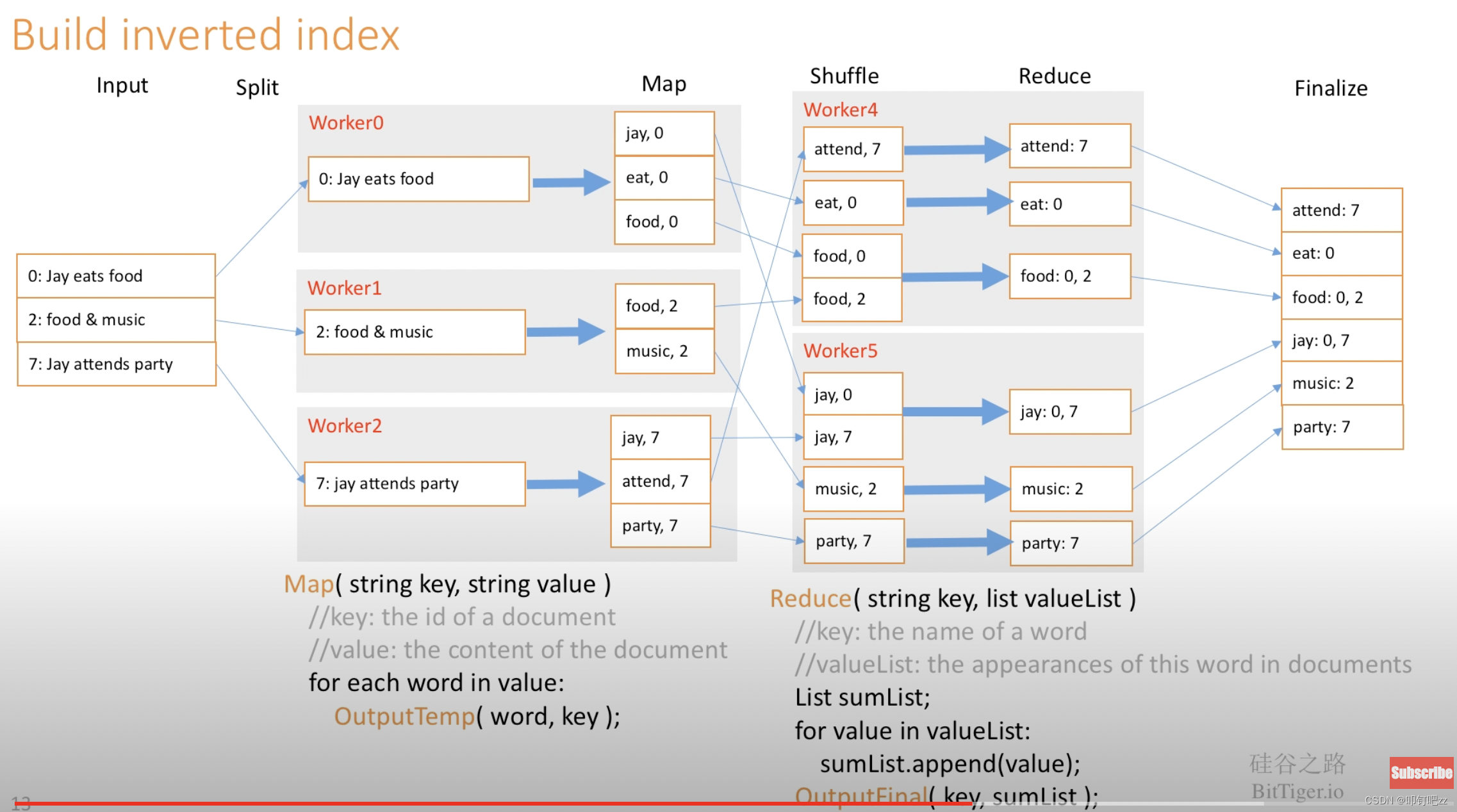
Figure 1 shows the overall flow of a MapReduce operation in our implementation. When the user program calls the MapReduce function, the following sequence of actions occurs (the numbered labels in Figure 1 correspond to the numbers in the list below): 1. The MapReduce library in the user program first splits the input files into M pieces of typically 16 megabytes to 64 megabytes (MB) per piece (controllable by the user via an optional parameter). It then starts up many copies of the program on a cluster of machines. 2. One of the copies of the program is special – the master. The rest are workers that are assigned work by the master. There are M map tasks and R reduce tasks to assign. The master picks idle workers and assigns each one a map task or a reduce task. 3. A worker who is assigned a map task reads the contents of the corresponding input split. It parses key/value pairs out of the input data and passes each pair to the user-defined Map function. The intermediate key/value pairs produced by the Map function are buffered in memory4. Periodically, the buffered pairs are written to local disk, partitioned into R regions by the partitioning function. The locations of these buffered pairs on the local disk are passed back to the master, who is responsible for forwarding these locations to the reduce workers. 5. When a reduce worker is notified by the master about these locations, it uses remote procedure calls to read the buffered data from the local disks of the map workers. When a reduce worker has read all intermediate data, it sorts it by the intermediate keys so that all occurrences of the same key are grouped together. The sorting is needed because typically many different keys map to the same reduce task. If the amount of intermediate data is too large to fit in memory, an external sort is used. 6. The reduce worker iterates over the sorted intermediate data and for each unique intermediate key encountered, it passes the key and the corresponding set of intermediate values to the user's Reduce function. The output of the Reduce function is appended to a final output file for this reduce partition7. When all map tasks and reduce tasks have been completed, the master wakes up the user program. At this point, the MapReduce call in the user program returns back to the user code.some ideas
Task Synchronous:
all map task should be earlier than reduce task!
some map task may wait seconds, so should first all map tasks done before reduce.
Lock:
workers run parallel, should add mutex to filelist when
Error Return:
workers may run some error, such as rpc sock connect and can not open files. When these errors happend, should return Error to master, other than just stop itself.
Heartbeat:
master should ask workers whether they are alive.
Implementation method:
- Set a new scheduled task and ask every 2 minutes.
- Every time a new worker requests a new task, add a judgment when rotating all tasks to assign tasks to the worker. If a task status is not Finish and times out, the task fails
- Write in the
Done()method and continuously rotate to ensure that all tasks are completed. And take the opportunity to determine if there is a task timeout.
Performance comparison: 1>2>3
Judging by frequency. The execution frequency of 3 is too high, constantly executing and discussing the sequence.
status of task and worker
worker:
- Finish: worker finish task X
- Ready: worker ask for a new task
- Wrong: worker meet some problems
- Close: worker will be closed when master ask worker to close
task:
- Run: some worker is running on this task
- Done: this task is finished
- (empty string): task not be allocated yet
lab test:
pass all the test!
这篇关于【6.824】分布式lab1 mapReduce的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






