本文主要是介绍B-Trees|CS 61B Data Structures, Spring 2019,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
B-Trees
- B-Trees
- BST Tree Height
- BST(binary search tree) Performance ,Height, Depth
- B-trees / 2-3 trees /2-3-4 trees
- Problom with Binary search tree
- solution:B Tree
- The Real Name for Splitting Trees is “B Trees”
- B-Tree Bushiness Invariants
- B-Tree Runtime Analysis
- Height of a B-Tree with Limit L(L: Max number of items per node.)
- Runtime for contains
- Runtime for contains:
- Runtime for add
- Summary
B-Trees
*** (Algs 424-431, 432-448 (extra))***
BST Tree Height
The difference in runtime between a worst-case tree and best-case tree is very dramati
- Worst case: Θ(N)
- Best-case: Θ(logN) (where N is number of nodes in the tree)
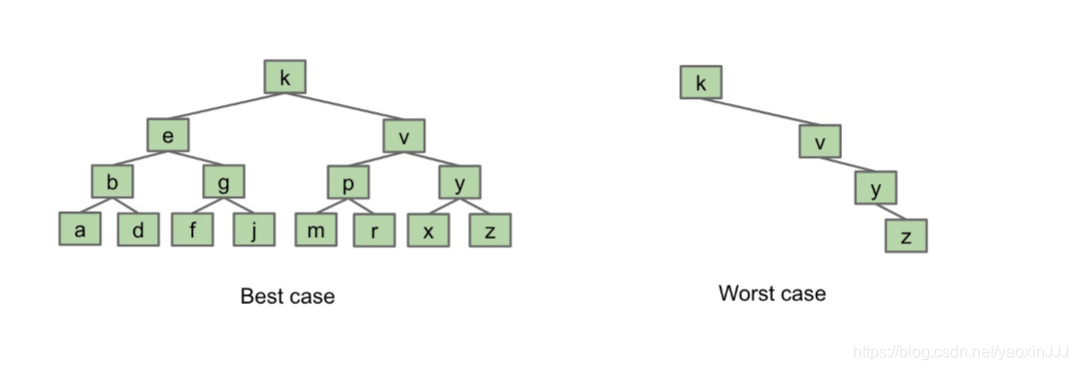
the tree on the left side called “bushy”,the tree on the right hand called “spindly”(n its basically a linked list and the runtime is linear)
BigO is not equivalent to worst case! Remember, BigO is an upper bound,Thus, even though we said the worst-case runtime of a BST is Θ(N), it also falls under O(N ).(意味着runtime的增长速度小于等于N)
BST(binary search tree) Performance ,Height, Depth
- depth: the number of links between a node and the root.
- height: the lowest depth of a tree.
- average depth: average of the total depths in the tree. You calculate this by taking :
 where d is depth and n is number of nodes at that depth.
where d is depth and n is number of nodes at that depth.
for exampel:

average depth of the exampel: (0x1 + 1x2 + 2x4 + 3x6 + 4x1)/(1+2+4+6+1) = 2.35
The height of the tree determines the worst-case runtime, because in the worst case the node we are looking for is at the bottom of the tree.
The average depth determines the average-case runtime.
Random trees in the real world have Θ(log N) average depth and height.
In other words: Random trees are bushy, not spindly.but in same cases we couldn’t always insert items randomly in our tree,in other world we may get a spindly tree.
In the next chapter we will learn about a tree that always maintains its balance(always get the tree like a bushy tree)
B-trees / 2-3 trees /2-3-4 trees
Problom with Binary search tree
The problem with BST’s is that we always insert at a leaf node. This is what causes the height to increase.
假设有四个点k,v,y,z.,选择k为root,因为其余三个点均比k大,最后会形成一个bushy tree,倒是搜索一个点所需的时间是Θ(N)而不是Θ(logN)
Θ(logN)比Θ(N)要小很多
solution:B Tree
example for B Tree:
The process of adding a node to a 2-3-4 tree(每个点最多可以包含三个item) is:
- We still always inserting into a leaf node, so take the node you want to insert and traverse down the tree with it, going left and right according to whether or not the node to be inserted is greater than or smaller than the items in each node.
- After adding the node to the leaf node, if the new node has 4 nodes, then pop up the middle left node and re-arrange the children accordingly.(若叶子节点现在有4个item,我们因该将左边第二个item移到父节点,并将剩余的三个item按照大小一次拆分)

- If this results in the parent node having 4 nodes, then pop up the middle left node again, rearranging the children accordingly.
- Repeat this process until the parent node can accommodate or you get to the root(若根节点中也有四个item,则把左边第二个拿出来作为新的root)

- more exampel:


Observation: Splitting-trees have perfect balance:
If we split the root, every node gets pushed down by exactly one level.
If we split a leaf node or internal node, the height doesn’t change
The Real Name for Splitting Trees is “B Trees”
Splitting tree is a better name, but I didn’t invent them, so we’re stuck with their real name: B-trees.
- B-trees of order L=3 (每个节点可以有三个item) are also called a 2-3-4 tree or a 2-4 tree.
- “2-3-4” refers to the number of children that a node can have, e.g. a 2-3-4 tree node may have 2, 3, or 4 children.
- B-trees of order L=2 are also called a 2-3 tree.
B-Trees are most popular in two specific contexts:
Small L (L=2 or L=3):
Used as a conceptually simple balanced search tree (as today).
L is very large (say thousands).
Used in practice for databases and filesystems (i.e. systems with very large records).
B-Tree Bushiness Invariants
Because of the way B-Trees are constructed, we get two nice invariants:
- All leaves must be the same distance from the source.
- A non-leaf node with k items must have exactly k+1 children.
- Example: The tree given below is impossible.
and [5 6 7]) are a different distance from the source.
Non-leaf node [2 3] has two items but only only one child. Should have three children.

These invariants guarantee that our trees will be bushy.
B-Tree Runtime Analysis
Height of a B-Tree with Limit L(L: Max number of items per node.)
L=2
- best case

- worst case

Height: Between between best and worst case is ~logL+1(N) and ~log2(N),Overall height is therefore Θ(log N).
Runtime for contains
Runtime for contains:
- Worst case number of nodes to inspect: H(Hight)
- Worst case number of items to inspect per node: L
- Overall runtime: O(HL)
Since H = Θ(log N), overall runtime is O(L log N).
Since L is a constant, runtime is therefore O(log N).
Runtime for add
Runtime for add:
- Worst case number of nodes to inspect: H + 1
- Worst case number of items to inspect per node: L
- Worst case number of split operations: H + 1(若在leaf增加一个item后,超过该节点能承载的最大ITEM数,需要将左边第二个节点向上移动,最坏的情况是,当所有节点中均装有L个ITEM,此时添加一个新item,会导致某个item向上移动的操作一直进行,知道出现一个新的root)

Overall runtime: O(HL)
Since H = Θ(log N), overall runtime is O(L log N).
Since L is a constant, runtime is therefore O(log N).
Bottom line: contains and add are both O(log N).
Summary
-
BSTs have best case height Θ(log N), and worst case height Θ(N).
-
Big O is not the same thing as worst case!
-
B-Trees are a modification of the binary search tree that avoids Θ(N) worst case.
-
Nodes may contain between 1 and L items.
-
contains works almost exactly like a normal BST.
-
add works by adding items to existing leaf nodes.
-
If nodes are too full, they split.
-
Resulting tree has perfect balance. Runtime for operations is O(log N).
-
Have not discussed deletion. See extra slides if you’re curious.
-
Have not discussed how splitting works if L > 3 (see some other class).
-
B-trees are more complex, but they can efficiently handle ANY insertion order.
这篇关于B-Trees|CS 61B Data Structures, Spring 2019的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





