本文主要是介绍VoLTE 驻网流程,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
原文链接:http://www.3glteinfo.com/volte-call-flow-procedures/
VoLTE Call Flow and Procedures
VoLTE call flow and procedures is very big area to cover because of the many scenarios to consider from both UE and network perspective.
In this article I will try to put some examples of VoLTE call flow from UE point of view. These procedures are the most important for VOLTE calls.
From the UE’s point of view the initial step is to camp on the network and read system information in the form of Master Information Blocks (MIBs) and System Information Blocks (SIBs). Once that information has been processed the UE can initiate its own processes.
EPS Attach for VoIP and Default Bearer Setup
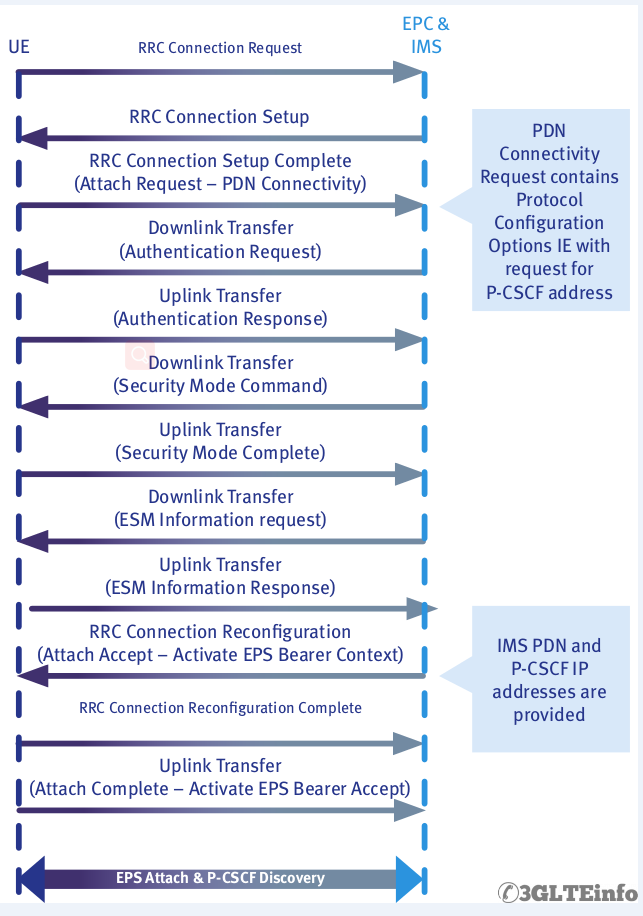
Let’s discuss how UE attach to network after camping on and how default bearer is created for IMS services. We are discussing the whole procedure from UE point of view. This process consists of some important sub-procedures as follows:
- PDN Connectivity
- Authentication
- Bearer Setup and EPS Attach
- P-SCCF Discovery
PDN Connectivity
UE starts connection by sending RRC Connection Request message. This is similar to UMTS registration. This is a UE originated message and it contains important information as what the UE wants.
For example the cause value in RRC Connection Request can be “Mobile Originated Signalling” or “Emergency”. If there is no problem in the network then network or eNodeB will respond with RRC Connection Setup message. This message contains signalling radio bearer information and is transmitted over downlink DCCH (Dedicated Control Channel) channel.
After receiving the RRC Connection Setup message UE responds with RRC Connection Complete message. At this point Attach Request is already sent to the network which is an exception from old UMTS system.
Authentication
To protect UE and network from security and man in the middle attacks all UEs in the network need to be checked and secured before they can use any network resources. To begin this process network send Authentication Request message or a challenge to make sure the UE is a valid entity. In response UE sends Authentication Response.
After that network sends Security Mode Command to UE. IT is also good to know that Security Mode Command is integrity protected. This message carries vital information on ciphering. In response UE sends Security Mode Complete message.
In order to protect EPS Session Management (ESM) information, the network now sends an ESM Information Request; the UE reacts with an ESM Information response describing the now-protected protocol configuration options.
Bearer Setup
At this point network must set up additional bearers to carry out IMS VoLTE call. To establish EPS bearer network sends Radio Bearer Reconfiguration message. UE responds with Radio Bearer Reconfiguration Complete message.
P-CSCF Discovery
Before sending any Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) requests, the UE must perform “P-CSCF Discovery”, the process of identifying (by address) the correct Proxy-Call Session Control Function (P-CSCF). The P-CSCF address may be discovered in one of three different ways:
- It may be stored in the IP Multimedia Services Identity Module (ISIM).
- The UE may request it as part of the PDN connectivity request during the Attach process.
- The UE may request an IP address and Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) from a DHCP server and then perform a DNS query on the returned IP address and FQDN.
SIP IMS Call Flow
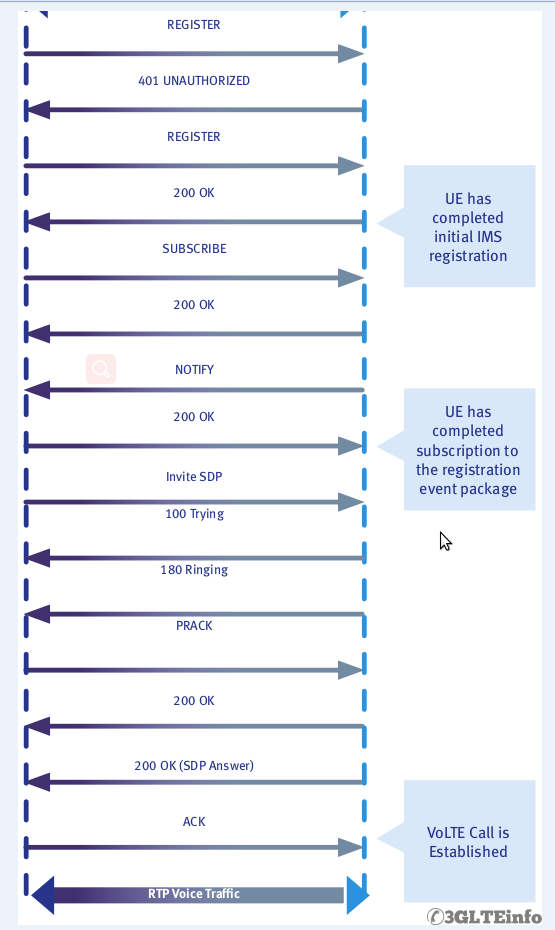
SIP Registration
After UE finishes radio procedures and it establishes radio bearers UE can start SIP registration towards the IMS for VoLTE call.
Here is a typical IMS SIP registration call flow.
- The IMS client attempts to register by sending a REGISTER request to the P-CSCF.
- The P-CSCF forwards the REGISTER request to the I-CSCF.
- The I-CSCF polls the HSS for data used to decide which S-CSCF should manage the REGISTER request. The I-CSCF then makes that decision.
- The I-CSCF forwards the REGISTER request to the appropriate S-CSCF.
- The S-CSCF typically sends the P-CSCF a 401 (UNAUTHORIZED) response as well as a challenge string in the form of a “number used once” or “nonce”.
- The P-CSCF forwards the 401 – UNAUTHORIZED response to the UE.
- Both the UE and the network have stored some Shared Secret Data (SSD), the UE in its ISIM or USIM and the network on the HSS. The UE uses an algorithm per RFC 33101 (e.g. AKAv2-MD5) to hash the SSD and the nonce.”
- The UE sends a REGISTER request to the P-CSCF. This time the request includes the result of the hashed nonce and SSD.
- The P-CSCF forwards the new REGISTER request to the I-CSCF.
- The I-CSCF forwards the new REGISTER request to the S-CSCF.
- The S-CSCF polls the HSS (via the I-CSCF) for the SSD, hashes it against the nonce and determines whether the UE should be allowed to register. Assuming the hashed values match, the S-CSCF sends 200 – OK response to the P-CSCF. At this point an IPSec security association is established by the P-CSCF.
- The P-CSCF forwards the 200 – OK response to the UE.
NOTE: It is typical that UE makes a deliberate unauthenticated registration attempt. It waits for the expected 401 response, extracts the nonce from the response and hashes it with the SSD before including the result in a second REGISTER request.
QoS Class Identifier (QCI)
QCI parameter generally targets a specific service type based on delay and packet loss requirements. For VoLTE call the bearer is associated with QCI value from row 1 as described in the following table.
Chapter #5 – IMS SIP Requests and Codes
这篇关于VoLTE 驻网流程的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



