本文主要是介绍2020ICPC·小米 网络选拔赛第一场题解(D,J),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/7501
来源:牛客网
D-Router Mesh
时间限制:C/C++ 1秒,其他语言2秒
空间限制:C/C++ 262144K,其他语言524288K
64bit IO Format: %lld
judge:牛客竞赛
In a Mesh networking system, there are n n n MI Routers, where m m m pairs of MI Routers are bidirectionally connected. In order to check the stability of the system, for each MI Router, we should determine the number of connected components after removing it and relative connections from the system. And then assess that if we should add more MI Routers into the system. Print the numbers of connected components in residual system after removing each MI Router.
输入描述:
The first line contains two integers n , m ( 1 ≤ n , m ≤ 3 × 1 0 5 ) n,m~(1\le n,m\le 3\times 10^5) n,m (1≤n,m≤3×105), denoting the number of MI Routers and bidirectional connections in the Mesh networking system.
Following m m m lines each contains two integers u , v ( 1 ≤ u < v ≤ n ) u,v(1 \le u < v \le n) u,v(1≤u<v≤n), denoting the u u u-th MI Router has a bidirectional connection with the v v v-th MI Router.
It’s guaranteed that there are no duplicated connections in input.
输出描述:
Print one line containing n n n integers, where i i i-th integer denotes the number of connected components after removing i i i-th MI Router and relative connections.
输入
4 2
1 2
1 3
输出
3 2 2 1
说明
After removing the 1st MI Router and relative connections, there are 3 3 3 connected components: { 2 } , { 3 } , { 4 } \{2\}, \{3\}, \{4\} {2},{3},{4}.
After removing the 2nd MI Router and relative connections, there are 2 2 2 connected components: { 1 , 3 } , { 4 } \{1, 3\}, \{4\} {1,3},{4}.
After removing the 3rd MI Router and relative connections, there are 2 2 2 connected components: { 1 , 2 } , { 4 } \{1, 2\}, \{4\} {1,2},{4}.
After removing the 4th MI Router and relative connections, there is only 1 1 1 connected component: { 1 , 2 , 3 } \{1, 2, 3\} {1,2,3}.
题意
给一个无向图,对每一个结点做一个询问,询问为,若删掉该点(及所有与其相关的连边),整个图有几个连通块?
前置知识:强连通
回顾一下相关知识:
dfn[x]: D F S DFS DFS 中, x x x 实际被访问的时间点。
low[x]: D F S DFS DFS 中, x x x 通过无向边,可回溯到的最早的时间点。
割点:无向连通图中,某点及其相连的边去掉后,图不再联通。
例如:
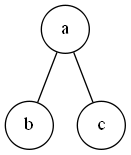
a , b , c a,b,c a,b,c 组成一个连通图, a a a 点去掉后,图将不再联通。所以 a a a 点就是一个割点。
判断一个点是不是割点:
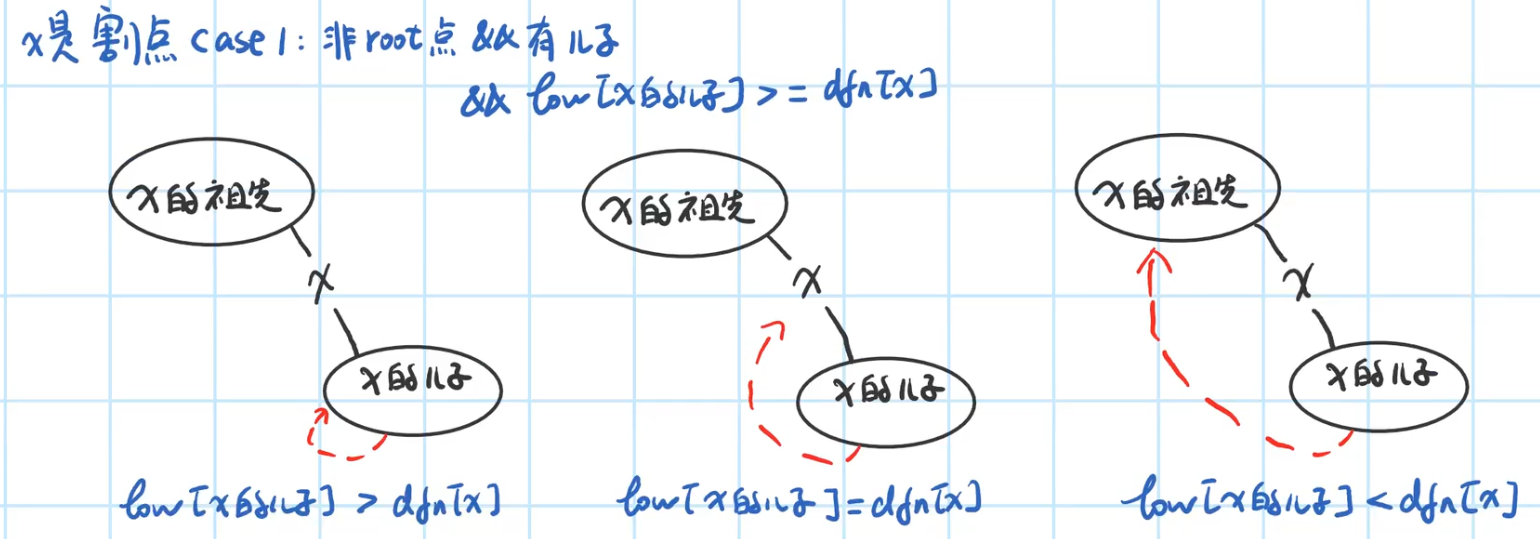

图片来自https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Q7411e7bM?p=2,有兴趣的小伙伴可以去观看视频
解释一下Case2的图二:虽然 A A A 和 B B B 是联通的,但是深度优先搜索的顺序是 root->A->B,所以 B B B 是 A A A 的儿子,那么 r o o t root root 就只有一个儿子。故不符合条件。
对于不是根节点的点,我们需要找出,从这个点分支出去,有几个不相连的子树。就是删掉这个点之后增加几个连通块。对于根节点,儿子(“儿子”指的是DFS时的儿子)数量就是增加的联通块数量。注意根节点时不只有增加,还会减少一个连通块,下文会解释。
-
当 x x x 不是根节点时,考虑与 x x x 相连的点 y y y,如果 y y y 无法回溯到 x x x 以上的节点,那么当 x x x 被删除后, y y y 就与 x x x 的父亲所在的连通块断开了。所以 y y y 所在分支就贡献了一个连通块。统计 x x x 的所有儿子节点,对贡献求和就是删除 x x x 节点后增加的连通块的数量。
有同学可能要问:
这种情况的话不是多加了答案吗?

和上面解释根节点的Case2一样,在 d f s dfs dfs 遍历时, d d d 是 c c c 的儿子节点,不是 b b b 的儿子节点,所以 b b b 只有一个儿子节点,那么对答案的贡献就是1. -
当 x x x 是根节点时,同样计算所有儿子分支的贡献求和。会发现由于 x x x 没有父亲节点,所以就不存在“ y y y 就与 x x x 的父亲所在的连通块断开了”的情况,只有 y y y 形成了一个新的分支。根节点的所有儿子节点(同上,“儿子节点”是指 d f s dfs dfs 遍历时的儿子节点)都会对答案有贡献,然后原来的连通块就只剩 x x x,然后随着 x x x 的删除消失。所以删除根节点后增加的连通块数量是对儿子贡献的求和再减一。
那么删除 x x x 节点后的连通块的数量就是原来的连通块数量+删去 x x x 后增加的联通块数量。
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define m_p make_pair
#define p_i pair<int, int>
#define _for(i, a) for(int i = 0, lennn = (a); i < lennn; ++i)
#define _rep(i, a, b) for(int i = (a), lennn = (b); i <= lennn; ++i)
#define outval(a) cout << "Debuging...|" << #a << ": " << a << "\n"
#define mem(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define mem0(a) memset(a, 0, sizeof(a))
#define fil(a, b) fill(a.begin(), a.end(), b);
#define scl(x) scanf("%lld", &x)
#define sc(x) scanf("%d", &x)
#define pf(x) printf("%d\n", x)
#define pfl(x) printf("%lld\n", x)
#define abs(x) ((x) > 0 ? (x) : -(x))
#define PI acos(-1)
#define lowbit(x) (x & (-x))
#define dg if(debug)
#define nl(i, n) (i == n - 1 ? "\n":" ")
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
// typedef __int128 LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
const int maxn = 300005;
const int maxm = 1000005;
const int maxp = 30;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1000000007;
const double eps = 1e-8;
const double e = 2.718281828;
int debug = 0;inline int read() {int x(0), f(1); char ch(getchar());while (ch<'0' || ch>'9') { if (ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); }while (ch >= '0'&&ch <= '9') { x = x * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar(); }return x * f;
}int n, m;
vector<int> G[maxn];
int num[maxn];int scccnt; //强连通分量的数量
int sccno[maxn]; //每个点所在的强连通分量的编号,编号从1开始递增
int dfn[maxn]; //深度优先搜索遍历时结点 u 被搜索的次序
int low[maxn]; //u或u的子树能够追溯到的最早的栈中节点的次序号
int tclock; //用于递增dfn
stack<int> q;
void init() {memset(dfn, 0, sizeof(dfn));memset(low, 0, sizeof(low));memset(sccno, 0, sizeof(sccno));scccnt = tclock = 0;
}
void tarjin(int u) {++num[u];dfn[u] = low[u] = ++tclock;q.push(u);for(auto &v : G[u]) {if (!dfn[v]) {tarjin(v);low[u] = min(low[u], low[v]);num[u] += (dfn[u] <= low[v]);}else if (!sccno[v]) {low[u] = min(low[u], dfn[v]);}}if (dfn[u] == low[u]) {scccnt++;int v = -1;while (v != u) {v = q.top();q.pop();sccno[v] = scccnt;}}
}void sol() {init();_for(i, m) {int u = read(), v = read();G[u].push_back(v);G[v].push_back(u);}_rep(i, 1, n) {if(!dfn[i]) {tarjin(i);--num[i];}}_rep(i, 1, n) {printf("%d%s", scccnt - 1 + num[i], i == n ? "\n":" ");}
}int main() {//ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
#ifdef ONLINE_JUDGE
#elsefreopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);debug = 1;
#endiftime_t beg, end;if(debug) beg = clock();n = read(), m = read();sol();if(debug) {end = clock();printf("time:%.2fs\n", 1.0 * (end - beg) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);}return 0;
}
J-Matrix Subtraction
时间限制:C/C++ 1秒,其他语言2秒
空间限制:C/C++ 262144K,其他语言524288K
64bit IO Format: %lld
题目描述
Given a matrix M M M of size n × m n\times m n×m and two integers a , b a, b a,b, determine weither it is possible to make all entrys of M M M zero by repeatedly choosing a × b a\times b a×b submatrices and reduce the values in the chosen matrices by 1. If possible, print “_” in one line, or print “QAQ” in one line.
输入描述:
The first line contains one integer T ( 1 ≤ T ≤ 100 ) T(1\le T \le 100) T(1≤T≤100), denoting the number of test cases.
For each test case:
The first line contains four integers n , m , a , b ( 1 ≤ n , m ≤ 1000 , 1 ≤ a ≤ n , 1 ≤ b ≤ m ) n,m,a,b(1\le n,m \le 1000, 1\le a\le n, 1\le b\le m) n,m,a,b(1≤n,m≤1000,1≤a≤n,1≤b≤m), denoting the size of given matrix and the size of chosen submatrices respectively.
The next n n n lines each contains m m m integers M i , j ( 0 ≤ M i , j ≤ 1 0 9 ) M_{i,j}(0\le M_{i,j} \le 10^9) Mi,j(0≤Mi,j≤109), denoting the entrys of matrix M M M.
It’s guaranteed that ∑ n m ≤ 1 0 6 \sum nm \le 10^6 ∑nm≤106.
输出描述:
Print T T T lines each containing a string “_” or “QAQ”, denoting the answer to each test case.
输入
2
2 2 1 2
1 2
1 2
2 3 1 2
1 2 1
1 2 1
输出
QAQ
^_^
说明
For the second case, one possible scheme is to choose ( 1 , 1 ) − ( 1 , 2 ) , ( 1 , 2 ) − ( 1 , 3 ) , ( 2 , 1 ) − ( 2 , 2 ) , ( 2 , 2 ) − ( 2 , 3 ) (1, 1) - (1, 2), (1, 2) - (1, 3), (2, 1) - (2, 2), (2, 2) - (2, 3) (1,1)−(1,2),(1,2)−(1,3),(2,1)−(2,2),(2,2)−(2,3) respectively.
题解
给你一个 n × m n \times m n×m 的矩阵,判断其是否是由若干个 a × b a \times b a×b 的矩阵叠加而来。
二维差分裸题。奈何本人愚钝,赛场上没做出来,后来看了好久才理解。
建议没有学过二维差分的同学一定要先补一下,其实很简单的,只是一开始不知道的话会很难理解。
首先我们知道,在一维数组里,对差分数组求前缀和得出的值就是它实际的值。二维也一样,我们先对给出的矩阵对每一位求其相对于左上角的数字的差分矩阵,然后再对其求二维前缀和就可以得到它原本的值。
对于 M ( 1 , 1 ) M(1,1) M(1,1) 而言,因为它上边和左边都没有其他数字,所以它的值只能被 ( 1 , 1 ) − ( a , b ) (1,1)-(a,b) (1,1)−(a,b) 的矩阵消掉。那么 M ( 1 , 1 ) M(1,1) M(1,1) 就是覆盖 ( 1 , 1 ) (1,1) (1,1) 位置的子矩阵的数量。我们趁热打铁,把这个子矩阵内的所有数字都减去 M ( 1 , 1 ) M(1,1) M(1,1),就相当于把这片子矩阵消掉了。矩阵内减的操作可以利用差分矩阵 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1) 复杂度内完成。
这样 ( 1 , 2 ) (1,2) (1,2) 的位置和 ( 2 , 1 ) (2,1) (2,1) 的位置就没有了左边和上边的数字了,利用之前维护的差分矩阵求出前缀和就是 M ( 1 , 2 ) M(1,2) M(1,2) 了,同样把子矩阵内的所有数字都减去 M ( 1 , 2 ) M(1,2) M(1,2) 的数字。
以此类推即可消去所有位置的数字,那么正常情况,此时差分矩阵的任意一位都应该是0,否则就说明不能由子矩阵凑出。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define _for(i, a) for(int i = 0, lennn = (a); i < lennn; ++i)
#define _rep(i, a, b) for(int i = (a), lennn = (b); i <= lennn; ++i)
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int maxn = 1005;inline LL read() {LL x(0), f(1); char ch(getchar());while (ch<'0' || ch>'9') { if (ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); }while (ch >= '0'&&ch <= '9') { x = x * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar(); }return x * f;
}int n, m, a, b;
LL c[maxn][maxn], d[maxn][maxn];int sol() {_rep(i, 1, n) _rep(j, 1, m) {c[i][j] = read();// 求出差分矩阵d[i][j] = c[i][j] - c[i - 1][j] - c[i][j - 1] + c[i - 1][j - 1];}for(int i = 1; i + a - 1 <= n; ++i) {for(int j = 1; j + b - 1 <= m; ++j) {// 求出覆盖(i, j)位置的子矩阵的数量int k = d[i][j] + d[i - 1][j] + d[i][j - 1] - d[i - 1][j - 1];if(k < 0) return 0;// 更新差分矩阵,相当于子矩阵内的数字都减去M(i, j)d[i][j] += -k;d[i + a][j] -= -k;d[i][j + b] -= -k;d[i + a][j + b] += -k;}}// 此时,矩阵内的值都应该是0_rep(i, 1, n) _rep(j, 1, m) if(d[i][j]) return 0;return 1;
}int main() {int T = read();_for(i, T) {n = read(), m = read(), a = read(), b = read();printf("%s", sol() ? "^_^\n":"QAQ\n");}return 0;
}
这篇关于2020ICPC·小米 网络选拔赛第一场题解(D,J)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






