本文主要是介绍源码解析AQS的PROPAGATE有什么用?,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- AQS的PROPAGATE有什么用?
- bug修复前的代码(Java 5)
- 正常流程
- 产生 bug 的情况
- bug 修复后的代码 (java 7)
AQS的PROPAGATE有什么用?
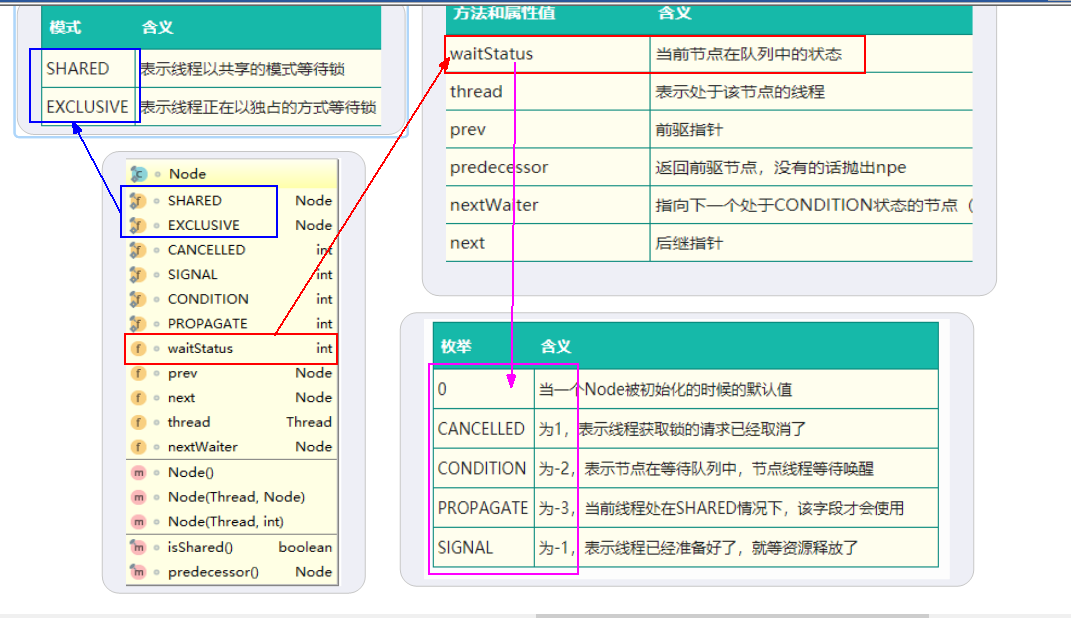
waitStatus=PROPAGATE值为-3,当前线程处在SHARED共享模式下,该字段才会使用
比如信号量Semaphore,读写锁ReentrantReadWriteLock的读锁等
这里用信号量Semaphore为例
bug修复前的代码(Java 5)
假设存在某次循环中队列里排队的结点情况为 head(-1)->t1(-1)->t2(-1)
假设存在将要信号量释放的 T3 和 T4,释放顺序为先 T3 后 T4
正常流程

产生 bug 的情况
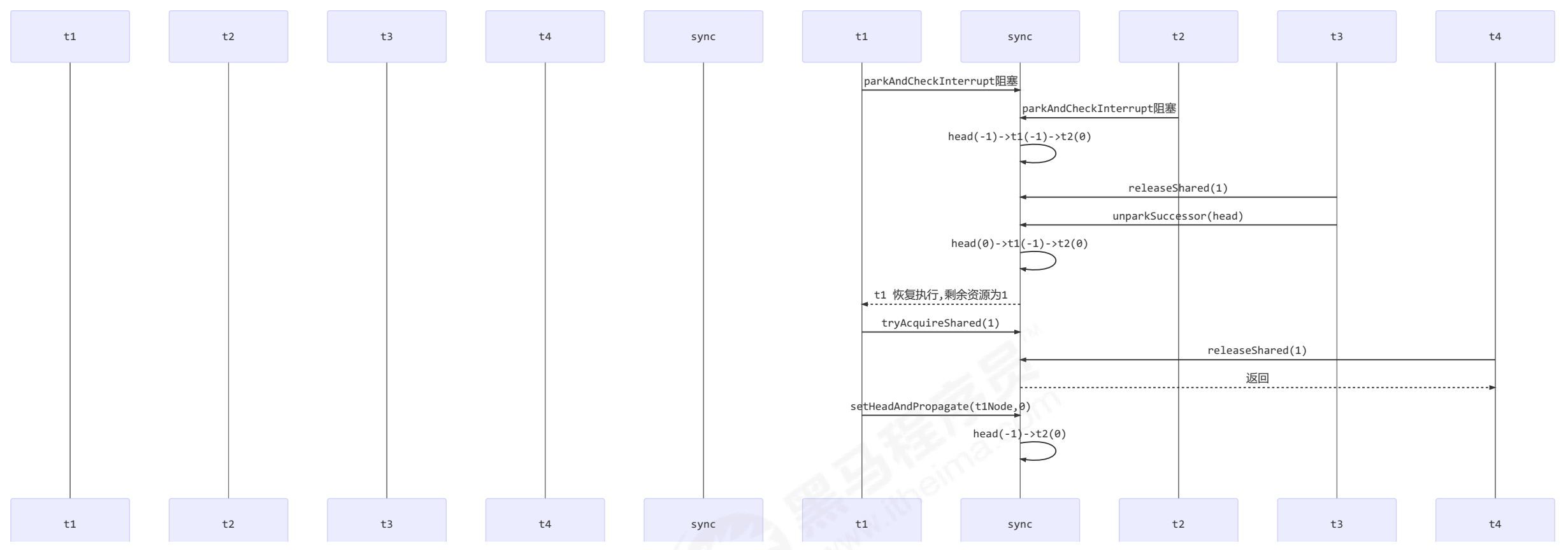
修复前版本执行流程
- T3 调用 releaseShared(1),直接调用了 unparkSuccessor(head),head 的等待状态从 -1 变为 0
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg)
{if(tryReleaseShared(arg)){Node h = head;if(h != null && h.waitStatus != 0) unparkSuccessor(h);return true;}return false;
}
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {/** If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.*/int ws = node.waitStatus;if (ws < 0)compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);//哨兵节点的waitStatus从-1改为0/** Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual* non-cancelled successor.*/Node s = node.next;if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {s = null;for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)if (t.waitStatus <= 0)s = t;}if (s != null)//唤醒t1LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
- T1 由于 T3 释放信号量被唤醒,调用 tryAcquireShared,假设返回值为 0(获取锁成功,但没有剩余资源
量)
private void doAcquireShared(int arg)
{final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);boolean failed = true;try{boolean interrupted = false;for(;;){final Node p = node.predecessor();if(p == head){int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);//尝试获取资源 获取资源成功返回0 该场景t1会在这里停留一段时间,t4 释放资源,t1才获取锁成功if(r >= 0){// 这里会有空档 setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);p.next = null; // help GCif(interrupted) selfInterrupt();failed = false;return;}}if(shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()) interrupted = true;}}finally{if(failed) cancelAcquire(node);}
}
tryAcquireShared(arg)的实现方法
final int nonfairTryAcquireShared(int acquires) {for (;;) {int available = getState();//1int remaining = available - acquires;//0if (remaining < 0 ||compareAndSetState(available, remaining))//1改为0return remaining;}
}
- T4 释放资源调用 releaseShared(1),此时 head.waitStatus 为 0(此时读到的 head 和 1 中为同一个head),不满足条件,因此不调用 unparkSuccessor(head)
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg)
{if(tryReleaseShared(arg)){Node h = head;if(h != null && h.waitStatus != 0) unparkSuccessor(h);return true;}return false;
}
- T1 获取信号量成功,调用 setHeadAndPropagate 时,因为不满足 propagate > 0(2 的返回值也就是propagate(剩余资源量) == 0),从而不会唤醒后继结点, T2 线程得不到唤醒
private void doAcquireShared(int arg)
{final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);boolean failed = true;try{boolean interrupted = false;for(;;){final Node p = node.predecessor();if(p == head){int r = tryAcquireShared(arg); if(r >= 0){// 这里会有空档 假设在这里停留一段时间//等到t4释放了资源才执行到 setHeadAndPropagate(node, r)setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);//此时state是 tryAcquireShared(arg)返回的0,而非t4释放后的1p.next = null; // help GCif(interrupted) selfInterrupt();failed = false;return;}}if(shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()) interrupted = true;}}finally{if(failed) cancelAcquire(node);}
}
private void setHeadAndPropagate(Node node, int propagate)
{setHead(node);// 传过来的propagate=0 ,就无法唤醒t2了。if(propagate > 0 && node.waitStatus != 0){Node s = node.next;// 下一个if(s == null || s.isShared()) unparkSuccessor(node);}
}
总结:
t3释放资源,会唤醒哨兵节点的后继节点t1尝试获取锁,并将哨兵节点的waitStatus改为0
在t1获取锁,t4释放资源,并唤醒哨兵节点的后继节点(此时t1还未获取到锁,所以这里唤醒的还是t1),此时哨兵节点的waitStatus=0唤醒失败。
当t1获得锁成功后,此时将t1所在的节点作为新的哨兵节点(waitStatus=-1),GC回收旧的哨兵节点,
由于此时传过来的propagate是t1获取锁成功的返回值0(实际此时state=1),就无法继续唤醒t2
bug 修复后的代码 (java 7)
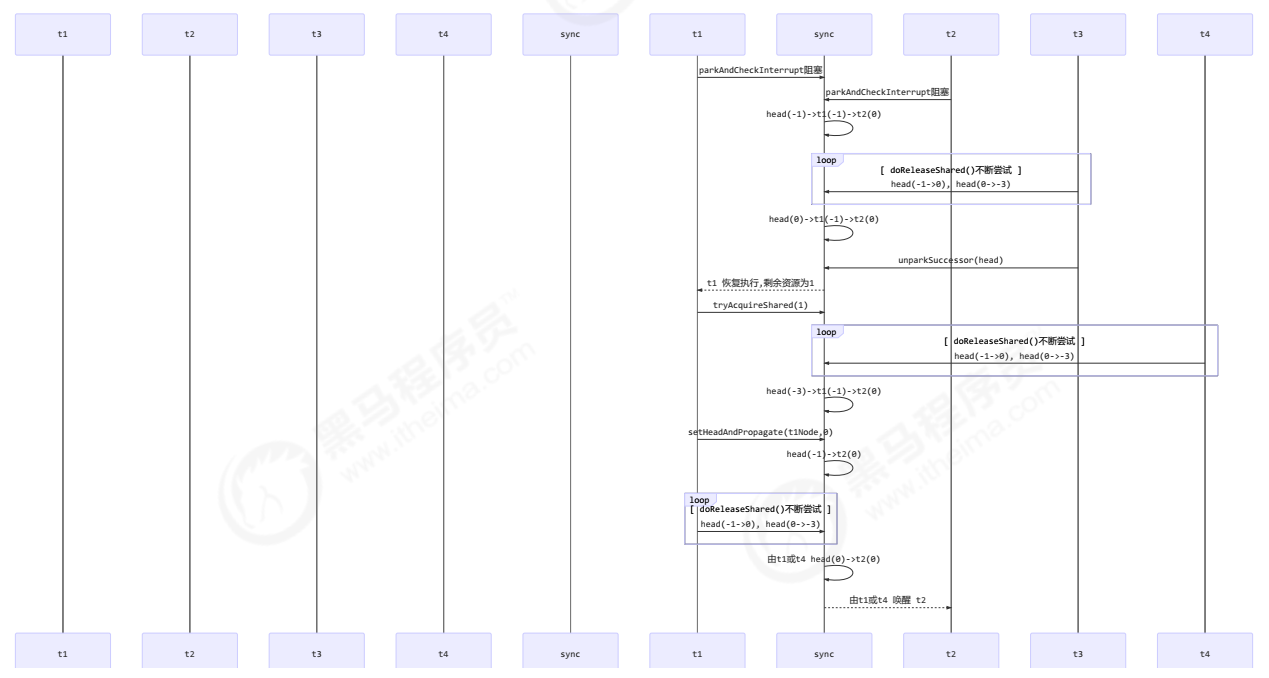
- T3 调用 releaseShared(),直接调用了 unparkSuccessor(head),head 的等待状态从 -1 变为 0
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {doReleaseShared();return true;}return false;
}
private void doReleaseShared() {/** Ensure that a release propagates, even if there are other* in-progress acquires/releases. This proceeds in the usual* way of trying to unparkSuccessor of head if it needs* signal. But if it does not, status is set to PROPAGATE to* ensure that upon release, propagation continues.* Additionally, we must loop in case a new node is added* while we are doing this. Also, unlike other uses of* unparkSuccessor, we need to know if CAS to reset status* fails, if so rechecking.*/// 如果 head.waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL(-1) ==> 0 成功, 下一个节点 unpark// 如果 head.waitStatus == 0 ==> Node.PROPAGATE(-3)for (;;) {Node h = head;if (h != null && h != tail) {int ws = h.waitStatus;if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))continue; // loop to recheck casesunparkSuccessor(h);//唤醒后继节点}else if (ws == 0 &&!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))continue; // loop on failed CAS}if (h == head) // loop if head changedbreak;}
}
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {/** If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.*/int ws = node.waitStatus;if (ws < 0)compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);//哨兵节点的waitStatus从-1改为0/** Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual* non-cancelled successor.*/Node s = node.next;if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {s = null;for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)if (t.waitStatus <= 0)s = t;}if (s != null)LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
- T1 由于 T3 释放信号量被唤醒,调用 tryAcquireShared,假设返回值为 0(获取锁成功,但没有剩余资源
量)
private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)throws InterruptedException {final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);boolean failed = true;try {for (;;) {final Node p = node.predecessor();//前驱节点if (p == head) {int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);//获取锁成功返回0if (r >= 0) {//此时t4释放锁 t1停留一段时间setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);//t1,0p.next = null; // help GCfailed = false;return;}}if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&parkAndCheckInterrupt())throw new InterruptedException();}} finally {if (failed)cancelAcquire(node);}
}
- T4 调用 releaseShared(),此时 head.waitStatus 为 0(此时读到的 head 和 1 中为同一个 head),调用doReleaseShared() 将等待状态置为PROPAGATE(-3)
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {doReleaseShared();return true;}return false;
}
private void doReleaseShared() {/** Ensure that a release propagates, even if there are other* in-progress acquires/releases. This proceeds in the usual* way of trying to unparkSuccessor of head if it needs* signal. But if it does not, status is set to PROPAGATE to* ensure that upon release, propagation continues.* Additionally, we must loop in case a new node is added* while we are doing this. Also, unlike other uses of* unparkSuccessor, we need to know if CAS to reset status* fails, if so rechecking.*/// 如果 head.waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL(-1) ==> 0 成功, 下一个节点 unpark// 如果 head.waitStatus == 0 ==> Node.PROPAGATE(-3)for (;;) {Node h = head;if (h != null && h != tail) {int ws = h.waitStatus;//0if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))continue; // loop to recheck casesunparkSuccessor(h);//唤醒后继节点}//waitStatus将0改为-3 else if (ws == 0 &&!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))continue; // loop on failed CAS}//都不满足。结束自旋if (h == head) // loop if head changedbreak;}
}
- T1 获取锁成功,调用 setHeadAndPropagate 时,读到 h.waitStatus < 0,从而调用doReleaseShared() 唤醒 T2
private void setHeadAndPropagate(Node node, int propagate)//t1 ,0
{Node h = head; // Record old head for check below //旧的哨兵节点// 设置自己为 headsetHead(node);//t1变为新的哨兵节点 此时的哨兵节点的waitStatus=-1// propagate 表示有共享资源(例如共享读锁或信号量)// head waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL 或 Node.PROPAGATE//h.waitStatus=-3if(propagate > 0 || h == null || h.waitStatus < 0 || (h = head) == null || h.waitStatus < 0){Node s = node.next;//t2// 如果是最后一个节点或者是等待共享读锁的节点if(s == null || s.isShared()){//唤醒t2doReleaseShared();}}
}
private void doReleaseShared() {/** Ensure that a release propagates, even if there are other* in-progress acquires/releases. This proceeds in the usual* way of trying to unparkSuccessor of head if it needs* signal. But if it does not, status is set to PROPAGATE to* ensure that upon release, propagation continues.* Additionally, we must loop in case a new node is added* while we are doing this. Also, unlike other uses of* unparkSuccessor, we need to know if CAS to reset status* fails, if so rechecking.*/for (;;) {Node h = head;if (h != null && h != tail) {int ws = h.waitStatus;//-1if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))continue; // loop to recheck casesunparkSuccessor(h);//唤醒t2}else if (ws == 0 &&!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))continue; // loop on failed CAS}if (h == head) // loop if head changedbreak;}
}
总结:
t3释放资源,会唤醒哨兵节点的后继节点t1尝试获取锁,并将哨兵节点的waitStatus改为0
在t1获取锁,t4释放资源,并唤醒哨兵节点的后继节点,此时判断哨兵节点的waitStatus=0,会将waitStatus改为PROPAGATE(-3)。此时所有条件都不满足结束
当t1获得锁成功后,只要 head waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL 或 Node.PROPAGATE满足一个条件 都会唤醒t2(前提是哨兵节点的后继节点t2是共享模式 或者为null)
PROPAGATE(-3)保证当一个线程被唤醒获取锁成功到将这个线程节点当做新的哨兵节点,回收旧哨兵节点的过程中,如果又有资源得到释放,不会再执行多余的唤醒操作
因为当这个线程获取锁后会尝试唤醒他的后继节点(共享模式的节点)
这篇关于源码解析AQS的PROPAGATE有什么用?的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



