本文主要是介绍深度学习作业L5W1(3):Improvise a Jazz Solo with an LSTM Network,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
利用LSTM创作爵士歌曲
数据处理
题目已经为我们做好,输入X是(60, 30, 78)的矩阵,代表60个歌曲,每个歌曲分30个时间片,一个时间片对应78个音符中的一个。
模型结构
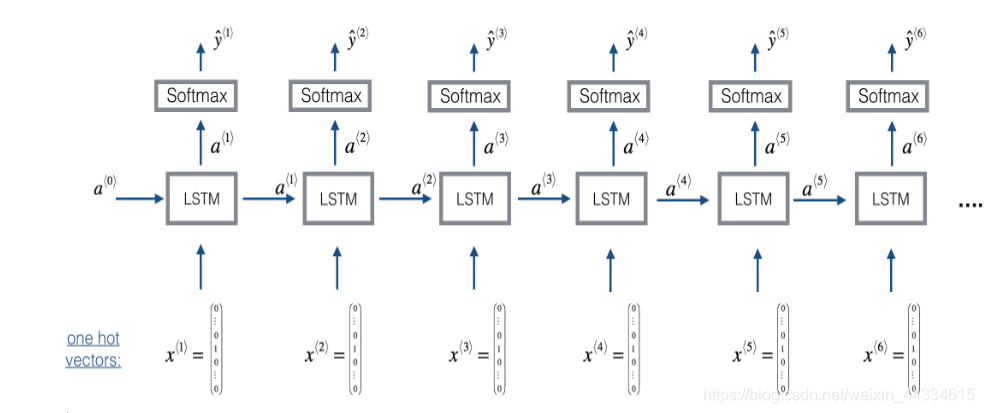
一个LSTM上面套一个softmax
LSTM的隐藏状态a为64个
n_a = 64
reshapor = Reshape((1, 78)) # Used in Step 2.B of djmodel(), below
LSTM_cell = LSTM(n_a, return_state = True) # Used in Step 2.C
densor = Dense(n_values, activation='softmax') # Used in Step 2.D
# GRADED FUNCTION: djmodeldef djmodel(Tx, n_a, n_values):"""Implement the modelArguments:Tx -- length of the sequence in a corpusn_a -- the number of activations used in our modeln_values -- number of unique values in the music data Returns:model -- a keras model with the """# Define the input of your model with a shape X = Input(shape=(Tx, n_values))# Define s0, initial hidden state for the decoder LSTMa0 = Input(shape=(n_a,), name='a0')c0 = Input(shape=(n_a,), name='c0')a = a0c = c0### START CODE HERE ### # Step 1: Create empty list to append the outputs while you iterate (≈1 line)outputs = []# Step 2: Loopfor t in range(Tx):# Step 2.A: select the "t"th time step vector from X. x = Lambda(lambda x: X[:,t,:])(X)# Step 2.B: Use reshapor to reshape x to be (1, n_values) (≈1 line)x = reshapor(x)# Step 2.C: Perform one step of the LSTM_cella, _, c = LSTM_cell(x, initial_state=[a, c])# Step 2.D: Apply densor to the hidden state output of LSTM_Cellout = densor(a)# Step 2.E: add the output to "outputs"outputs.append(out)# Step 3: Create model instancemodel = Model(inputs=[X,a0,c0],outputs=outputs)### END CODE HERE ###return model
由于需要按照时间顺序输出一个列表,因此将LSTM单元等声明为全局变量,以保证我们每一次前向传播用的是相同的LSTM单元
model = djmodel(Tx = 30 , n_a = 64, n_values = 78)
opt = Adam(lr=0.01, beta_1=0.9, beta_2=0.999, decay=0.01)model.compile(optimizer=opt, loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])m = 60
a0 = np.zeros((m, n_a))
c0 = np.zeros((m, n_a))
model.fit([X, a0, c0], list(Y), epochs=100)
完成模型训练
生成音乐
由于训练和sampling需要不同的模型(输入方式不同),因此再构建一个sample的model
# GRADED FUNCTION: music_inference_modeldef music_inference_model(LSTM_cell, densor, n_values = 78, n_a = 64, Ty = 100):"""Uses the trained "LSTM_cell" and "densor" from model() to generate a sequence of values.Arguments:LSTM_cell -- the trained "LSTM_cell" from model(), Keras layer objectdensor -- the trained "densor" from model(), Keras layer objectn_values -- integer, umber of unique valuesn_a -- number of units in the LSTM_cellTy -- integer, number of time steps to generateReturns:inference_model -- Keras model instance"""# Define the input of your model with a shape x0 = Input(shape=(1, n_values))# Define s0, initial hidden state for the decoder LSTMa0 = Input(shape=(n_a,), name='a0')c0 = Input(shape=(n_a,), name='c0')a = a0c = c0x = x0### START CODE HERE #### Step 1: Create an empty list of "outputs" to later store your predicted values (≈1 line)outputs = []# Step 2: Loop over Ty and generate a value at every time stepfor t in range(Ty):# Step 2.A: Perform one step of LSTM_cell (≈1 line)a, _, c = LSTM_cell(x, initial_state=[a, c])# Step 2.B: Apply Dense layer to the hidden state output of the LSTM_cell (≈1 line)out = densor(a)# Step 2.C: Append the prediction "out" to "outputs". out.shape = (None, 78) (≈1 line)outputs.append(out)# Step 2.D: Select the next value according to "out", and set "x" to be the one-hot representation of the# selected value, which will be passed as the input to LSTM_cell on the next step. We have provided # the line of code you need to do this. x = Lambda(one_hot)(out)# Step 3: Create model instance with the correct "inputs" and "outputs" (≈1 line)inference_model = Model(inputs=[x0,a0,c0],outputs=outputs)### END CODE HERE ###return inference_model
inference_model = music_inference_model(LSTM_cell, densor, n_values = 78, n_a = 64, Ty = 50)
x_initializer = np.zeros((1, 1, 78))
a_initializer = np.zeros((1, n_a))
c_initializer = np.zeros((1, n_a))
# GRADED FUNCTION: predict_and_sampledef predict_and_sample(inference_model, x_initializer = x_initializer, a_initializer = a_initializer, c_initializer = c_initializer):"""Predicts the next value of values using the inference model.Arguments:inference_model -- Keras model instance for inference timex_initializer -- numpy array of shape (1, 1, 78), one-hot vector initializing the values generationa_initializer -- numpy array of shape (1, n_a), initializing the hidden state of the LSTM_cellc_initializer -- numpy array of shape (1, n_a), initializing the cell state of the LSTM_celReturns:results -- numpy-array of shape (Ty, 78), matrix of one-hot vectors representing the values generatedindices -- numpy-array of shape (Ty, 1), matrix of indices representing the values generated"""### START CODE HERE #### Step 1: Use your inference model to predict an output sequence given x_initializer, a_initializer and c_initializer.pred = inference_model.predict([x_initializer, a_initializer, c_initializer])# Step 2: Convert "pred" into an np.array() of indices with the maximum probabilitiesindices = np.argmax(pred, axis = -1)# Step 3: Convert indices to one-hot vectors, the shape of the results should be (1, )results = to_categorical(indices,num_classes=78)### END CODE HERE ###return results, indices
调用model.predict进行预测,同时将输出处理成onehot形式方便生成音乐
out_stream = generate_music(inference_model)
IPython.display.Audio('./data/30s_trained_model.mp3')
利用实验提供的方法生成了音乐
这篇关于深度学习作业L5W1(3):Improvise a Jazz Solo with an LSTM Network的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





