本文主要是介绍【LeetCode】 387. 字符串中的第一个唯一字符,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
题目链接

文章目录
- Python3
- 方法一:collections.Counter() 统计频次
- 方法二:哈希映射 { key字符:value【首次出现的索引 or -1 出现多次】}
- 方法三: collections.deque() 元素为 (字符,第一次出现的索引) 维护队首 + dict 记录是否重复
- Python3 函数模块
- collections.Counter() {键:计数}
- collections.deque() 双端队列
- C++
- 方法一:哈希表 存储 频次 unordered_map
- 方法二:哈希映射 { key字符:value【首次出现的索引 or -1 出现多次】}
- unordered_map 并非 元素插入顺序
- 方法三: queue 元素为 (字符,第一次出现的索引) 维护队首 + unordered_map记录是否重复
- queue
- 方法四: find 函数 和 rfind 函数
- unordered_map 遍历 2种 方式
所有方法 复杂度 ( O ( n ) O(n) O(n)、 O ( ∣ Σ ∣ ) O(|\Sigma|) O(∣Σ∣))
Python3
方法一:collections.Counter() 统计频次
针对 s ,进行两次遍历:
第一次遍历:使用哈希映射统计出字符串中每个字符出现的次数。
第二次遍历: 只要遍历到了一个只出现一次的字符,直接返回它的索引,否则在遍历结束后返回 −1。

class Solution:def firstUniqChar(self, s: str) -> int:frequency = collections.Counter(s) # 会 按照计数频次 排序,其次 出现位置前后for i, ch in enumerate(s):if frequency[ch] == 1:return i return -1补充:
import collectionsprint(collections.Counter("leetcode"))
Counter({‘e’: 3, ‘l’: 1, ‘t’: 1, ‘c’: 1, ‘o’: 1, ‘d’: 1})
方法二:哈希映射 { key字符:value【首次出现的索引 or -1 出现多次】}


class Solution:def firstUniqChar(self, s: str) -> int:dic = {}for i in range(len(s)): # 另一种遍历方式 for i, ch in enumerate(s):if s[i] not in dic:dic[s[i]] = i else:dic[s[i]] = -1for v in dic.values():if v != -1: ## 找到不是 -1 的,直接返回。照理说,dic 是无序的,这里会报错,但没有。看起来dict() 默认是 元素插入顺序。return vreturn -1
补充:这里与 C++ 不同, 会按照 元素插入 顺序进行排列

dic = {}
s = "loveleetcode"
for i in range(len(s)): # 另一种遍历方式 for i, ch in enumerate(s):if s[i] not in dic:dic[s[i]] = i else:dic[s[i]] = -1
print(dic)
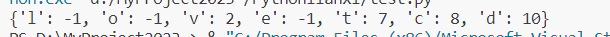
set 仍是无序的
方法三: collections.deque() 元素为 (字符,第一次出现的索引) 维护队首 + dict 记录是否重复
双端队列 存储 二元组 (字符,第一次出现的索引)
队列维护技巧: 「延迟删除」
在维护队列时,即使队列中有一些字符出现了超过一次,但它只要不位于队首,那么就不会对答案造成影响,我们也就可以不用去删除它。只有当它前面的所有字符被移出队列,它成为队首时,我们才需要将它移除。
class Solution:def firstUniqChar(self, s: str) -> int:dic = {}q = collections.deque() # 存储 (字符, 第一次出现索引)for i, ch in enumerate(s):if ch not in dic:dic[ch] = iq.append((ch, i))else: dic[ch] = -1 ## 重复 维护 dict## 重复了,核对队首的字符 【延迟删除】while q and dic[q[0][0]] == -1: ## 队首 重复了。 因为前面处理时,只针对队首。重复时只修改了 dic。这里 用while。直到找到后续 无重复的 第一个字符q.popleft() ## 当 队首 重复,才维护return -1 if not q else q[0][1]

Python3 函数模块
collections.Counter() {键:计数}
官网链接https://docs.python.org/3.12/library/collections.html#collections.Counter
Counter是用于计数可哈希对象的字典子类。它是一个集合,其中元素被存储为字典键,它们的计数被存储为字典值。计数可以是任何整数值,包括0或负数计数。Counter类类似于其他语言中的bags或multiset。
元素从可迭代对象中计数或从另一个映射(或计数器)中初始化:
c = Counter() # a new, empty counter
c = Counter('gallahad') # a new counter from an iterable
c = Counter({'red': 4, 'blue': 2}) # a new counter from a mapping
c = Counter(cats=4, dogs=8) # a new counter from keyword args
Counter('abracadabra').most_common(3) # 返回 计数最多的前3组
[(‘a’, 5), (‘b’, 2), (‘r’, 2)]
c.total() # total of all counts
c.clear() # reset all counts
list(c) # list unique elements
set(c) # convert to a set
dict(c) # convert to a regular dictionary
c.items() # convert to a list of (elem, cnt) pairs
Counter(dict(list_of_pairs)) # convert from a list of (elem, cnt) pairs
########
c.most_common()[:-n-1:-1] # n least common elements
+c # remove zero and negative counts
c = Counter(a=2, b=-4)
+c # Counter({'a': 2})
-c # Counter({'b': 4})
collections.deque() 双端队列
官方文档链接
Deques = stacks + queues
the name is pronounced “deck” and is short for “double-ended queue”
双端队列
append(x) # 默认 右添加
appendleft(x)
clear()
copy()
count(x)
extend(iterable)
extendleft(iterable)
index(x[, start[, stop]])
insert(i, x)
pop() ## 会返回 值
popleft()
remove(value)
reverse()
maxlen
rotate(n=1)
- Rotate the deque n steps to the right. If n is negative, rotate to the left.
C++
方法一:哈希表 存储 频次 unordered_map
针对 s ,进行两次遍历:
第一次遍历:使用哈希映射统计出字符串中每个字符出现的次数。
第二次遍历: 只要遍历到了一个只出现一次的字符,直接返回它的索引,否则在遍历结束后返回 −1。
class Solution {
public:int firstUniqChar(string s) {unordered_map<int, int> frequency; // 按照语法应该是 <char, int>, 但这里不会报错,会强制转换。这里不需要输出,影响不大。用整型快点???不理解for (char ch : s){++frequency[ch];}for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i){if (frequency[s[i]] == 1){return i;}}return -1;}
};
方法二:哈希映射 { key字符:value【首次出现的索引 or -1 出现多次】}
unordered_map函数文档
官方解法的 字典遍历方式在 IDE 里无法运行
class Solution {
public:int firstUniqChar(string s) {unordered_map<int, int> dic; // 这里 用 char 或 int 都可以?int n = s.size();for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {if (dic.count(s[i])) {dic[s[i]] = -1;}else {dic[s[i]] = i;}}int first = n; // 字典 中的元素 不是 按照 元素插入顺序 排列,要处理for (auto [_, pos]: dic) {if (pos != -1 && pos < first) {first = pos;}}if (first == n) {// 遍历完毕 , 无 不重复的first = -1;}return first;}
};遍历方式 2
class Solution {
public:int firstUniqChar(string s) {unordered_map<int, int> dic; // 这里 用 char 或 int 都可以?int n = s.size();for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {if (dic.count(s[i])) {// 重复了dic[s[i]] = -1;}else {dic[s[i]] = i;}}int first = n; // 字典 中的元素 不是 按照 元素插入顺序 排列,要处理for (const auto& c: dic) { // 遍历方式 2if (c.second != -1 &&c.second < first) {first = c.second;}}if (first == n) {// 遍历完毕 , 无 不重复的first = -1;}return first;}
};遍历方式 3
class Solution {
public:int firstUniqChar(string s) {unordered_map<int, int> dic; // 这里 用 char 或 int 都可以?int n = s.size();for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {if (dic.count(s[i])) {// 重复了dic[s[i]] = -1;}else {dic[s[i]] = i;}}int first = n; // 字典 中的元素 不是 按照 元素插入顺序 排列,要处理for (unordered_map<int, int>::const_iterator it = dic.begin(); it != dic.end(); ++it) { // 遍历方式 3if (it->second != -1 && it->second < first) {first = it->second ;}}if (first == n) {// 遍历完毕 , 无 不重复的first = -1;}return first;}
};unordered_map 并非 元素插入顺序
#include <unordered_map>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{unordered_map<char, int> position;string s = "loveleetcode";int n = s.size();for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {if (position.count(s[i])) {position[s[i]] = -1;}else {position[s[i]] = i;}}for (unordered_map<char, int> ::const_iterator it = position.begin();it != position.end(); ++it)std::cout << " [" << it->first << ", " << it->second << "]";std::cout << std::endl;}
并非 元素插入的顺序

s = “leetcode”

方法三: queue 元素为 (字符,第一次出现的索引) 维护队首 + unordered_map记录是否重复
class Solution {
public:int firstUniqChar(string s) {unordered_map<char, int> dic;queue<pair<char, int>> q; // 队列 维护 字母 和 第一次出现的索引for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i){if (!dic.count(s[i])){dic[s[i]] = i;q.emplace(s[i], i); // 默认 右边 添加}else{dic[s[i]] = -1;while (!q.empty() && dic[q.front().first] == -1){q.pop(); // 弹出 左端 元素}}}return q.empty() ? -1 : q.front().second;}
};
queue
queue 文档
方法四: find 函数 和 rfind 函数
s.find(s[i]) : 返回字符串s中 从左向右 查找s[i]第一次出现的位置; s.rfind(s[i]) : 返回字符串s中 从右向左 查找s[i]第一次出现的位置;
class Solution {
public:int firstUniqChar(string s) {for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i){if (s.find(s[i]) == s.rfind(s[i])) // 该字符第一次出现的位置和最后一次出现的位置一样,就证明不重复。return i;}return -1;}
};
unordered_map 遍历 2种 方式
整理自 unordered_map函数文档
#include<unordered_map>
#include<iostream>
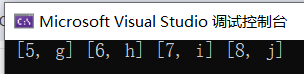
using namespace std;int main(){unordered_map<int, char> c5({ { 5, 'g' }, { 6, 'h' }, { 7, 'i' }, { 8, 'j' } });for (const auto& c : c5) {cout << " [" << c.first << ", " << c.second << "]";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
#include <unordered_map>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{unordered_map<int, char> dic({ { 5, 'g' }, { 6, 'h' }, { 7, 'i' }, { 8, 'j' } });for (unordered_map<int, char>::const_iterator it = dic.begin(); it != dic.end(); ++it)std::cout << " [" << it->first << ", " << it->second << "]";std::cout << std::endl; // 只能通过 -> 取值return 0;
}

这篇关于【LeetCode】 387. 字符串中的第一个唯一字符的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




