本文主要是介绍分布式空间分析引擎-Simba架构分析与源码阅读之索引部分源码,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Simba实现了五种类型的数据索引,并结合Spark的RDD结构构建了two-level index的机制:在数据分区内部构建local index,以及为各个数据分区构建global index。本章会首先介绍simba的two-level机制,然后具体介绍几种类型的two-level index的具体实现,最后会结合上一章的分区器对几种索引进行总结与比较。
two-level index机制
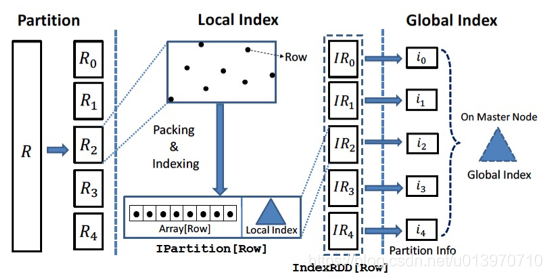
构建索引有助提高查询效率,Simba构建了two-level index来减少spatial join过程中参与计算的数据量:simba首先通过global index定位到实际参与运算的partitionID,再对于满足条件分区根据内部的localindex定位到参与运算的数据,过滤掉大部分不满足过滤条件的无关数据。其实多级索引的概念并不是simba的首创,phoenix里面就应用了多级索引来加速查询,TSDB-Gaia中geomesa层也应用了多级索引。
Simba首先对转化为RDD[Row]格式的数据表划分partition,然后对于每个partition内的数据建立local index(local index支持Hash index,RTree等),每个partition的数据生成一个由local index和实际的Row类型的数据Array组成的IPartition[Row]:
IPartition[Row](Data: Array[Row], I: Index)
然后各个数据分区的IPartition组成这个table的IndexRDD:
IndexRDD[Row] = RDD[IPartition[Row]]
然后simba对这些IPartition建立global index,global index可以是各个IPartition boundary的数组,也可以是支持多维数据点的KDTree。
HashMap索引
HashMap索引的逻辑比较简单:
val partitionedRDD = HashPartition(dataRDD, numShufflePartitions)val indexed = partitionedRDD.mapPartitions(iter => {val data = iter.toArrayval index = HashMapIndex(data)Array(IPartition(data.map(_._2), index)).iterator}).persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER) 首先调用哈希分区器对数据进行分区,然后对每个分区的数据调用HashMapIndex建立local index,将所有分区的data和index放入数组中作为global index。
object HashMapIndex {def apply[T](data: Array[(T, InternalRow)]): HashMapIndex[T] = {val res = new HashMapIndex[T]for (i <- data.indices) {res.index.put(data(i)._1, i)}res}
}建立local index的逻辑就是对分区内的每一条数据,将其key作为map-key,在数组中index作为map-value放到HashMap中。
QuadTree索引(四叉树索引)
QuadTree索引建立流程如下:
val (partitionedRDD, _, global_qtree) = QuadTreePartitioner(dataRDD, dimension,numShufflePartitions, sampleRate, tranferThreshold)
val indexed = partitionedRDD.mapPartitions { iter =>
val data = iter.toArray
val index: QuadTree =if (data.length > 0) QuadTree(data.map(_._1).zipWithIndex)else nullArray(IPartition(data.map(_._2), index)).iterator}.persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER)首先调用QuadTree分区器对数据进行分区,然后对每个分区的数据调用QuadTree方法建立local index,然后在分区器划分出的MBR上构建RTree作为global index。
四叉树索引QuadTree的构建方法与KDTree类似,主要区别在于QuadTree在每次节点分裂的时候会分裂出四个子节点,而KDTree二分出两个子节点。QuadTree构建逻辑如下:
1)统计数据取值范围,建立根节点:
def apply(entries: Array[(Double, Double, Int)],boundary: (Double, Double, Double, Double) = null): QuadTree = {// collect the border of the total entriesval (x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max) =if (boundary == null) entries.aggregate((Double.MaxValue, Double.MaxValue, Double.MinValue, Double.MinValue))((a: (Double, Double, Double, Double), b: (Double, Double, Int)) =>(math.min(a._1, b._1), math.min(a._2, b._2), math.max(a._3, b._1), math.max(a._4, b._2)),(a: (Double, Double, Double, Double), b: (Double, Double, Double, Double)) =>(math.min(a._1, b._1), math.min(a._2, b._2), math.max(a._3, b._3), math.max(a._4, b._4)))else boundaryval root = new QuadTreeNode(x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max, null, entries)val quadTree = new QuadTree(root)quadTree.bulkload()quadTree}2)递归地从根节点开始四分裂,如果分裂出的某个子节点包含的数据条数大于等于给定的参数MAX_NODES,则继续分裂这个子节点:
case class QuadTreeNode(x_low: Double, y_low: Double, x_high: Double, y_high: Double,var children: Array[QuadTreeNode], var objects: Array[(Double, Double, Int)]){private val center_x = (x_low + x_high) / 2private val center_y = (y_low + y_high) / 2def whichChild(obj: (Double, Double)): Int = {(if (obj._1 > center_x) 1 else 0) + (if (obj._2 > center_y) 2 else 0)}def makeChildren(): Unit = {children = Array(QuadTreeNode(x_low, y_low, center_x, center_y, null, null),QuadTreeNode(center_x, y_low, x_high, center_y, null, null),QuadTreeNode(x_low, center_y, center_x, y_high, null, null),QuadTreeNode(center_x, center_y, x_high, y_high, null, null))}def makeChildren(grouped: Map[Int, Array[(Double, Double, Int)]]): Unit = {children = Array(QuadTreeNode(x_low, y_low, center_x, center_y, null, grouped.getOrElse(0, Array())),QuadTreeNode(center_x, y_low, x_high, center_y, null, grouped.getOrElse(1, Array())),QuadTreeNode(x_low, center_y, center_x, y_high, null, grouped.getOrElse(2, Array())),QuadTreeNode(center_x, center_y, x_high, y_high, null, grouped.getOrElse(3, Array())))}
}
case class QuadTree(root: QuadTreeNode) extends Index with Serializable{val MAX_NODES = 3def bulkload(): QuadTreeNode = this.bulkload(root)private def bulkload(root: QuadTreeNode): QuadTreeNode = {val grouped = root.objects.groupBy(obj => root.whichChild(obj._1, obj._2))root.makeChildren(grouped)for (child <- root.children) {if (child.objects.length >= MAX_NODES) bulkload(child)}root.objects = nullroot}Treap索引
Treap=Tree+Heap。Treap是一棵二叉排序树,能够通过二分的方式提高数据查询性能,同时又具有堆的性质:两个子节点的值小于根节点的值,从而避免了二叉排序树在极端情况退化为链式的情况。为了同时达到这两种性质,Treap为每个树节点生成一个随机的权重值,从而通过树的旋转基于真实value实现二叉排序树的性质,基于权重值实现堆的性质。Treap索引的实现如下:
val (partitionedRDD, tmp_bounds) = RangePartition.rowPartition(dataRDD, numShufflePartitions)range_bounds = tmp_boundsval indexed = partitionedRDD.mapPartitions(iter => {val data = iter.toArrayval index = Treap(data)Array(IPartition(data.map(_._2), index)).iterator}).persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER)首先调用Range分区器对数据进行分区,然后对每个分区的数据建立Treap索引作为local index,然后把分区器划分出的分割数组rangeBounds作为global index,支持通过二分查找快速定位到partition。
Treap索引的构建过程主要是递归地插入和旋转构建过程如下:
private def leftRotate(p: TreapNode[K]): TreapNode[K] = {val t = p.leftp.left = t.rightt.right = pp.update()t.update()t}private def rightRotate(p: TreapNode[K]): TreapNode[K] = {val t = p.rightp.right = t.leftt.left = pp.update()t.update()t}private def insert(p: TreapNode[K], key: K, data: Int): TreapNode[K] = {if (p == null) {new TreapNode(key, Array(data), null, null, Random.nextLong(), 1, 1)} else if (ordering.equiv(key, p.key)) {p.count += 1p.size += 1p.data = p.data :+ datap} else if (ordering.lt(key, p.key)) {p.left = insert(p.left, key, data)if (p.left.rand < p.rand) leftRotate(p)else {p.update()p}} else {p.right = insert(p.right, key, data)if (p.right.rand < p.rand) rightRotate(p)else {p.update()p}}}def insert(key: K, data: Int): Unit = {root = insert(root, key, data)}TreeMap索引
TreeMap是一种有序的Map结构,基于红黑树实现,simba中TreeMap索引的构建过程如下:
val (partitionedRDD, tmp_bounds) = RangePartition.rowPartition(dataRDD, numShufflePartitions)range_bounds = tmp_boundsval indexed = partitionedRDD.mapPartitions(iter => {val data = iter.toArrayval index = TreeMapIndex(data)Array(IPartition(data.map(_._2), index)).iterator}).persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER)首先调用Range分区器对数据进行分区,然后对每个分区的数据建立TreeMap索引作为local index,然后把分区器划分出的分割数组rangeBounds作为global index,支持通过二分查找快速定位到partition。
TreeMap的构建主要是通过jdk的原生API来实现,直接初始化了util包的TreeMapIndex:
object TreeMapIndex {def apply[T](data: Array[(T, InternalRow)]): TreeMapIndex[T] = {val res = new TreeMapIndex[T]for (i <- data.indices)res.index.put(data(i)._1, i)res}
}RTree索引
RTree是一种经典的空间索引,在Simba中也应用的十分广泛,构建流程如下:
val (partitionedRDD, mbr_bounds) =STRPartition(dataRDD, dimension, numShufflePartitions, sampleRate, transferThreshold, max_entries_per_node)
val indexed = partitionedRDD.mapPartitions { iter =>val data = iter.toArrayvar index: RTree = nullif (data.length > 0) index = RTree(data.map(_._1).zipWithIndex, max_entries_per_node)Array(IPartition(data.map(_._2), index)).iterator}.persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER)val partitionSize = indexed.mapPartitions(iter => iter.map(_.data.length)).collect()global_rtree = RTree(mbr_bounds.zip(partitionSize).map(x => (x._1._1, x._1._2, x._2)), max_entries_per_node)首先调用STR分区器对数据进行分区,然后对每个分区的数据建立RTree索引作为local index,在分区器划分出的MBR上构建RTree作为global index。RTree的构建逻辑如下:
1.对原始数据建立RTree:
1.1、对数据递归分组,分组规则参照STR算法,并对最终生成的每个数据分组建立MBR:
def recursiveGroupPoint(entries: Array[(Point, Int)],cur_dim: Int, until_dim: Int): Array[Array[(Point, Int)]] = {val len = entries.length.toDoubleval grouped = entries.sortWith(_._1.coord(cur_dim) < _._1.coord(cur_dim)).grouped(Math.ceil(len / dim(cur_dim)).toInt).toArrayif (cur_dim < until_dim) {grouped.flatMap(now => recursiveGroupPoint(now, cur_dim + 1, until_dim))} else grouped}val grouped = recursiveGroupPoint(entries, 0, dimension - 1)val rtree_nodes = mutable.ArrayBuffer[(MBR, RTreeNode)]()grouped.foreach(list => {val min = new Array[Double](dimension).map(x => Double.MaxValue)val max = new Array[Double](dimension).map(x => Double.MinValue)list.foreach(now => {for (i <- 0 until dimension) min(i) = Math.min(min(i), now._1.coord(i))for (i <- 0 until dimension) max(i) = Math.max(max(i), now._1.coord(i))})val mbr = MBR(new Point(min), new Point(max))rtree_nodes += ((mbr, new RTreeNode(mbr, list)))})1.2、把1.1生成的节点分组作为叶子层,自底向上递归地对每一层进行分组生成多叉树结构,直至生成根节点只包含一个RTreeNode。
def recursiveGroupRTreeNode(entries: Array[(MBR, RTreeNode)], cur_dim: Int, until_dim: Int): Array[Array[(MBR, RTreeNode)]] = {val len = entries.length.toDoubleval grouped = entries.sortWith(comp(cur_dim)).grouped(Math.ceil(len / dim(cur_dim)).toInt).toArrayif (cur_dim < until_dim) {grouped.flatMap(now => recursiveGroupRTreeNode(now, cur_dim + 1, until_dim))} else grouped}while (!over(dim)) {val grouped = recursiveGroupRTreeNode(cur_rtree_nodes, 0, dimension - 1)var tmp_nodes = mutable.ArrayBuffer[(MBR, RTreeNode)]()grouped.foreach(list => {val min = new Array[Double](dimension).map(x => Double.MaxValue)val max = new Array[Double](dimension).map(x => Double.MinValue)list.foreach(now => {for (i <- 0 until dimension) min(i) = Math.min(min(i), now._1.low.coord(i))for (i <- 0 until dimension) max(i) = Math.max(max(i), now._1.high.coord(i))})val mbr = MBR(new Point(min), new Point(max))tmp_nodes += ((mbr, new RTreeNode(mbr, list)))})cur_rtree_nodes = tmp_nodes.toArraycur_len = cur_rtree_nodes.length.toDoubleremaining = cur_len / max_entries_per_nodefor (i <- 0 until dimension) {dim(i) = Math.ceil(Math.pow(remaining, 1.0 / (dimension - i))).toIntremaining /= dim(i)}}2.对已划分的MBR建立RTree:
2.1、对输入的MBR进行分组,递归地生成叶子层RTreeNode:
def recursiveGroupMBR(entries: Array[(MBR, Int, Int)], cur_dim: Int, until_dim: Int): Array[Array[(MBR, Int, Int)]] = {val len = entries.length.toDoubleval grouped = entries.sortWith(compMBR(cur_dim)).grouped(Math.ceil(len / dim(cur_dim)).toInt).toArrayif (cur_dim < until_dim) {grouped.flatMap(now => recursiveGroupMBR(now, cur_dim + 1, until_dim))} else grouped}val grouped = recursiveGroupMBR(entries, 0, dimension - 1)val rtree_nodes = mutable.ArrayBuffer[(MBR, RTreeNode)]()grouped.foreach(list => {val min = new Array[Double](dimension).map(x => Double.MaxValue)val max = new Array[Double](dimension).map(x => Double.MinValue)list.foreach(now => {for (i <- 0 until dimension) min(i) = Math.min(min(i), now._1.low.coord(i))for (i <- 0 until dimension) max(i) = Math.max(max(i), now._1.high.coord(i))})val mbr = MBR(new Point(min), new Point(max))rtree_nodes += ((mbr, new RTreeNode(mbr, list)))})2.2、自底向上递归地对每一层进行分组生成多叉树结构,这部分的逻辑与1.2完全一致。
索引的比较
| 索引类型 | 对应分区器 | local index | global index | 适用数据类型 | 优势 | 劣势 |
| HashMap | Range | HashMapIndex | rangeBounds数组 | 不限 | 构建效率高 | 空间占用相对其他索引较大 |
| QuadTree | QuadTree | QuadTree | RTree | 二维数据 | 相对map类索引节省空间,对spatial类算子有优化 | 普通查询由于需要递归遍历树效率较低。 |
| Treap | Range | TreeMap | rangeBounds数组 | 不限 | 堆的性质限制了树高度不会特别失衡 | 二叉树树深度可能会比较深,影响查询效率 |
| RTree | STR | RTree | RTree | 高维数据点 | 大多数空间算子基于RTree设计,做了特别优化 | 无 |
| TreeMap | Range | TreeMap | rangeBounds数组 | 不限 | 区间查询效率高 | 空间占用相对其他索引较大 |
索引部分源码就介绍到这里,这部分的代码还是值得一看的,可以帮助理解数据库,特别是OLAP数据库的索引到底是怎么样实现的。
这篇关于分布式空间分析引擎-Simba架构分析与源码阅读之索引部分源码的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








