本文主要是介绍数据分析案例实战:泰坦尼克船员获救,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
学习唐宇迪《python数据分析与机器学习实战》视频
一、数据分析
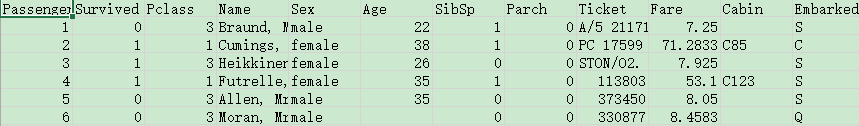
可以看到有些数据是字符串形式,有些是数值形式,有数据缺失。
survived:1代表存活,0代表死亡,目标tag。
Pclass:船舱,较重要。
sex:性别,较重要。
age:年龄,有缺失值,较重要。
SibSp:兄弟姐妹。Parch:父母孩子。
Ticket:票。
Fare:船票价格,特征可能与船舱特征重复,也较重要。
Cabin:缺失值很多,先忽略。
Embarked:上船港口的地点,有三个取值,需要转换成数值。
二、数据预处理
1.读入数据“titanic_train.csv”
import pandas as pd
#读入数据
titanic = pd.read_csv('titanic_train.csv')
titanic.head()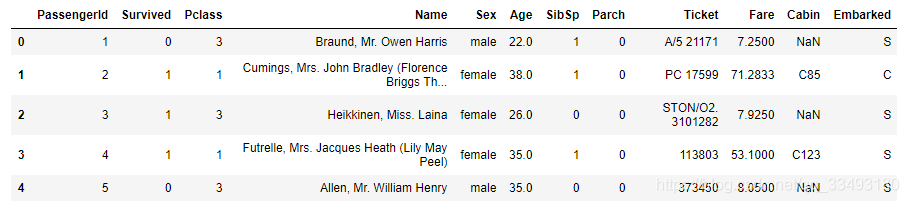
2.使用.describe()函数查看数据一些统计特征
#查看数据的一些统计特征
#count:个数,mean:均值 std:标准差 min:最小值 max:最大值
#25%:数值从小到大排列位于25%的数 50%: 75%:
print(titanic.describe())
#Age中存在缺失值
#利用pandas的.fillna函数对缺失值进行填充,使用.median()平均值填充
titanic['Age']=titanic['Age'].fillna(titanic['Age'].median())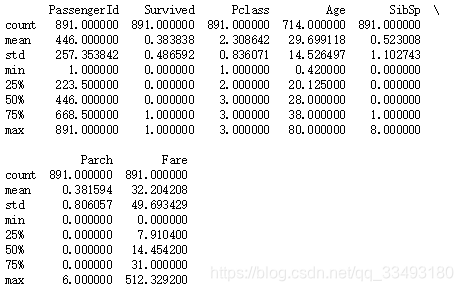
3.将一些字符串特征属性转换成数值
#将特征的字符串转换成数值
print(titanic['Sex'].unique())
#用0代表male 1代表female
titanic.loc[titanic['Sex']=='male','Sex']=0
titanic.loc[titanic['Sex']=='female','Sex']=1print(titanic['Embarked'].unique())
#有缺失值,以出现次数最多的‘S’进行填充 再转换成数值
titanic['Embarked']=titanic['Embarked'].fillna('S')
titanic.loc[titanic['Embarked']=='S','Embarked']=0
titanic.loc[titanic['Embarked']=='C','Embarked']=1
titanic.loc[titanic['Embarked']=='Q','Embarked']=2![]()
4.对测试集数据进行处理
#对测试集数据进行处理
titanic_test=pd.read_csv('test.csv')
#print(titanic_test.describe())
titanic_test['Age']=titanic_test['Age'].fillna(titanic['Age'].median())
titanic_test['Fare']=titanic_test['Fare'].fillna(titanic_test['Fare'].median())titanic_test.loc[titanic_test['Sex']=='male','Sex']=0
titanic_test.loc[titanic_test['Sex']=='female','Sex']=1titanic_test['Embarked']=titanic_test['Embarked'].fillna('S')
titanic_test.loc[titanic_test['Embarked']=='S','Embarked']=0
titanic_test.loc[titanic_test['Embarked']=='C','Embarked']=1
titanic_test.loc[titanic_test['Embarked']=='Q','Embarked']=2三、模型训练
1.sklearn线性回归算法
#使用sklearn线性回归算法进行分类
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold#选择使用的特征
predictors=['Pclass','Sex','Age','SibSp','Parch','Fare','Embarked']
#初始化模型对象
alg=LinearRegression()
#将m个样本分成3组
kf=KFold(3,random_state=1)predictions=[]
for train,test in kf.split(titanic):#print('train=',train) 输出的是索引值#print('test=',test) 输出的是索引值#kf.split()得到#训练集train(2份)和验证集test(1份)都是划分后的索引train_predictors=(titanic[predictors].iloc[train,:])#.iloc[train,:]通过训练集的索引,提取样本特征数据。train_target=titanic['Survived'].iloc[train]#.iloc[train]通过训练集的索引,提取样本标签。#训练模型alg.fit(train_predictors,train_target)#用验证集进行验证,得到预测结果test_predictions=alg.predict(titanic[predictors].iloc[test,:])predictions.append(test_predictions)import numpy as np
#np.concatenate拼接三组数据
predictions=np.concatenate(predictions,axis=0)
predictions[predictions>0.5]=1
predictions[predictions<0.5]=0
print(len(predictions[predictions==titanic['Survived']]))
accuracy=len(predictions[predictions==titanic['Survived']])/len(predictions)
print(accuracy)![]()
2.sklearn逻辑回归算法
cross_val_score、cross_validate二者均用于交叉验证,返回值就是scores(每次交叉验证的得分,list形式)。
cross_validate和cross_val_score的区别在于以下两点
允许传入多个metrics作为评价指标它的返回值是个dict而非list,内容包括5类:test_score, train_score, fit_time, score_times, training scores ,(fitted) estimators,它们分别是:验证集得分、训练集得分、每一折cv的estimator fit训练集的时间、每一折cv的estimator对验证集打分的时间、每一折cv的estimator对象。
#使用sklearn逻辑回归算法
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_validate
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression#使用逻辑回归交叉验证
alg=LogisticRegression(random_state=1)
cv_results=cross_validate(alg,titanic[predictors],titanic['Survived'],cv=3)
print(cv_results['test_score'].mean())scores = cross_val_score(alg, titanic[predictors], titanic["Survived"], cv=3)
print(scores.mean())
![]()
3.使用随机森林算法进行分类
样本是随机的,有放回的取样
特征的选择也是随机的,防止过拟合
多颗决策树,取平均值
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_validate
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifierpredictors=['Pclass','Sex','Age','SibSp','Parch','Fare','Embarked']
#random_state=1设置随机种子使代码多次运行得到的随机值都是一样的
#n_estimators: 也就是弱学习器的最大迭代次数,或者说最大的弱学习器的个数。
#内部节点再划分所需最小样本数min_samples_split: 这个值限制了子树继续划分的条件,如果某节点的样本数少于min_samples_split,则不会继续再尝试选择最优特征来进行划分。
#叶子节点最少样本数min_samples_leaf: 这个值限制了叶子节点最少的样本数,如果某叶子节点数目小于样本数,则会和兄弟节点一起被剪枝。
alg=RandomForestClassifier(random_state=1,n_estimators=10,min_samples_split=2,min_samples_leaf=1)
kf=KFold(3,random_state=1)
cv_results=cross_validate(alg,titanic[predictors],titanic['Survived'],cv=kf)
print(cv_results['test_score'].mean())![]()
#更改RF的参数试试
alg=RandomForestClassifier(random_state=1,n_estimators=100,min_samples_split=4,min_samples_leaf=2)
kf=KFold(3,random_state=1)
cv_results=cross_validate(alg,titanic[predictors],titanic['Survived'],cv=kf)
print(cv_results['test_score'].mean())![]()
4.提取新特征
#SibSp是兄弟姐妹数量,Parch是老人小孩數量,可以得到家庭人数
titanic['FamilySize']=titanic['SibSp']+titanic['Parch']
#名字长度……
titanic['NameLength']=titanic['Name'].apply(lambda x:len(x))import redef get_title(name):#正则表达式:(+)代表匹配一一个或多个,\代表转义#总的来说就是匹配带.号的称谓并且前面至少有一个字母title_search=re.search('([A-Za-z]+)\.',name)if title_search:#返回匹配到的元組,group(1)代表返回匹配到的第一个()里的內容return title_search.group(1)return ''
titles=titanic['Name'].apply(get_title)
print(pd.value_counts(titles))
#用数字来代替不同的称谓
title_mapping={'Mr':1,'Miss':2,'Mrs':3,'Master':4,'Dr':5,'Rev':6, "Major": 7, "Col": 7, "Mlle": 8, "Mme": 8, "Don": 9, "Lady": 10, "Countess": 10, "Jonkheer": 10, "Sir": 9, "Capt": 7, "Ms": 2}
for k,v in title_mapping.items():titles[titles==k]=vprint(pd.value_counts(titles))
titanic['Title']=titles
5.选择特征
#利用 feature_selection 对指定特征进行进一步的选择,找出影响较大的特征
import numpy as np
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectKBest,f_classif
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#指定一下特征
predictors = ["Pclass", "Sex", "Age", "SibSp", "Parch", "Fare", "Embarked", "FamilySize", "Title", "NameLength"]
#选择特性
selector=SelectKBest(f_classif,k=5)
selector.fit(titanic[predictors],titanic['Survived'])
scores=-np.log10(selector.pvalues_)
#利用直方图显示不同特征的重要性
plt.bar(range(len(predictors)),scores)
plt.xticks(range(len(predictors)),predictors,rotation='vertical')
plt.show()#选择出几个重要的特征,使用RF重新进行计算
predictors=['Pclass','Sex','Fare','Title']
alg=RandomForestClassifier(random_state=1,n_estimators=50,min_samples_split=8,min_samples_leaf=4)
kf=KFold(3,random_state=1)
cv_results=cross_validate(alg,titanic[predictors],titanic['Survived'],cv=kf)
print(cv_results['test_score'].mean())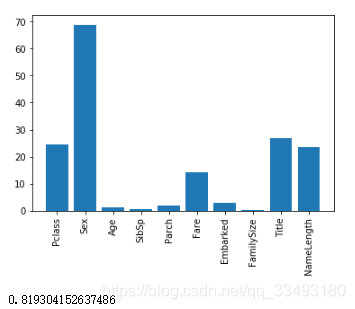
6.集成多个分类器方法
#竞赛中常用的耍赖的方法:集成多种算法,取平均值
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
import numpy as np
#GradientBoostingClassifier也是一种随机森林算法,可以集成多个弱分类器,然后变成强分类器
algorithms=[[GradientBoostingClassifier(random_state=1,n_estimators=25,max_depth=3), ["Pclass", "Sex", "Age", "Fare", "Embarked", "FamilySize", "Title"]],[LogisticRegression(random_state=1), ["Pclass", "Sex", "Fare", "FamilySize", "Title", "Age", "Embarked"]]
]kf=KFold(3,random_state=1)predictions=[]
for train,test in kf.split(titanic):train_target=titanic['Survived'].iloc[train]full_test_predictions=[]for alg,predictors in algorithms:alg.fit(titanic[predictors].iloc[train,:],train_target)test_predictions=alg.predict_proba(titanic[predictors].iloc[test,:].astype(float))[:,1]full_test_predictions.append(test_predictions)test_predictions=(full_test_predictions[0]+full_test_predictions[1])/2test_predictions[test_predictions<=0.5]=0test_predictions[test_predictions>0.5]=1predictions.append(test_predictions)predictions=np.concatenate(predictions,axis=0)
accuracy=len(predictions[predictions==titanic['Survived']])/len(predictions)
print(accuracy)![]()
四、预测
将新的特征加入测试集数据,预测测试集中每个人的获救几率
titles=titanic_test['Name'].apply(get_title)
title_mapping = {"Mr": 1, "Miss": 2, "Mrs": 3, "Master": 4, "Dr": 5, "Rev": 6, "Major": 7, "Col": 7, "Mlle": 8, "Mme": 8, "Don": 9, "Lady": 10, "Countess": 10, "Jonkheer": 10, "Sir": 9, "Capt": 7, "Ms": 2, "Dona": 10}
for k,v in title_mapping.items():titles[titles==k]=v
titanic_test['Title']=titles
print(pd.value_counts(titanic_test['Title']))
titanic_test['FamilySize']=titanic_test['SibSp']+titanic_test['Parch']
predictors = ["Pclass", "Sex", "Age", "Fare", "Embarked", "FamilySize", "Title"]algorithms = [[GradientBoostingClassifier(random_state=1, n_estimators=25, max_depth=3), predictors],[LogisticRegression(random_state=1), ["Pclass", "Sex", "Fare", "FamilySize", "Title", "Age", "Embarked"]]
]full_predictions = []
for alg, predictors in algorithms:# Fit the algorithm using the full training data.alg.fit(titanic[predictors], titanic["Survived"])# Predict using the test dataset. We have to convert all the columns to floats to avoid an error.predictions = alg.predict_proba(titanic_test[predictors].astype(float))[:,1]full_predictions.append(predictions)# The gradient boosting classifier generates better predictions, so we weight it higher.
predictions = (full_predictions[0] * 3 + full_predictions[1]) / 4
predictions
这篇关于数据分析案例实战:泰坦尼克船员获救的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




