本文主要是介绍python讲师陈越_【数据结构_浙江大学MOOC】第一讲 基本概念,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
本系列数据结构专题为中国大学MOOC-陈越、何钦铭-数据结构-2018秋课程的学习记录。主要记录内容为编程题解答。每篇内容将会不定期更新,以补充更好的方法。
函数题
01-复杂度3 二分查找(20 分)
本题要求实现二分查找算法。
函数接口定义:
Position BinarySearch( List L, ElementType X );
其中List结构定义如下:
typedef int Position;
typedef struct LNode *List;
struct LNode {
ElementType Data[MAXSIZE];
Position Last; /* 保存线性表中最后一个元素的位置 */
};
L是用户传入的一个线性表,其中ElementType元素可以通过>、==、
裁判测试程序样例:
#include
#include
#define MAXSIZE 10
#define NotFound 0
typedef int ElementType;
typedef int Position;
typedef struct LNode *List;
struct LNode {
ElementType Data[MAXSIZE];
Position Last; /* 保存线性表中最后一个元素的位置 */
};
List ReadInput(); /* 裁判实现,细节不表。元素从下标1开始存储 */
Position BinarySearch( List L, ElementType X );
int main()
{
List L;
ElementType X;
Position P;
L = ReadInput();
scanf("%d", &X);
P = BinarySearch( L, X );
printf("%d\n", P);
return 0;
}
/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
输入样例1:
5
12 31 55 89 101
31
输出样例1:
2
输入样例2:
3
26 78 233
31
输出样例2:
0
代码
编译器:C (gcc)
Position BinarySearch( List L, ElementType X ){
Position position;
Position left = 0;
Position right = L->Last;
ElementType flag = 0;
while(left <= right){
Position mid = left + (right -left)/2;
if(L->Data[mid] == X){
position = mid;
flag = 1;
break;
}
else if(L->Data[mid] > X){
right = mid-1;
}else{
left = mid+1;
}
}
if(flag == 0)
position = NotFound;
return position;
}
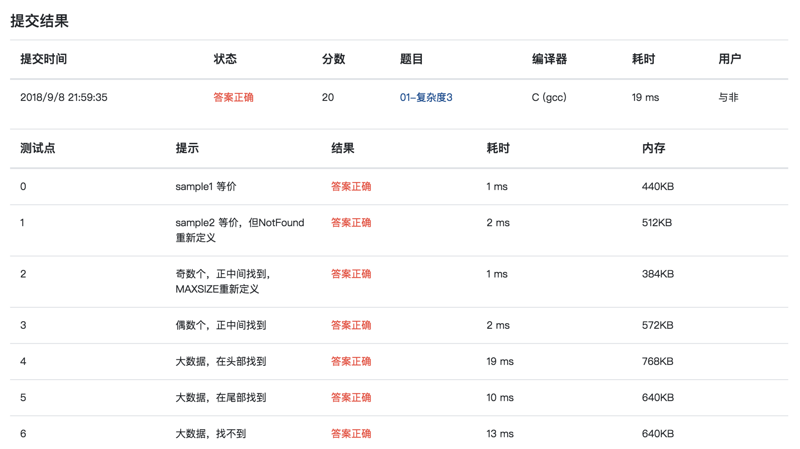
提交结果:
编程题
01-复杂度1 最大子列和问题(20 分)
给定K个整数组成的序列 $\{N_1,N_2, ···,N_k \}$,“连续子列”被定义为 $\{N_i,N_{i+1}, ···,N_j \}$,其中 $1≤i≤j≤K$。“最大子列和”则被定义为所有连续子列元素的和中最大者。例如给定序列 { -2, 11, -4, 13, -5, -2 },其连续子列 { 11, -4, 13 } 有最大的和20。现要求你编写程序,计算给定整数序列的最大子列和。
本题旨在测试各种不同的算法在各种数据情况下的表现。各组测试数据特点如下:
数据1:与样例等价,测试基本正确性;
数据2:$10^2$ 个随机整数;
数据3:$10^3$ 个随机整数;
数据4:$10^4$ 个随机整数;
数据5:$10^5$ 个随机整数;
输入格式:
输入第 1 行给出正整数 $K (≤100000)$;第 2 行给出 $K$ 个整数,其间以空格分隔。
输出格式:
在一行中输出最大子列和。如果序列中所有整数皆为负数,则输出 0。
输入样例:
6
-2 11 -4 13 -5 -2
输出样例:
20
代码
编译器:C (gcc)
/*
编程题-01【最大子列和问题】
中国大学MOOC-陈越、何钦铭-数据结构-2018秋
标签:复杂度
2018-09-08
*/
# include
int MaxSubseqSum(int A[], int N);
int main()
{
int numK;
int maxSum;
int k;
scanf("%d", &numK);
int a[numK];
for(k=0; k
scanf("%d", &a[k]);
maxSum = MaxSubseqSum(a, numK);
printf("%d\n", maxSum);
return 0;
}
int MaxSubseqSum (int A[], int N)
{
int thisSum, maxSum;
int i, j;
thisSum = maxSum = 0;
/* 逐个向右累加 */
for( i = 0; i < N; i++) //i 为子列左端位置
{
/* A[i]到A[j]的子列和 */
thisSum = 0;
for(j=i; j
{
/* 对于相同起点的一系列子列和,只需更新终点即可 */
/* 即对于相同的i,不同的j,只需在j-1次循环的基础上累加1项 */
/* 降低了算法复杂度 */
thisSum +=A[j];
/* 当前子列和大于最大子列和,更新 */
if(thisSum > maxSum)
maxSum = thisSum;
/* 当前子列和为负,后面再加子列和不可能变大,故抛弃 */
else if(thisSum < 0)
thisSum = 0;
}
}
return maxSum;
}
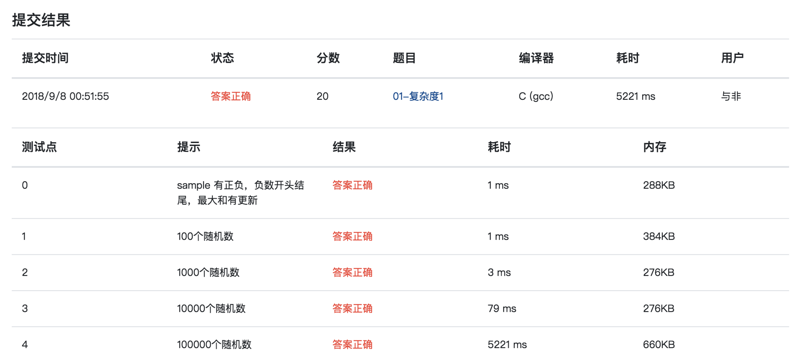
提交结果:
01-复杂度2 Maximum Subsequence Sum(25 分)
Given a sequence of $K$ integers $\{N_1,N_2, ···,N_k \}$. A continuous subsequence is defined to be $\{N_i,N_{i+1}, ···,N_j \}$ where $1≤i≤j≤K$ . The Maximum Subsequence is the continuous subsequence which has the largest sum of its elements. For example, given sequence { -2, 11, -4, 13, -5, -2 }, its maximum subsequence is { 11, -4, 13 } with the largest sum being 20.
Now you are supposed to find the largest sum, together with the first and the last numbers of the maximum subsequence.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case occupies two lines. The first line contains a positive integer $K (≤10000)$. The second line contains $K$ numbers, separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, output in one line the largest sum, together with the first and the last numbers of the maximum subsequence. The numbers must be separated by one space, but there must be no extra space at the end of a line. In case that the maximum subsequence is not unique, output the one with the smallest indices i and j (as shown by the sample case). If all the $K$ numbers are negative, then its maximum sum is defined to be 0, and you are supposed to output the first and the last numbers of the whole sequence.
Sample Input:
10
-10 1 2 3 4 -5 -23 3 7 -21
Sample Output:
10 1 4
代码
编译器:C++ (g++)
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, const char * argv[])
{
//input
int K;
cin>>K;
vector vec;
int value;
for (int i=0; i
{
cin>>value;
vec.push_back(value);
}
//Process
int first=0,last=0,sum=0,max=-1;
int flag_max=0;//flag represent whether max has been rewrite
int flag=0;//sum归零一次,有可能后续子数列会出现大于当前max的数列
int maybe_first=0;//可能成为最大子列和的第一个结点
for (int i=0; i
{
sum+=vec[i];
if (sum>max)//更新最大子列和
{
flag_max=1;
if (flag==0)//sum更新为0后再次出现大于之前max的最大子列和,更新最大子列和的第一个结点
{
first=maybe_first;
flag=1;
}
max=sum;
last=i;//每次出现新的最大子列和都要更新该子列的最后一个结点
}else if(sum<0)//sum出现小于0的情况,后续子列若出现更大的子列和,则该子列的第一个结点保存为maybe_first
{
maybe_first=i+1;
sum=0;
flag=0;
}
}
//Output
if (flag_max==0)
{
cout<
}else
{
cout<
}
return 0;
}
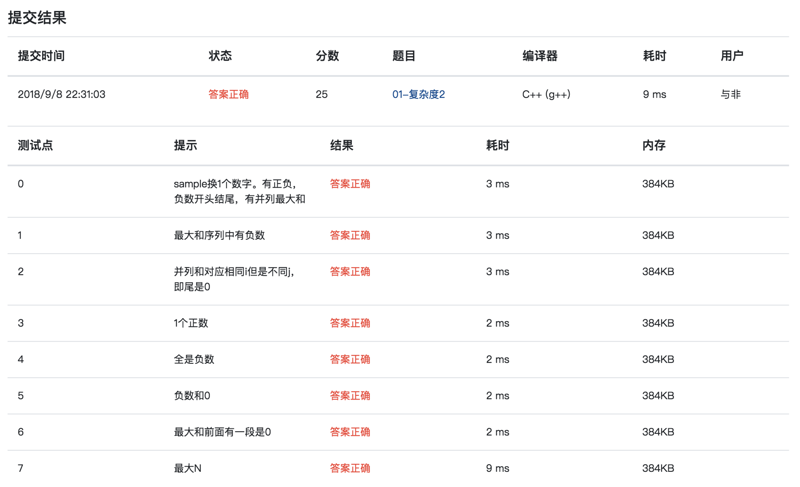
提交结果:
编译器:Python (python3)
num = int(input())
a = input()
a = a.split(' ')
max = -1
sum = 0
temp = 0
first = 0
last = 0
for i in range(0,num):
sum = sum + int(a[i])
if sum > max:
max = sum
last = i
first = temp
elif sum < 0:
sum = 0
temp = i+1
if(max >= 0):
print(max,a[first],a[last],sep=' ')
else:
print(0,a[0],a[len(a) -1],sep=' ')
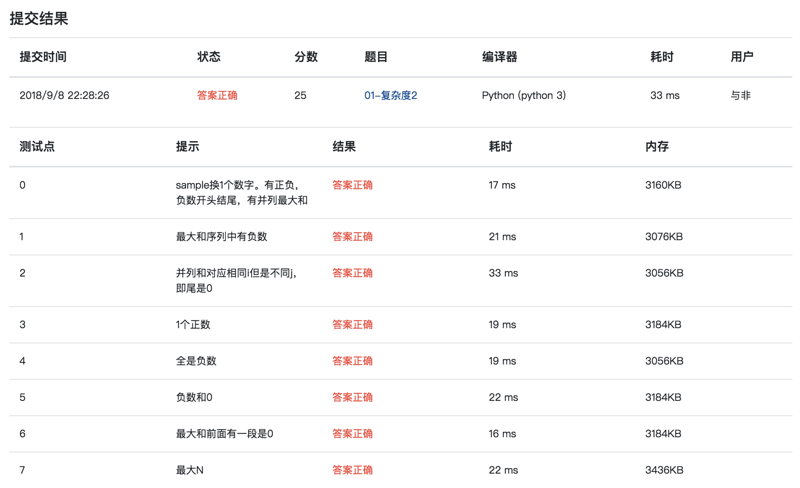
提交结果:
不足之处,欢迎指正。
$$$$
这篇关于python讲师陈越_【数据结构_浙江大学MOOC】第一讲 基本概念的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





