2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 
<h1>Summary</h1>
Currently, we KVM team are maintaining the code repository of the virtualization software(such as QEMU, Libvirt, Kimchi, Linux, etc.) for PowerKVM development team and delivering corresponding RPM packages. We collect patches from mailing list and build update RPM packages every workday. The work load is extremely heavy if we manually download the patches from mailing list, apply them to the repository, and build RPM packages covering all the supported platforms.
This environment, based on Jenkins and Koji, can automatically manage the code(apply the patches from mailing lists to the appropriate repository and branch) and build the required RPM packages covering all supported platforms nightly or triggered manually. By using this automation environment, developers can easily get the updated RPM packages just by sending the patches to the given e-mail address or mailing list. Furthermore, the time cost for daily routine work is dramatically reduced and the quality of the packages will be improved by eliminating human errors. This environment also can be used to other projects by making few changes to configure files.
<h1>Challenges</h1>
In PowerKVM development, we have to ship all the significant bug fixes frequently, usually a couple days. All the fix patches of QEMU, Libvirt, Linux, Kimchi will be sent to a certain mailing list. After the code cut-off day, we download all the patches from the mailing list and manually apply them to different git repositories accordingly. Then copy all the git repositories to different platform(RHEL,Fedora,etc) and do build. Last step, copy all the output RPM packages to different RPM repositories accordingly. Sometimes, we can not deliver the packages on time because the workload is extremely heavy. Furthermore, errors occur frequently such as some patches may get lost during the process due to lack of time. In order to solve these problems, we decided to make use of Jenkins and Koji to establish the CI environment.
During the construction of this environment, we have to resolve the following problems:
- Define the rules of sending patches for developers in order to make the CI know where the patches should go.
- Define the regular expression to distinguish patches from other e-mails.
- How to handle exceptions.
<h1>Experience</h1>
<1>. Tools and Framework Overview
In order to implement this automation environment, several tools are needed:
- Jenkins: Jenkins is a software that monitors executions of repeated jobs. This automation environment use Jenkins as the user interface and the manager of all the underlying jobs.
- Koji: Koji can build RPMs packages for multiple platforms. This automation environment make use of Koji to build RPMs for all supported platform.
- Python scripts: implement the function that collect patches from mailing list, organize and archive these patches.
- Shell scripts: Apply the patches to the appropriate git repositories, process build and release the output RPM packages via web server.
- Apache HTTP server: Release the RPMs via web page. Below is the chart about the framework overview of this automation environment and the relationship among these tools.
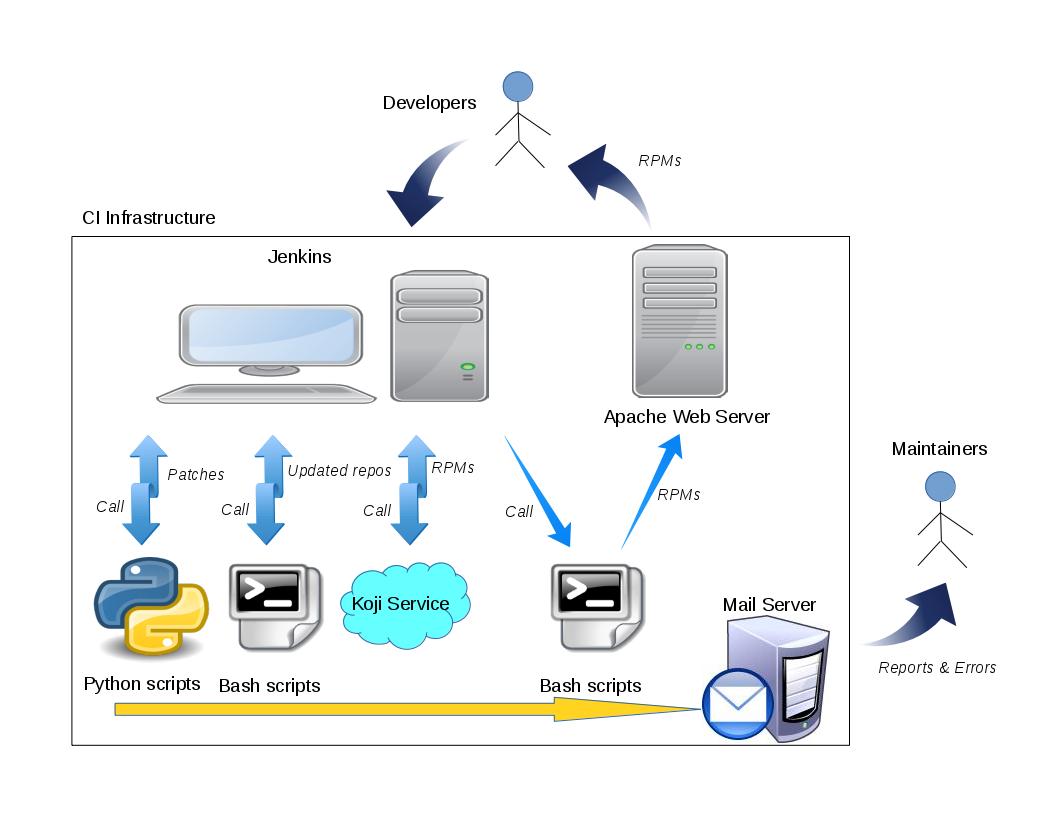
<2>. User Interface
The automation environment runs nightly. However, if the developer want to get the RPM packages immediately, he or she can simply click the start button of Jenkins. See below chart.
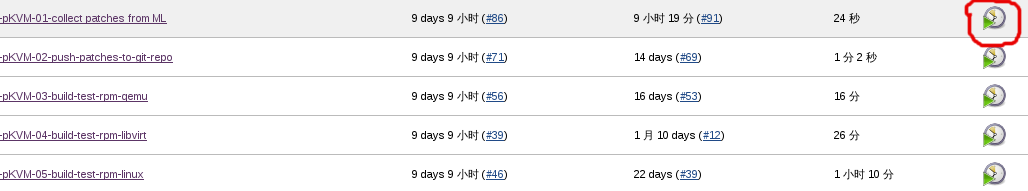
<3>. Execution flow
After the developers click the first run button, jenkins will call python scripts to collect emails matching certain regular expression(We advise developers send patches to mailing list in fixed forms, such as [branch_name PATCH repo_name]xxx) and archive all the patches by date. Then, Jenkins will call shell scripts to apply these patches to the appropriate git repositories. After that, Koji will be noticed to build the RPM packages of all the supported platforms. Finally, Jenkins will call the shell scripts to copy all the RPM packages to certain directory of Apache web server.
<4>. Handle exception
The automation environment will send report containing how many patches received and where the RPM packages are published to the mailing list if all the jobs are successfully executed. If a certain job failed, it also sends report to the mailing list or email boxes configured in the configuration file. Different job has different error report message. For example, when the job who collects patches from mailing list fails, it will send out the failed patches' name, but when the job who builds RPM packages fails, it will send out the build log.
<h1>Benefit</h1>
For the repositories maintainers, this automation environment can save much time costs for their daily routing work. What they need to do is just check reports via email clients if this automation environment start to work. The time costs dramatically reduce from several hours to a few minutes.
For the developers, they can get the RPM packages by themselves whenever they want to build one, instead of asking the maintainers spend much time to build for them. What they need to do is simply click a button.
Furthermore, the quality of the RPM packages will be improved because this automation environment can eliminate human errors effectively.
<h1>Next Steps and Recommendations</h1>
Currently, this automation environment is just used for code management and RPM packages build. Since it can save much time cost for developers and repository maintainers, we are planing to involve test cases. We can make use of automation test technology and integrate the test cases into this automation environment. After that, test engineers will be set free from burdensome test work.




