本文主要是介绍autoML 前瞻与实践 ---- H2O Sparkling Water简介,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章大纲
- 简介
- Sparkling Water
- 典型应用场景 Typical Use Case
- Requirements
- Installing and Starting
- PySparkling
- 安装
- 典型应用场景
- Model Building
- Data Munging
- Stream Processing
- 参考文档
- H2O Sparkling Water
- PySparkling
简介
Sparkling Water allows users to combine the fast, scalable machine learning algorithms of H2O with the capabilities of Spark. With Sparkling Water, users can drive computation from Scala/R/Python and utilize the H2O Flow UI, providing an ideal machine learning platform for application developers.
Spark is an elegant and powerful general-purpose, open-source, in-memory platform with tremendous momentum. H2O is an in-memory application for machine learning that is reshaping how people apply math and predictive analytics to their business problems.
Integrating these two open-source environments provides a seamless experience for users who want to make a query using Spark SQL, feed the results into H2O to build a model and make predictions, and then use the results again in Spark. For any given problem, better interoperability between tools provides a better experience.
Sparkling Water is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0.
Sparking Water擅长利用现有的基于Spark的工作流,这些工作流需要调用高级机器学习算法。一个典型的例子是借助sparkapi进行数据挖掘,其中一个准备好的表被传递给H2O深度学习算法。构建的深度学习模型基于测试数据估计不同的度量,这些度量可用于Spark工作流的其余部分。
Sparkling Water
- github :https://github.com/h2oai/sparkling-water
典型应用场景 Typical Use Case
Sparkling Water excels in leveraging existing Spark-based workflows that need to call advanced machine learning algorithms. A typical example involves data munging with the help of a Spark API, where a prepared table is passed to the H2O DeepLearning algorithm. The constructed DeepLearning model estimates different metrics based on the testing data, which can be used in the rest of the Spark workflow.
Sparking Water擅长利用现有的基于Spark的工作流,这些工作流需要调用高级机器学习算法。一个典型的例子是借助spark api进行数据挖掘, 使用一个准备好的表被传递给H2O进行深度学习算法自动学习。构建的深度学习模型基于测试数据估计不同的度量,这些度量可用于Spark工作流的其余部分。
Requirements
-
Linux/OS X/Windows
-
Java 1.8+
-
Python 2.7+ For Python version of Sparkling Water (PySparkling)
-
Spark 2.2 and SPARK_HOME shell variable must point to your local Spark installation
Installing and Starting
h2o 基本设计理念
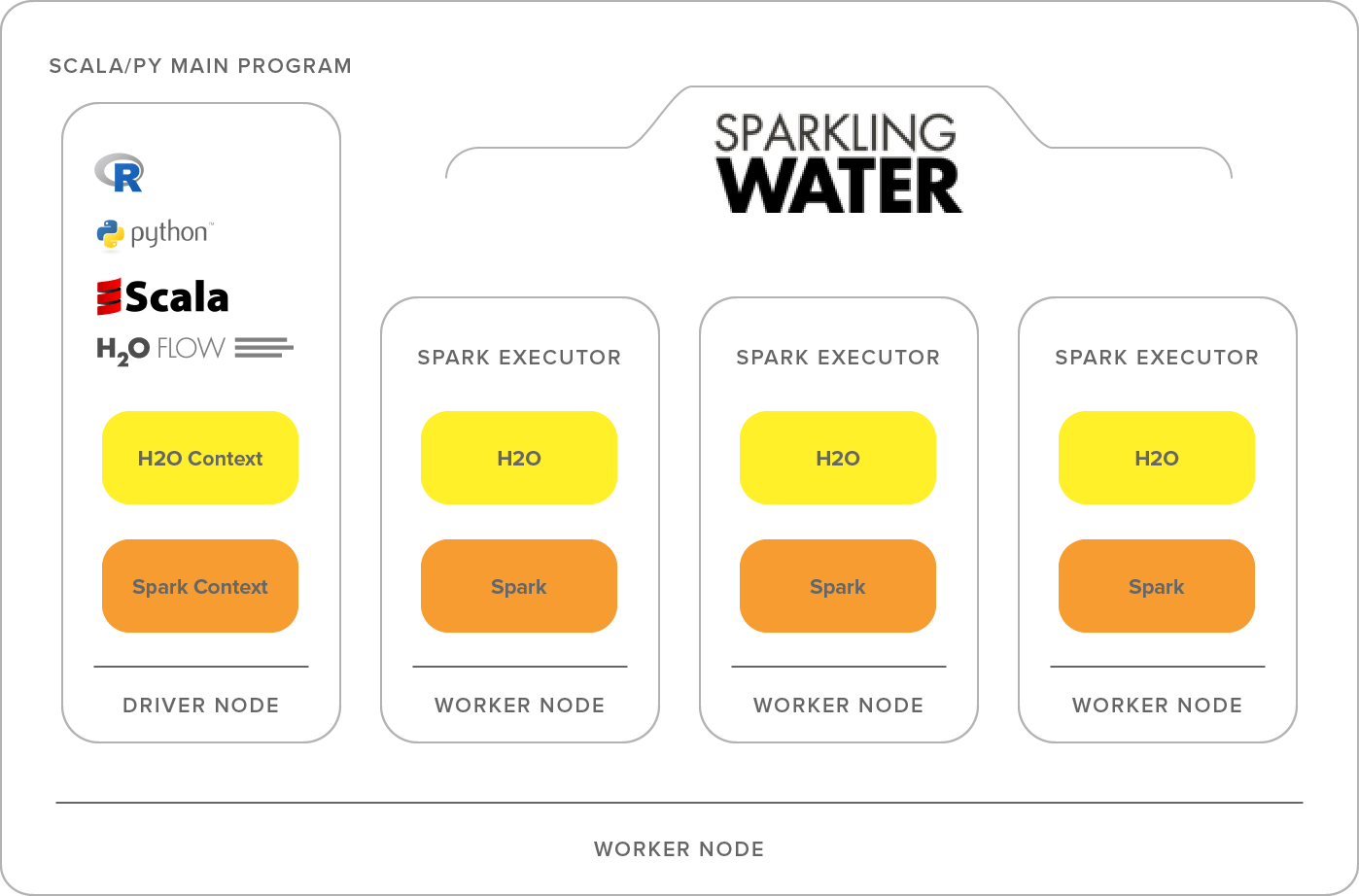

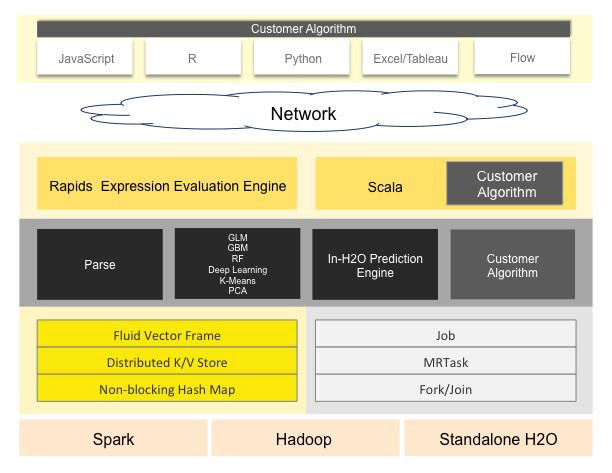
Sparkling Water supports two types of backends: internal and external.


PySparkling
文档:
https://docs.h2o.ai/sparkling-water/2.3/latest-stable/doc/pysparkling.html#pysparkling
安装:
https://docs.h2o.ai/sparkling-water/3.1/latest-stable/doc/install/install_and_start.html#download-and-run-locally
代码样例:
https://github.com/h2oai/sparkling-water/tree/master/examples#step-by-step-weather-data-example
安装
Which H2O package should I install?
The H2O distribution zip file contains two Python installation artifacts (wheel files): h2o and h2o_client. You can install the full-featured “h2o” package that can be used in a standalone setup (as well as cluster deployment), or you can choose client-only version of the package - “h2o_client”.
-
h2o: Universal deployment package - can be used in standalone mode (eg. H2O started on users laptop) or it can be used to connect to an H2O cluster. This is what most users will choose to install.
-
h2o_client: A variant of the h2o package that doesn’t come with the H2O java code and cannot be used in standalone deployments. This version is suited especially for enterprise deployments where users are connecting to H2O clusters, and starting a standalone H2O instance on an edge node needs to be prevented.
Both packages provide identical APIs and sets of features.
PySparkling is an integration of Python with Sparkling Water. It allows the user to start H2O services on a Spark cluster from Python API.
In the PySparkling driver program, the Spark Context, which uses Py4J to start the driver JVM and the Java Spark Context, is used to create the H2O Context (hc). That, in turn, starts an H2O cloud (cluster) in the Spark ecosystem. Once the H2O cluster is up, the H2O Python package is used to interact with it and run H2O algorithms. All pure H2O calls are executed via H2O’s REST API interface. Users can easily integrate their regular PySpark workflow with H2O algorithms using PySparkling.
PySparkling programs can be launched as an application or in an interactive shell or notebook environment.
安装脚本
conda create -n myspark312 python=3.9
conda activate myspark312
conda install ipykernelpip install pyspark==3.1.2
pip install numpypip install h2o_pysparkling_3.1
我们安装后的主要目标是直接使用h2o 的api 调用pyspark 的 sparksession
先来看看源文件:
#
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
#import h2o
import numbers
import warnings
from ai.h2o.sparkling.H2OConf import H2OConf
from ai.h2o.sparkling.Initializer import Initializer
from h2o.frame import H2OFrame
from h2o.utils.typechecks import assert_is_type, Enum
from pyspark.rdd import RDD
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark.sql.dataframe import DataFrame
from pyspark.sql.types import StringType, BooleanType, IntegerType, LongType, FloatTypeclass H2OContext(object):__isConnected = Falsedef __init__(self):"""This constructor is used just to initialize the environment. It does not start H2OContext.To start H2OContext use one of the getOrCreate methods. This constructor is internally used in those methods"""try:Initializer.load_sparkling_jar()except:raisedef __h2o_connect(h2o_context):schema = h2o_context._jhc.getConf().getScheme()conf = h2o_context._confkwargs = {}kwargs["https"] = schema == "https"kwargs["verify_ssl_certificates"] = conf.verifySslCertificates()kwargs["cacert"] = conf.sslCACert()if conf.userName() and conf.password():kwargs["auth"] = (conf.userName(), conf.password())url = "{}://{}:{}".format(schema, h2o_context._client_ip, h2o_context._client_port)if conf.contextPath() is not None:url = "{}/{}".format(url, conf.contextPath())return h2o.connect(url=url, **kwargs)@staticmethoddef getOrCreate(conf=None):"""Get existing or create new H2OContext based on provided H2O configuration. If the conf parameter is set thenconfiguration from it is used. Otherwise the configuration properties passed to Sparkling Water are used.If the values are not found the default values are used in most of the cases. The default cluster modeis internal, ie. spark.ext.h2o.external.cluster.mode=false:param conf: H2O configuration as instance of H2OConf:return: instance of H2OContext"""# Workaround for bug in Spark 2.1 as SparkSession created in PySpark is not seen in Java# and call SparkSession.builder.getOrCreate on Java side creates a new session, which is not# desirableactiveSession = SparkSession._instantiatedSessionjvm = activeSession.sparkContext._jvmjvm.org.apache.spark.sql.SparkSession.setDefaultSession(activeSession._jsparkSession)if conf is not None:selected_conf = confelse:selected_conf = H2OConf()selected_conf.set("spark.ext.h2o.client.language", "python")h2o_context = H2OContext()# Create backing H2OContexth2o_context._jvm = jvmpackage = getattr(jvm.ai.h2o.sparkling, "H2OContext$")module = package.__getattr__("MODULE$")jhc = module.getOrCreate(selected_conf._jconf)h2o_context._jhc = jhch2o_context._conf = selected_confh2o_context._client_ip = jhc.h2oLocalClientIp()h2o_context._client_port = jhc.h2oLocalClientPort()# Create H2O REST API clientif not h2o_context.__isClientConnected() or not H2OContext.__isConnected:h2o_context.__h2o_connect()H2OContext.__isConnected = Trueh2o_context.__setClientConnected()print(h2o_context)return h2o_contextdef __isStopped(self):hc = self._jhcfield = hc.getClass().getDeclaredField("stopped")field.setAccessible(True)return field.get(hc)def __isClientConnected(self):field = self.__getClientConnectedField()return field.get(self._jhc)def __setClientConnected(self):field = self.__getClientConnectedField()field.set(self._jhc, True)def __getClientConnectedField(self):field = self._jhc.getClass().getDeclaredField("clientConnected")field.setAccessible(True)return fielddef stop(self, stopSparkContext=False):h2o.connection().close()scalaStopMethod = getattr(self._jhc, "ai$h2o$sparkling$H2OContext$$stop")scalaStopMethod(stopSparkContext, False, False) # stopSpark = False, stopJVM = False, inShutdownHook = Falsedef downloadH2OLogs(self, destination, container="ZIP"):assert_is_type(container, Enum("ZIP", "LOG"))return self._jhc.downloadH2OLogs(destination, container)def __str__(self):if self.__isClientConnected() and not self.__isStopped():return self._jhc.toString()else:return "H2OContext has been stopped or hasn't been created. Call H2OContext.getOrCreate() or " \"H2OContext.getOrCreate(conf) to create a new one."def __repr__(self):self.show()return ""def show(self):print(self)def getConf(self):return self._confdef setH2OLogLevel(self, level):self._jhc.setH2OLogLevel(level)def getH2OLogLevel(self):return self._jhc.getH2OLogLevel()def importHiveTable(self, database="default", table=None, partitions=None, allowMultiFormat=False):return h2o.import_hive_table(database, table, partitions, allowMultiFormat)def asSparkFrame(self, h2oFrame, copyMetadata=True):"""Transforms given H2OFrame to Spark DataFrameParameters----------h2oFrame : H2OFramecopyMetadata: Bool = TrueReturns-------Spark DataFrame"""if isinstance(h2oFrame, H2OFrame):frame_id = h2oFrame.frame_idjdf = self._jhc.asSparkFrame(frame_id, copyMetadata)sqlContext = SparkSession.builder.getOrCreate()._wrappeddf = DataFrame(jdf, sqlContext)# Attach h2o_frame to dataframe which forces python not to delete the frame when we leave the scope of this# method.# Without this, after leaving this method python would garbage collect the frame since it's not used# anywhere and spark. when executing any action on this dataframe, will fail since the frame# would be missing.df._h2o_frame = h2oFramereturn dfdef asH2OFrame(self, sparkFrame, h2oFrameName=None, fullCols=-1):"""Transforms given Spark RDD or DataFrame to H2OFrame.Parameters----------sparkFrame : Spark RDD or DataFrameh2oFrameName : Optional name for resulting H2OFramefullCols : number of first n columns which are sent to the client together with the dataReturns-------H2OFrame which contains data of original input Spark data structure"""assert_is_type(sparkFrame, DataFrame, RDD)df = H2OContext.__prepareSparkDataForConversion(self._jvm, sparkFrame)if h2oFrameName is None:key = self._jhc.asH2OFrame(df._jdf).frameId()else:key = self._jhc.asH2OFrame(df._jdf, h2oFrameName).frameId()return H2OFrame.get_frame(key, full_cols=fullCols, light=True)@staticmethoddef __prepareSparkDataForConversion(_jvm, sparkData):if isinstance(sparkData, DataFrame):return sparkDataelif sparkData.isEmpty():return sparkData.toDF()else:session = SparkSession.builder.getOrCreate()first = sparkData.first()if isinstance(first, (str, bool, numbers.Integral, float)):if isinstance(first, str):return session.createDataFrame(sparkData, StringType())elif isinstance(first, bool):return session.createDataFrame(sparkData, BooleanType())elif (isinstance(sparkData.min(), numbers.Integral) and isinstance(sparkData.max(), numbers.Integral)):if sparkData.min() >= _jvm.Integer.MIN_VALUE and sparkData.max() <= _jvm.Integer.MAX_VALUE:return session.createDataFrame(sparkData, IntegerType())elif sparkData.min() >= _jvm.Long.MIN_VALUE and sparkData.max() <= _jvm.Long.MAX_VALUE:return session.createDataFrame(sparkData, LongType())else:warnings.warn("Maximal or minimal number in RDD is too big to convert to Java. Treating numbers as strings.")return session.createDataFrame(sparkData, StringType())elif isinstance(first, float):## Spark would fail when creating data frame if there is int type in RDD[Float]## Convert explicitly all to floatreturn session.createDataFrame(sparkData.map(lambda x: float(x)), FloatType())else:raise ValueError('Unreachable code')else:return session.createDataFrame(sparkData)
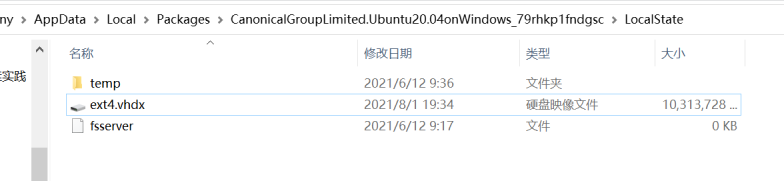
上面的安装,我使用,windows 子系统,还以为 文件可以在系统上找到,结果发现,wsl 现在直接使用了一个虚拟磁盘文件:
wsl 路径:C:\Users\wangyny\AppData\Local\Packages\CanonicalGroupLimited.Ubuntu20.04onWindows_79rhkp1fndgsc\LocalState
典型应用场景
Model Building
A typical example involves multiple data transformations with the help of Spark
API, where a final form of data is transformed into an H2O frame and passed
to an H2O algorithm. The constructed model estimates different metrics based
on the testing data or gives a prediction that can be used in the rest of the
data pipeline (see Figure 1).

Data Munging
Another use-case includes Sparkling Water as a provider of ad-hoc data transformations. Figure 2 shows a data pipeline benefiting from H2O’s parallel
data load and parse capabilities, while Spark API is used as another provider
of data transformations. Furthermore, H2O can be used as an in-place data
transformer.
Stream Processing
The last use-case depicted in Figure 3 introduces two data pipelines. The first
one, called an off-line training pipeline, is invoked regularly (e.g., every hour or
every day), and utilizes both Spark and H2O API. The off-line pipeline provides
an H2O model as output. The H2O API allows the model to be exported in a
form independent on H2O run-time. The second pipeline processes streaming
data (with help of Spark Streaming or Storm) and utilizes the model trained in
the first pipeline to score the incoming data. Since the model is exported with

no run-time dependency on H2O, the streaming pipeline can be lightweight and
independent on H2O or Sparkling Water infrastructure.

Sparkling Water used as an off-line model producer feeding models
into a stream-based data pipeline.
参考文档
H2O Sparkling Water
H2O Sparkling Water documentation
- https://databricks.com/blog/2014/06/30/sparkling-water-h20-spark.html
PySparkling
PySparkling
-
https://github.com/MachineLP/CodeFun/blob/master/05-auto_ml_dl/01-auto_ml/01-%E8%87%AA%E5%8A%A8%E5%8C%96%E7%89%B9%E5%BE%81%E5%B7%A5%E7%A8%8B.md
-
https://bbs.huaweicloud.com/blogs/134113
-
可视化与拖拽式建模
这篇关于autoML 前瞻与实践 ---- H2O Sparkling Water简介的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






