本文主要是介绍【Java】关于ByteArrayOutputStream的源码分析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、问题
1.1、环境
电脑环境:Windows 10;
开发工具:IntelliJ IDEA;
数据库环境:Redis 3.2.100
JDK环境: Jdk1.8;
1.2、问题
ByteArrayOutputStream 是经常用到的字符数组输出流,下面我们就来分析一下该类;JDK 1.8的 ByteArrayOutputStream 源码请见附录;
二、解答
1、概述
ByteArrayOutputStream 实现了OutputStream类,这个缓冲数据,会自动根据写入的数据而增长;数组里的数据还可以通过toByteArray方法来还原成数组或者toString方法来还原成字符串;关闭一个ByteArrayOutputStream是无效的;关闭方法可以在stream被关闭后,再调用
2、具体方法分析:
①、protected byte buf[];
用来缓存数据;
②、 protected int count;
用来统计缓存数据的有效字节数;
③、无参构造
public ByteArrayOutputStream() {this(32);}
创建一个新的字节数组流,如果没有给定ByteArrayOutputStream流的缓存容量,系统默认初始化大小为32;并且这个大小可以在适当情况下增长;
④、
public ByteArrayOutputStream(int size) {if (size < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative initial size: "+ size);}buf = new byte[size];}创建一个新的字节数组输出流,专门声明了字节的容量大小;注意,如果容量小于0(可以等于0),会抛出非法的参数异常:无效的初始化大小,并且显示之前声明的错误字节容量;见下图:
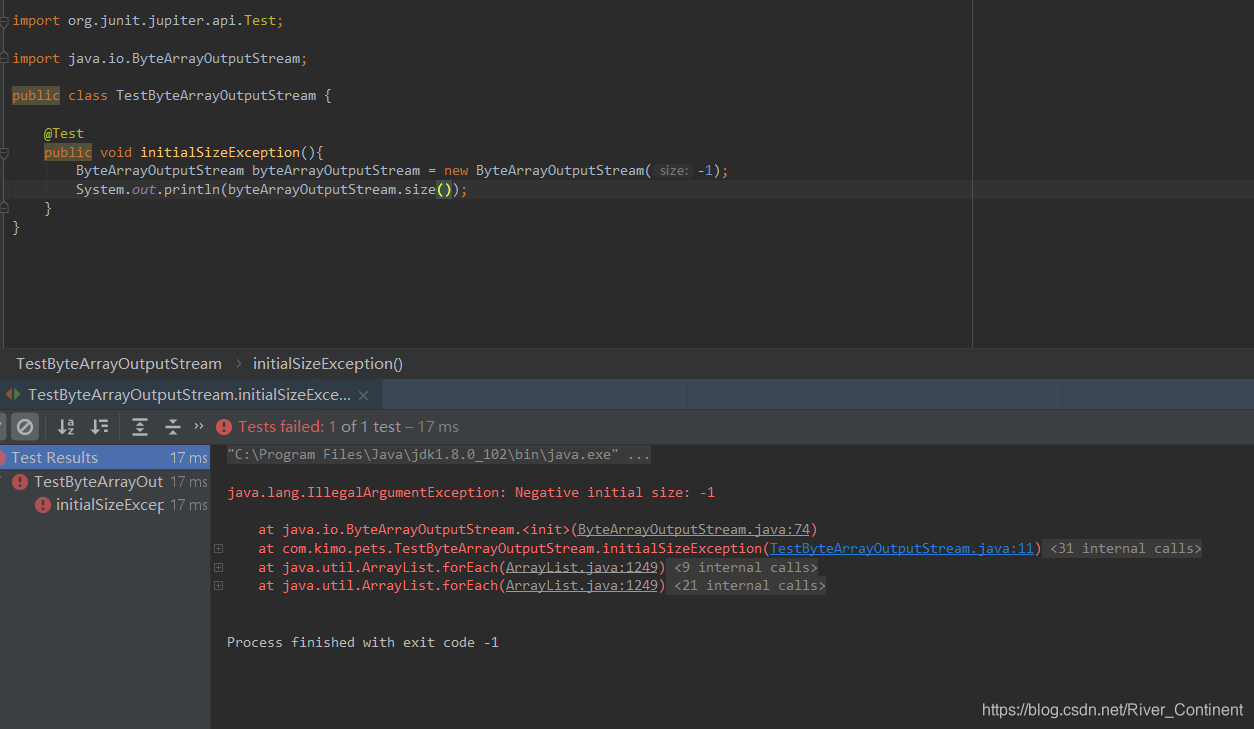
⑤、
private void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {// overflow-conscious codeif (minCapacity - buf.length > 0)grow(minCapacity);}
确保容量;如果必须,【字节数组输出流】会增加容量以容纳其最小的元素个数;minCapacity 是最小容量大小;OutOfMemoryError 是超出存储限制错误;如果minCapacity小于0,则会抛出异常;如果不适用当前最大容量时,则会增加容量;增加的校验机制是:如果最小容量减去元素长度大于0,则会增加容量;
这里怎么理解呢,就是写代码的过程中,如果你不能确定当前【字节数组输出流】的容纳元素大小,或者已经确定不能容纳下,则可以调用该方法来确保可容纳;
⑥、
/*** The maximum size of array to allocate.* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
最大数组容量:Integer封装类的最大值减去8,为啥要减去8呢?因为一些虚拟机会在数组中还原一些头部单词;往往分配的数组回避实际结果大;所以这里减去了8个字节大小;
TODO
⑦、增长规则:
private void grow(int minCapacity) {// overflow-conscious codeint oldCapacity = buf.length;int newCapacity = oldCapacity << 1;if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)newCapacity = minCapacity;if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);buf = Arrays.copyOf(buf, newCapacity);}入参为最小容量,
- 【旧的容量】大小为【字节数组输出流】中元素的长度;
- 【新的容量】大小为:先将【旧的容量】大小进行左位运算,即扩充1倍,变成原来的2倍;
- 如果【新的容量】小于【最小容量】,则将【新的容量】赋值为最小容量;
- 如果【新的容量】大于数组最大容量,则这里会创建一个大容量的数组,并且将原来【字节数组输出流】中的元素复制到新的大容量数组中去;
⑧、创建大容量【字节数组输出流】
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {if (minCapacity < 0) // overflowthrow new OutOfMemoryError();return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?Integer.MAX_VALUE :MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;}
入参为最小容量大小;如果值小于0,则会抛出超出存储错误;
如果入参的最小容量大于最大的数组容量,则该大数组的容量为Integer的最大值;否则就是当前数组的最大容量;
⑨、单个字节写出方法
/*** Writes the specified byte to this byte array output stream.** @param b the byte to be written.*/public synchronized void write(int b) {ensureCapacity(count + 1);buf[count] = (byte) b;count += 1;}
线程同步
入参为int类型的字节;
首先调用ensureCapacity方法,确保容量不会超出存储限制;这里是容量+1,为什么是容量+1呢?因为这个wirte方法时1个字节一个字节写出的;
然后每写出一次,则容量增加1;
⑩、字节数组写出方法;
/*** Writes <code>len</code> bytes from the specified byte array* starting at offset <code>off</code> to this byte array output stream.** @param b the data.* @param off the start offset in the data.* @param len the number of bytes to write.*/public synchronized void write(byte b[], int off, int len) {if ((off < 0) || (off > b.length) || (len < 0) ||((off + len) - b.length > 0)) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();}ensureCapacity(count + len);System.arraycopy(b, off, buf, count, len);count += len;}
入参为数组,开始写出的起始点的下标,写出的数组的长度;
如果【起始点】小于0,或者【起始点】大于入参数组的长度,或者需要写出的数组的长度小于0,则会抛出下标越界的错误;
因为我们要在原来的容量的基础上再写入len长度的元素,所以这里要确保容量安全;调用ensureCapacity()方法;
然后需要调用复制方法,将b数组从b数组的off下标开始,复制len长度到buf数组的末尾,count其实是buf数组最后一个元素后面1个位置的下标;
(11)、copyTo方法
/*** Writes the complete contents of this byte array output stream to* the specified output stream argument, as if by calling the output* stream's write method using <code>out.write(buf, 0, count)</code>.** @param out the output stream to which to write the data.* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.*/public synchronized void writeTo(OutputStream out) throws IOException {out.write(buf, 0, count);}
入参为 OutputStream 输出流;将此【字节数组输出流】写出到一个特定的输出流中,使用了输出流out的write方法;类比管道间水流的接力;或者空中加油机之间接力;
(12)、重置方法
/*** Resets the <code>count</code> field of this byte array output* stream to zero, so that all currently accumulated output in the* output stream is discarded. The output stream can be used again,* reusing the already allocated buffer space.** @see java.io.ByteArrayInputStream#count*/public synchronized void reset() {count = 0;}
将此【字节数组输出流】的长度置为0;因此所有当前的基类的输出流会被丢弃;输出流可以被重新使用;可以重新使用已经被分配的缓存空间;
(13)
/*** Creates a newly allocated byte array. Its size is the current* size of this output stream and the valid contents of the buffer* have been copied into it.** @return the current contents of this output stream, as a byte array.* @see java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream#size()*/public synchronized byte toByteArray()[] {return Arrays.copyOf(buf, count);}
创建一个新分配的byte数组;大小等于当前输出流的大小,并且元素为当前输出流的元素;
14、size()方法
/*** Returns the current size of the buffer.** @return the value of the <code>count</code> field, which is the number* of valid bytes in this output stream.* @see java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream#count*/public synchronized int size() {return count;}
返回当前输出流缓存的元素的个数大小;(注意是同步的)
(15)、toString()方法
/*** Converts the buffer's contents into a string decoding bytes using the* platform's default character set. The length of the new <tt>String</tt>* is a function of the character set, and hence may not be equal to the* size of the buffer.** <p> This method always replaces malformed-input and unmappable-character* sequences with the default replacement string for the platform's* default character set. The {@linkplain java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder}* class should be used when more control over the decoding process is* required.** @return String decoded from the buffer's contents.* @since JDK1.1*/public synchronized String toString() {return new String(buf, 0, count);}
将当前输出流中的内容,使用当前平台默认的编码格式转换成一个string字符串;新的String字符串的的长度取决于编码格式的方法;因此可能并不等于当前缓存的大小;
该方法始终会替换格式输入错误的,根据当前平台默认的编码格式下,不可映射的字符序列为默认的值;
(16)toString()方法
/*** Converts the buffer's contents into a string by decoding the bytes using* the named {@link java.nio.charset.Charset charset}. The length of the new* <tt>String</tt> is a function of the charset, and hence may not be equal* to the length of the byte array.** <p> This method always replaces malformed-input and unmappable-character* sequences with this charset's default replacement string. The {@link* java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder} class should be used when more control* over the decoding process is required.** @param charsetName the name of a supported* {@link java.nio.charset.Charset charset}* @return String decoded from the buffer's contents.* @exception UnsupportedEncodingException* If the named charset is not supported* @since JDK1.1*/public synchronized String toString(String charsetName)throws UnsupportedEncodingException{return new String(buf, 0, count, charsetName);}
入参为编码格式的名字;如果不支持该编码格式,则会抛出:不支持编码异常;
(17)toString 方法
/*** Creates a newly allocated string. Its size is the current size of* the output stream and the valid contents of the buffer have been* copied into it. Each character <i>c</i> in the resulting string is* constructed from the corresponding element <i>b</i> in the byte* array such that:* <blockquote><pre>* c == (char)(((hibyte & 0xff) << 8) | (b & 0xff))* </pre></blockquote>** @deprecated This method does not properly convert bytes into characters.* As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via the* <code>toString(String enc)</code> method, which takes an encoding-name* argument, or the <code>toString()</code> method, which uses the* platform's default character encoding.** @param hibyte the high byte of each resulting Unicode character.* @return the current contents of the output stream, as a string.* @see java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream#size()* @see java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream#toString(String)* @see java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream#toString()*/@Deprecatedpublic synchronized String toString(int hibyte) {return new String(buf, hibyte, 0, count);}
创建一个新分配string字符串;
(18)关闭方法
/*** Closing a <tt>ByteArrayOutputStream</tt> has no effect. The methods in* this class can be called after the stream has been closed without* generating an <tt>IOException</tt>.*/public void close() throws IOException {}
关闭ByteArrayOutputStream是没有效果的;这个类的方法只有当stream被关闭后不再创建才可以被调用;
附录:
/** Copyright (c) 1994, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.* ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.*********************/package java.io;import java.util.Arrays;/*** This class implements an output stream in which the data is* written into a byte array. The buffer automatically grows as data* is written to it.* The data can be retrieved using <code>toByteArray()</code> and* <code>toString()</code>.* <p>* Closing a <tt>ByteArrayOutputStream</tt> has no effect. The methods in* this class can be called after the stream has been closed without* generating an <tt>IOException</tt>.** @author Arthur van Hoff* @since JDK1.0*/public class ByteArrayOutputStream extends OutputStream {/*** The buffer where data is stored.*/protected byte buf[];/*** The number of valid bytes in the buffer.*/protected int count;/*** Creates a new byte array output stream. The buffer capacity is* initially 32 bytes, though its size increases if necessary.*/public ByteArrayOutputStream() {this(32);}/*** Creates a new byte array output stream, with a buffer capacity of* the specified size, in bytes.** @param size the initial size.* @exception IllegalArgumentException if size is negative.*/public ByteArrayOutputStream(int size) {if (size < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative initial size: "+ size);}buf = new byte[size];}/*** Increases the capacity if necessary to ensure that it can hold* at least the number of elements specified by the minimum* capacity argument.** @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity* @throws OutOfMemoryError if {@code minCapacity < 0}. This is* interpreted as a request for the unsatisfiably large capacity* {@code (long) Integer.MAX_VALUE + (minCapacity - Integer.MAX_VALUE)}.*/private void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {// overflow-conscious codeif (minCapacity - buf.length > 0)grow(minCapacity);}/*** The maximum size of array to allocate.* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit*/private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;/*** Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.** @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity*/private void grow(int minCapacity) {// overflow-conscious codeint oldCapacity = buf.length;int newCapacity = oldCapacity << 1;if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)newCapacity = minCapacity;if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);buf = Arrays.copyOf(buf, newCapacity);}private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {if (minCapacity < 0) // overflowthrow new OutOfMemoryError();return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?Integer.MAX_VALUE :MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;}/*** Writes the specified byte to this byte array output stream.** @param b the byte to be written.*/public synchronized void write(int b) {ensureCapacity(count + 1);buf[count] = (byte) b;count += 1;}/*** Writes <code>len</code> bytes from the specified byte array* starting at offset <code>off</code> to this byte array output stream.** @param b the data.* @param off the start offset in the data.* @param len the number of bytes to write.*/public synchronized void write(byte b[], int off, int len) {if ((off < 0) || (off > b.length) || (len < 0) ||((off + len) - b.length > 0)) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();}ensureCapacity(count + len);System.arraycopy(b, off, buf, count, len);count += len;}/*** Writes the complete contents of this byte array output stream to* the specified output stream argument, as if by calling the output* stream's write method using <code>out.write(buf, 0, count)</code>.** @param out the output stream to which to write the data.* @exception IOException if an I/O error occurs.*/public synchronized void writeTo(OutputStream out) throws IOException {out.write(buf, 0, count);}/*** Resets the <code>count</code> field of this byte array output* stream to zero, so that all currently accumulated output in the* output stream is discarded. The output stream can be used again,* reusing the already allocated buffer space.** @see java.io.ByteArrayInputStream#count*/public synchronized void reset() {count = 0;}/*** Creates a newly allocated byte array. Its size is the current* size of this output stream and the valid contents of the buffer* have been copied into it.** @return the current contents of this output stream, as a byte array.* @see java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream#size()*/public synchronized byte toByteArray()[] {return Arrays.copyOf(buf, count);}/*** Returns the current size of the buffer.** @return the value of the <code>count</code> field, which is the number* of valid bytes in this output stream.* @see java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream#count*/public synchronized int size() {return count;}/*** Converts the buffer's contents into a string decoding bytes using the* platform's default character set. The length of the new <tt>String</tt>* is a function of the character set, and hence may not be equal to the* size of the buffer.** <p> This method always replaces malformed-input and unmappable-character* sequences with the default replacement string for the platform's* default character set. The {@linkplain java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder}* class should be used when more control over the decoding process is* required.** @return String decoded from the buffer's contents.* @since JDK1.1*/public synchronized String toString() {return new String(buf, 0, count);}/*** Converts the buffer's contents into a string by decoding the bytes using* the named {@link java.nio.charset.Charset charset}. The length of the new* <tt>String</tt> is a function of the charset, and hence may not be equal* to the length of the byte array.** <p> This method always replaces malformed-input and unmappable-character* sequences with this charset's default replacement string. The {@link* java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder} class should be used when more control* over the decoding process is required.** @param charsetName the name of a supported* {@link java.nio.charset.Charset charset}* @return String decoded from the buffer's contents.* @exception UnsupportedEncodingException* If the named charset is not supported* @since JDK1.1*/public synchronized String toString(String charsetName)throws UnsupportedEncodingException{return new String(buf, 0, count, charsetName);}/*** Creates a newly allocated string. Its size is the current size of* the output stream and the valid contents of the buffer have been* copied into it. Each character <i>c</i> in the resulting string is* constructed from the corresponding element <i>b</i> in the byte* array such that:* <blockquote><pre>* c == (char)(((hibyte & 0xff) << 8) | (b & 0xff))* </pre></blockquote>** @deprecated This method does not properly convert bytes into characters.* As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via the* <code>toString(String enc)</code> method, which takes an encoding-name* argument, or the <code>toString()</code> method, which uses the* platform's default character encoding.** @param hibyte the high byte of each resulting Unicode character.* @return the current contents of the output stream, as a string.* @see java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream#size()* @see java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream#toString(String)* @see java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream#toString()*/@Deprecatedpublic synchronized String toString(int hibyte) {return new String(buf, hibyte, 0, count);}/*** Closing a <tt>ByteArrayOutputStream</tt> has no effect. The methods in* this class can be called after the stream has been closed without* generating an <tt>IOException</tt>.*/public void close() throws IOException {}}完毕~
三、总结
欢迎关注我的
CSDN博客: https://blog.csdn.net/River_Continent
微信公众号:幕桥社区

知乎:张牧野, https://www.zhihu.com/people/zhang-mu-ye-37-76/activities
简书: https://www.jianshu.com/u/02c0096cbfd3
这篇关于【Java】关于ByteArrayOutputStream的源码分析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








