本文主要是介绍Zookeeper官网Java示例代码解读(一),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
2024-08-22
1. 基本信息
-
官网地址:
https://zookeeper.apache.org/doc/r3.8.4/javaExample.html -
示例设计思路
Conventionally, ZooKeeper applications are broken into two units, one which maintains the connection, and the other which monitors data. In this application, the class called the Executor maintains the ZooKeeper connection, and the class called the DataMonitor monitors the data in the ZooKeeper tree. Also, Executor contains the main thread and contains the execution logic. It is responsible for what little user interaction there is, as well as interaction with the executable program you pass in as an argument and which the sample (per the requirements) shuts down and restarts, according to the state of the znode.
- Demo的功能
借助Zookeeper实现分布式环境中的配置文件实时更新
2. 环境准备
- 准备一台虚拟机(也可以在本机启动ZooKeeper)
- 安装ZooKeeper、JDK
- 启动ZooKeeper Server
- 启动客户端,创建znode,用于测试
3. 示例代码
3.1 Executor
package com.agileluo.zookeeperdemo.simple_watch; /** * A simple example program to use DataMonitor to start and * stop executables based on a znode. The program watches the * specified znode and saves the data that corresponds to the * znode in the filesystem. It also starts the specified program * with the specified arguments when the znode exists and kills * the program if the znode goes away. */import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream; import org.apache.zookeeper.KeeperException;
import org.apache.zookeeper.WatchedEvent;
import org.apache.zookeeper.Watcher;
import org.apache.zookeeper.ZooKeeper; public class Executor implements Watcher, Runnable, DataMonitor.DataMonitorListener
{ String znode; DataMonitor dm; ZooKeeper zk; String filename; String exec[]; Process child; static{ System.setProperty("zookeeper.sasl.client", "false"); } public Executor(String hostPort, String znode, String filename, String exec[]) throws KeeperException, IOException { this.filename = filename; this.exec = exec; zk = new ZooKeeper(hostPort, 3000, this); dm = new DataMonitor(zk, znode, null, this); } /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { if (args.length < 4) { System.err .println("USAGE: Executor hostPort znode filename program [args ...]"); System.exit(2); } String hostPort = args[0]; String znode = args[1]; String filename = args[2]; String exec[] = new String[args.length - 3]; System.arraycopy(args, 3, exec, 0, exec.length); try { new Executor(hostPort, znode, filename, exec).run(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /*************************************************************************** * We do process any events ourselves, we just need to forward them on. * * @see org.apache.zookeeper.Watcher #process(org.apache.zookeeper.proto.WatcherEvent) */ public void process(WatchedEvent event) { dm.process(event); } public void run() { try { synchronized (this) { while (!dm.dead) { wait(); } } } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } public void closing(int rc) { synchronized (this) { notifyAll(); } } static class StreamWriter extends Thread { OutputStream os; InputStream is; StreamWriter(InputStream is, OutputStream os) { this.is = is; this.os = os; start(); } public void run() { byte b[] = new byte[80]; int rc; try { while ((rc = is.read(b)) > 0) { os.write(b, 0, rc); } } catch (IOException e) { } } } /** * DataMonitor.DataMonitorListener 接口方法exists()的实现 * @param data */ public void exists(byte[] data) { if (data == null) { //zooKeeper客户端操作(delete /my_test)时触发 if (child != null) { System.out.println("Killing process"); child.destroy(); try { child.waitFor(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } child = null; } else { //zooKeeper客户端操作(set /my_test test_data)时触发 if (child != null) { System.out.println("Stopping child"); child.destroy(); try { child.waitFor(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } try { //将变化的配置写入文件,默认路径为项目源文件的根目录 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(filename); fos.write(data); fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { System.out.println("Starting child"); //从控制台读取命令行,并执行命令 child = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(exec); new StreamWriter(child.getInputStream(), System.out); new StreamWriter(child.getErrorStream(), System.err); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
}
3.2 DataMonitor
package com.agileluo.zookeeperdemo.simple_watch; /** * A simple class that monitors the data and existence of a ZooKeeper * node. It uses asynchronous ZooKeeper APIs. */import java.util.Arrays; import org.apache.zookeeper.KeeperException;
import org.apache.zookeeper.WatchedEvent;
import org.apache.zookeeper.Watcher;
import org.apache.zookeeper.ZooKeeper;
import org.apache.zookeeper.AsyncCallback.StatCallback;
import org.apache.zookeeper.KeeperException.Code;
import org.apache.zookeeper.data.Stat; public class DataMonitor implements Watcher, StatCallback { ZooKeeper zk; String znode; Watcher chainedWatcher; boolean dead; DataMonitorListener listener; byte prevData[]; public DataMonitor(ZooKeeper zk, String znode, Watcher chainedWatcher, DataMonitorListener listener) { this.zk = zk; this.znode = znode; this.chainedWatcher = chainedWatcher; this.listener = listener; // Get things started by checking if the node exists. We are going // to be completely event driven zk.exists(znode, true, this, null); } /** * Other classes use the DataMonitor by implementing this method */ public interface DataMonitorListener { /** * The existence status of the node has changed. */ void exists(byte data[]); /** * The ZooKeeper session is no longer valid. * * @param rc * the ZooKeeper reason code */ void closing(int rc); } public void process(WatchedEvent event) { String path = event.getPath(); if (event.getType() == Event.EventType.None) { // We are are being told that the state of the // connection has changed switch (event.getState()) { case SyncConnected: // In this particular example we don't need to do anything // here - watches are automatically re-registered with // server and any watches triggered while the client was // disconnected will be delivered (in order of course) break; case Expired: // It's all over dead = true; listener.closing(KeeperException.Code.SessionExpired); break; } } else { if (path != null && path.equals(znode)) { // Something has changed on the node, let's find out zk.exists(znode, true, this, null); } } if (chainedWatcher != null) { chainedWatcher.process(event); } } public void processResult(int rc, String path, Object ctx, Stat stat) { boolean exists; switch (rc) { case Code.Ok: exists = true; break; case Code.NoNode: exists = false; break; case Code.SessionExpired: case Code.NoAuth: dead = true; listener.closing(rc); return; default: // Retry errors zk.exists(znode, true, this, null); return; } byte b[] = null; if (exists) { try { b = zk.getData(znode, false, null); } catch (KeeperException e) { // We don't need to worry about recovering now. The watch // callbacks will kick off any exception handling e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { return; } } if ((b == null && b != prevData) || (b != null && !Arrays.equals(prevData, b))) { listener.exists(b); prevData = b; } }
}
4. 测试
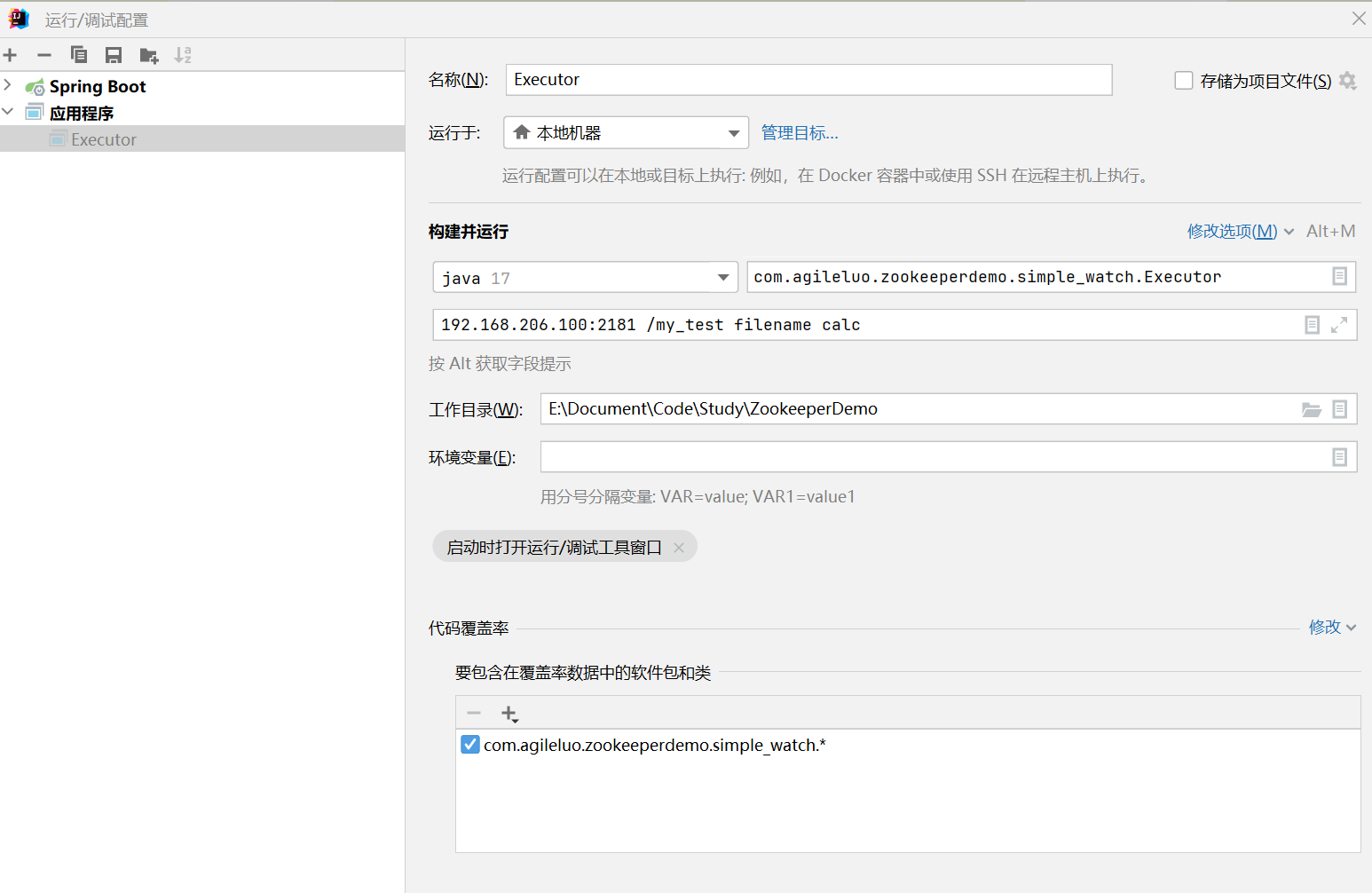
运行Executor,参数传入: 192.168.206.100:2181 /my_test filename calc
其中192.168.206.100:2181为ZooKeeper的访问串;
/my_test 是预先创建的Znode
filename 是变动的Znode数据写入的文件,只保留最后的数据,
calc 指定执行完成后,此例为打开计算器(因为是在Windows下跑,所以可以有cmd,run,calc可以用来做测试)
5 注意点
5.1 防火墙
查看防火墙的状态
systemctl status firewalld.service
firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemonLoaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)Active: active (running) since Tue 2024-08-27 19:41:00 PDT; 2s agoDocs: man:firewalld(1)Main PID: 2967 (firewalld)Tasks: 2CGroup: /system.slice/firewalld.service└─2967 /usr/bin/python2 -Es /usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopid关闭/开启VM的防火墙
systemctl stop|start firewalld.service
5.2 关闭SASL安全验证
Executor类中增加代码:
static{ System.setProperty("zookeeper.sasl.client", "false");
}
这篇关于Zookeeper官网Java示例代码解读(一)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




