本文主要是介绍C.Interface.And.Implementations—table(key-value系统)的实现,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1、An associative table is a set of key-value pairs. It’s like an array except that the indices can be values of any type.
C语言中宏的作用域是文件或者遇到undef为止。
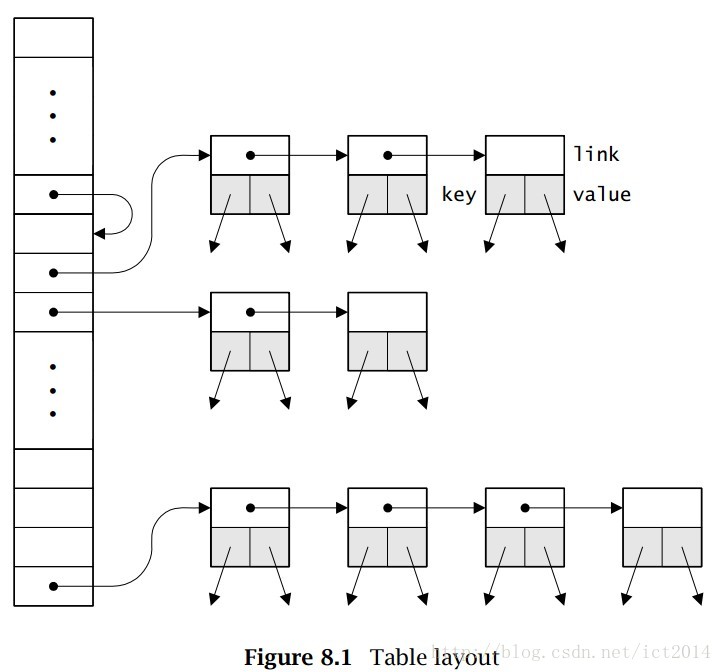
table的实现是以哈希表和链表实现。内存形式如下:
===========================table.h===============================
#ifndef TABLE_INCLUDED
#define TABLE_INCLUDED#define T Table_T
typedef struct T *T;//exported functions
extern T Table_new(int hint, int cmp(const void *x, const void *y),unsigned hash(const void *key));extern void Table_free(T *table);extern int Table_length(T table);
extern void *Table_put (T table, const void *key,void *value);
extern void *Table_get (T table, const void *key);
extern void *Table_remove(T table, const void *key);
extern void Table_map (T table, void apply(const void *key, void **value, void *cl),void *cl);
extern void **Table_toArray(T table, void *end);#undef T
#endif
=========================table.c===============================
#include <limits.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include "mem.h"
#include "assert.h"
#include "table.h"#define T Table_T//types
struct T{//fieldsint size;int (*cmp)(const void *x, const void *y);unsigned (*hash)(const void *key);int length;unsigned timestamp;struct binding{struct binding *link;const void *key;void *value;} **buckets;
};//static functions
static int cmpatom(const void *x, const void *y){return x != y;
}static unsigned hashatom(const void *key){return (unsigned long)key>>2;
}//functions
T Table_new(int hint,int cmp(const void *x, const void *y),unsigned hash(const void *key)){T table;int i;static int primes[] = {509, 509, 1021, 2053, 4093,8191, 16383, 32771, 65521, INT_MAX };assert(hint >= 0);for(i = 1; primes[i] < hint; ++i);table = ALLOC(sizeof(*table) + primes[i-1]*sizeof(table->buckets[0]));table->size = primes[i-1];table->cmp = cmp ? cmp : cmpatom;table->hash = hash ? hash : hashatom;table->buckets = (struct binding **)(table + 1);for(i = 0; i < table->size; ++i)table->buckets[i] = NULL;table->length = 0;table->timestamp = 0;return table;
}void *Table_get(T table, const void *key){int i;struct binding *p;assert(table);assert(key);i = (*table->hash)(key)%table->size;for(p = table->buckets[i]; p; p = p->link){if((*table->cmp)(key,p->key) == 0 )break;}return p ? p->value : NULL;
}void *Table_put(T table, const void *key, void *value){int i;struct binding *p;void *prev;assert(table);assert(key);//search table for keyi = (*table->hash)(key)%table->size;for(p = table->buckets[i]; p; p = p->link){if((*table->cmp)(key,p->key) == 0)break;}if(p == NULL){NEW(p);p->key = key;p->link = table->buckets[i];table->buckets[i] = p;table->length++;prev = NULL;}else{prev = p->value;}p->value = value;table->timestamp++;return prev;
}int Table_length(T table){assert(table);return table->length;
}void Table_map(T table,void apply(const void *key, void **value, void *cl),void *cl){int i;unsigned stamp;struct binding *p;assert(table);assert(apply);stamp = table->timestamp;for(i = 0; i < table->size; ++i){for(p = table->buckets[i]; p; p = p->link){apply(p->key, &p->value, cl);assert(table->timestamp == stamp);}}
}void *Table_remove(T table, const void *key){int i;struct binding **pp;assert(table);assert(key);table->timestamp++;i = (*table->hash)(key)%table->size;for(pp = &table->buckets[i]; *pp; pp = &(*pp)->link){if((*table->cmp)(key, (*pp)->key) == 0){struct binding *p = *pp;void *value = p->value;*pp = p->link;FREE(p);table->length--;return value;}}return NULL;
}void **Table_toArray(T table, void *end){int i, j = 0;void **array;struct binding *p;assert(table);array = ALLOC((2*table->length + 1)*sizeof(*array));for(i = 0; i < table->size; ++i){for(p = table->buckets[i]; p; p = p->link){array[j++] = (void *)p->key;array[j++] = p->value;}}array[j] = end;return array;
}void Table_free(T *table){assert(table && *table);if((*table)->length > 0){int i;struct binding *p, *q;for(i = 0; i < (*table)->size; ++i){for(p = (*table)->buckets[i]; p; p = q){q = p->link;FREE(p);}}}FREE(*table);
}
这篇关于C.Interface.And.Implementations—table(key-value系统)的实现的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!