本文主要是介绍深入浅出mybatis,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
mybatis是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持定制化 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集。MyBatis 可以使用简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原生类型、接口和 Java 的 POJO(Plain Old Java Objects,普通老式 Java 对象)为数据库中的记录。
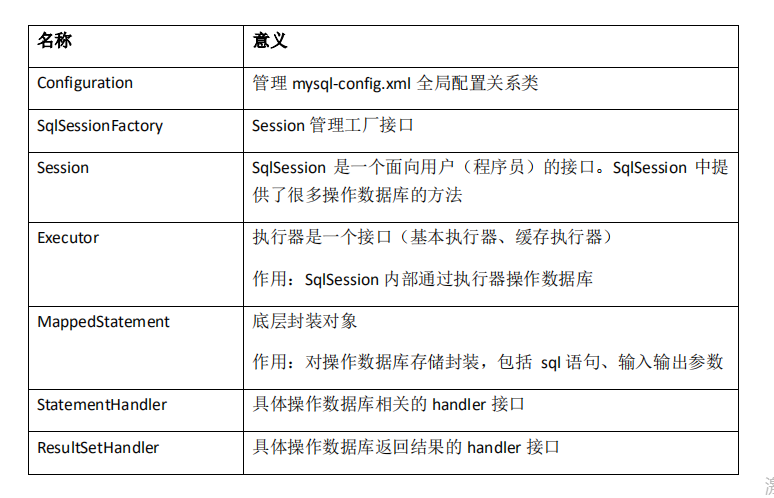
mybatis关键类
通过源码了解mybatis
1 @Slf4j2 public class MybatisTest {3 4 //一级缓存5 @Test6 public void test() throws IOException {7 8 String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";9 InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
10 SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory =new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
11 SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
12 sqlSession.selectOne("com.jiagouedu.mybatis.UserMapper.selectUser",3);
13 //log.info("user1:{}", sqlSession.selectOne("com.jiagouedu.mybatis.UserMapper.selectUser", 3));
14 //log.info("user2:{}", sqlSession.selectOne("com.jiagouedu.mybatis.UserMapper.selectUser", 3));
15 //sqlSession.commit();
16 // log.info("user3:{}", sqlSession.selectOne("com.jiagouedu.mybatis.UserMapper.selectUser", 3));
17 // log.info("user4:{}", sqlSession.selectOne("com.jiagouedu.mybatis.UserMapper.selectUser", 3));
18 }
19 }
我们使用的是常用的xml形式进行配置mybatis相关属性及SQL编写。
mybatis-config.xml
![]()
View Code
![]()
UserMapper.xml
我们先看一下build方法,主要进行构建xml并进行解析parse()方法。
1 public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {2 SqlSessionFactory var5;3 try {4 XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);5 var5 = this.build(parser.parse());6 } catch (Exception var14) {7 throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", var14);8 } finally {9 ErrorContext.instance().reset();
10
11 try {
12 inputStream.close();
13 } catch (IOException var13) {
14 ;
15 }
16
17 }
18
19 return var5;
20 }
我们再来看一下parser.parse()方法
1 public Configuration parse() {
2 if (this.parsed) {
3 throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
4 } else {
5 this.parsed = true;
6 this.parseConfiguration(this.parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
7 return this.configuration;
8 }
9 }
this.parser.evalNode("/configuration")大家应该猜到它是在找xml文件中的configuration节点,如果不确认大家可以进到this.parseConfiguration方法看一下
1 private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {2 try {3 this.propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));4 Properties settings = this.settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));5 this.loadCustomVfs(settings);6 this.typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));7 this.pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));8 this.objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));9 this.objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
10 this.reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
11 this.settingsElement(settings);
12 this.environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
13 this.databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
14 this.typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
15 this.mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
16 } catch (Exception var3) {
17 throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + var3, var3);
18 }
19 }
properties、settings、typeAliases。。。。这些属性大家都知道怎么去配置吧,所以受builder方法主要就是进行xml文件的读取并加载到内存当中。
解析完第一步的源码后,然后进行我们的第二步sqlSessionFactory.openSession()的源码,看看它做了哪些工作?
1 private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {2 Transaction tx = null;3 4 DefaultSqlSession var8;5 try {6 Environment environment = this.configuration.getEnvironment();7 TransactionFactory transactionFactory = this.getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);8 tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);9 Executor executor = this.configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
10 var8 = new DefaultSqlSession(this.configuration, executor, autoCommit);
11 } catch (Exception var12) {
12 this.closeTransaction(tx);
13 throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + var12, var12);
14 } finally {
15 ErrorContext.instance().reset();
16 }
17
18 return var8;
19 }
new DefaultSqlSession(this.configuration, executor, autoCommit);这是关键的一步,前面就是取我们xml中的配置并开启数据库事务。最后返回我们的sqlsession。
我们再看一下第三步,就是我们sqlSession.selectOne("com.jiagouedu.mybatis.UserMapper.selectUser",3);取数据的那句,
1 public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {2 List<T> list = this.selectList(statement, parameter);3 if (list.size() == 1) {4 return list.get(0);5 } else if (list.size() > 1) {6 throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());7 } else {8 return null;9 }
10 }
1 public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {2 List var5;3 try {4 MappedStatement ms = this.configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);5 var5 = this.executor.query(ms, this.wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);6 } catch (Exception var9) {7 throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + var9, var9);8 } finally {9 ErrorContext.instance().reset();
10 }
11
12 return var5;
13 }
this.configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);主要就是取出我们写的mapper。xml对象,以便后续进行sql拼写等操作。
this.executor.query(ms, this.wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);这个操作比较多,我们还是直接看源码
1 public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
2 BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
3 CacheKey key = this.createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
4 return this.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
5 }
boundSql 就是下列对象,大家肯定不陌生就是我们自己写的SQL,并且参数它也拿到了。

this.createCacheKey方法比较厉害,我们还是看源码
1 public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {2 if (this.closed) {3 throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");4 } else {5 CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey();6 cacheKey.update(ms.getId());7 cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset());8 cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit());9 cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql());
10 List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
11 TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = ms.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry();
12 Iterator var8 = parameterMappings.iterator();
13
14 while(var8.hasNext()) {
15 ParameterMapping parameterMapping = (ParameterMapping)var8.next();
16 if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
17 String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
18 Object value;
19 if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
20 value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
21 } else if (parameterObject == null) {
22 value = null;
23 } else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
24 value = parameterObject;
25 } else {
26 MetaObject metaObject = this.configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
27 value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
28 }
29
30 cacheKey.update(value);
31 }
32 }
33
34 if (this.configuration.getEnvironment() != null) {
35 cacheKey.update(this.configuration.getEnvironment().getId());
36 }
37
38 return cacheKey;
39 }
40 }
cacheKey.update(ms.getId());cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset());cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit());cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql()); 这就是大家所说的mybatis的一级缓存,用的是id+offset+limit+sql组合的key,然后我们在看this.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);方法
1 public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {2 Cache cache = ms.getCache();3 if (cache != null) {4 this.flushCacheIfRequired(ms);5 if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {6 this.ensureNoOutParams(ms, parameterObject, boundSql);7 List<E> list = (List)this.tcm.getObject(cache, key);8 if (list == null) {9 list = this.delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
10 this.tcm.putObject(cache, key, list);
11 }
12
13 return list;
14 }
15 }
16
17 return this.delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
18 }
我们看到,执行sql之前他会先查看缓存中是否有数据,如果有数据将会直接将缓存中的数据返回,如果没有将执行SQL,执行完SQL之后将会再次放入以及缓存当中,我们看一下源码是不是这样做的
1 public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {2 ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());3 if (this.closed) {4 throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");5 } else {6 if (this.queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {7 this.clearLocalCache();8 }9
10 List list;
11 try {
12 ++this.queryStack;
13 list = resultHandler == null ? (List)this.localCache.getObject(key) : null;
14 if (list != null) {
15 this.handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
16 } else {
17 list = this.queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
18 }
19 } finally {
20 --this.queryStack;
21 }
22
23 if (this.queryStack == 0) {
24 Iterator var8 = this.deferredLoads.iterator();
25
26 while(var8.hasNext()) {
27 BaseExecutor.DeferredLoad deferredLoad = (BaseExecutor.DeferredLoad)var8.next();
28 deferredLoad.load();
29 }
30
31 this.deferredLoads.clear();
32 if (this.configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
33 this.clearLocalCache();
34 }
35 }
36
37 return list;
38 }
39 }
我们再看看this.queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
1 private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {2 this.localCache.putObject(key, ExecutionPlaceholder.EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);3 4 List list;5 try {6 list = this.doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);7 } finally {8 this.localCache.removeObject(key);9 }
10
11 this.localCache.putObject(key, list);
12 if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
13 this.localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
14 }
15
16 return list;
17 }
正如我们想的那样,他就是在查询完之后走的缓存存放,以便下次重新查询的时候提高效率,就不用再次查询数据库,来减少数据库压力。
ps:关注一下本人公众号,每周都有新更新哦!
这篇关于深入浅出mybatis的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



