本文主要是介绍Linux-笔记 全志平台镜像中添加git提交号,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
引言
通过在镜像中某个位置添加git提交号,可以方便排查与追溯是哪个提交编译出来的。 这里使用的全志T113平台,SDK为Tina5.0。
实现的办法有:
1、内核/proc/cpuinfo的打印信息及设备树中查看提交号
2、从设备树查看提交号
3、从uboot启动版本号查看提交号
实现:
内核/proc/cpuinfo查看提交号
1、添加打印函数
前面说到可以通过cpuinfo去查看git提交号,cpuinfo的实现函数位于 <SDK>/kernel/linux-5.4/arch/arm/kernel/setup.c 中的c_show函数,我们想要打印的信息可以放到函数里面去,如下图所示,添加了一行打印提交号。
static int c_show(struct seq_file *m, void *v)
{ char mac_eth[20] = {0};char name[20] = {0};int i, j;u32 cpuid;seq_printf(m, "Version: %s\n", GIT_COMMIT_INFO); // 打印提交号for_each_online_cpu(i) {//省略}get_custom_mac_address(1, name, mac_eth);seq_printf(m, "Hardware\t: %s\n", machine_name);seq_printf(m, "Revision\t: %04x\n", system_rev);seq_printf(m, "Serial\t\t: %s\n", tqserialnum);seq_printf(m, "Mac\t\t: %s\n", macnum);return 0;
}GIT_COMMIT_INFO是一个宏,使用宏的原因是因为如果一直有新的提交,那这个提交号就需要修改,源码修改了必定会产生新的提交和提交号,就会一直无法对应提交号,将宏定义在一个被git忽略的头文件内,编译就自动获取提交号并生成头文件以解决问题。
2、获取提交号
git提交号是在<sdk>/kernel/linux-5.4/scriptsscripts/setlocalversion中获取的,由顶层makefile调用,生成内核版本号,我们可以利用源码脚本来实现我们的目的,该函数会判断是否使用git进行版本控制,如果是会输出提交号,反之为空,我们主要关注脚本内的scm_version()函数即可。
scm_version()
{local shortshort=falsecd "$srctree"if test -e .scmversion; thencat .scmversionreturnfiif test "$1" = "--short"; thenshort=truefi# Check for git and a git repo.if test -z "$(git rev-parse --show-cdup 2>/dev/null)" &&head=`git rev-parse --verify --short HEAD 2>/dev/null`; thenif [ -n "$android_release" ] && [ -n "$kmi_generation" ]; thenprintf '%s' "-$android_release-$kmi_generation"fi# If we are at a tagged commit (like "v2.6.30-rc6"), we ignore# it, because this version is defined in the top level Makefile.if [ -z "`git describe --exact-match 2>/dev/null`" ]; then# If only the short version is requested, don't bother# running further git commandsif $short; thenecho "+"returnfi# If we are past a tagged commit (like# "v2.6.30-rc5-302-g72357d5"), we pretty print it.if atag="`git describe 2>/dev/null`"; thenecho "$atag" | awk -F- '{printf("-%05d-%s", $(NF-1),$(NF))}'# If we don't have a tag at all we print -g{commitish}.elseprintf '%s%s' -g $headfifi# Is this git on svn?if git config --get svn-remote.svn.url >/dev/null; thenprintf -- '-svn%s' "`git svn find-rev $head`"fi# Check for uncommitted changes.# First, with git-status, but --no-optional-locks is only# supported in git >= 2.14, so fall back to git-diff-index if# it fails. Note that git-diff-index does not refresh the# index, so it may give misleading results. See# git-update-index(1), git-diff-index(1), and git-status(1).if {git --no-optional-locks status -uno --porcelain 2>/dev/null ||git diff-index --name-only HEAD} | grep -qvE '^(.. )?scripts/package'; thenprintf '%s' -dirtyfi# All done with gitreturnfi# Check for mercurial and a mercurial repo.if test -d .hg && hgid=`hg id 2>/dev/null`; then# Do we have an tagged version? If so, latesttagdistance == 1if [ "`hg log -r . --template '{latesttagdistance}'`" = "1" ]; thenid=`hg log -r . --template '{latesttag}'`printf '%s%s' -hg "$id"elsetag=`printf '%s' "$hgid" | cut -d' ' -f2`if [ -z "$tag" -o "$tag" = tip ]; thenid=`printf '%s' "$hgid" | sed 's/[+ ].*//'`printf '%s%s' -hg "$id"fifi# Are there uncommitted changes?# These are represented by + after the changeset id.case "$hgid" in*+|*+\ *) printf '%s' -dirty ;;esac# All done with mercurialreturnfi# Check for svn and a svn repo.if rev=`LANG= LC_ALL= LC_MESSAGES=C svn info 2>/dev/null | grep '^Last Changed Rev'`; thenrev=`echo $rev | awk '{print $NF}'`printf -- '-svn%s' "$rev"# All done with svnreturnfi
}
可以看到函数内其实最关键是”git rev-parse --verify --short HEAD“这条命令,它可以直接获取提交号。
但是为了能够做其他处理,我们不修改源码,新建一个scripts/scm_version.sh脚本文件,把整个函数复制进去,并添加一些脚本用于获取提交号并做相应的处理,给出完整脚本:
#!/bin/bashINFO_DIR=../../../../kernel/linux-5.4/include/dt-bindings/cpuinfo.lstscm_version()
{local shortshort=falsecd "$srctree"if test -e .scmversion; thencat .scmversion returnfiif test "$1" = "--short"; thenshort=truefi# Check for git and a git repo.if head=`git rev-parse --verify --short HEAD 2>/dev/null`; thenif [ -n "$android_release" ] && [ -n "$kmi_generation" ]; thenprintf '%s' "-$android_release-$kmi_generation"fi# If we are at a tagged commit (like "v2.6.30-rc6"), we ignore# it, because this version is defined in the top level Makefile.if [ -z "`git describe --exact-match 2>/dev/null`" ]; then# If only the short version is requested, don't bother# running further git commandsif $short; then# echo "+"returnfi# If we are past a tagged commit (like# "v2.6.30-rc5-302-g72357d5"), we pretty print it.if atag="`git describe 2>/dev/null`"; thenecho "$atag" | awk -F- '{printf("-%05d-%s", $(NF-1),$(NF))}'# If we don't have a tag at all we print -g{commitish}.elseprintf '%s%s' -g $headfifi# Is this git on svn?if git config --get svn-remote.svn.url >/dev/null; thenprintf -- '-svn%s' "`git svn find-rev $head`"fi# Check for uncommitted changes.# First, with git-status, but --no-optional-locks is only# supported in git >= 2.14, so fall back to git-diff-index if# it fails. Note that git-diff-index does not refresh the# index, so it may give misleading results. See# git-update-index(1), git-diff-index(1), and git-status(1).if {git --no-optional-locks status -uno --porcelain 2>/dev/null ||git diff-index --name-only HEAD} | read dummy; thenprintf '%s' -dirtyfi# All done with gitreturnfi# Check for mercurial and a mercurial repo.if test -d .hg && hgid=`hg id 2>/dev/null`; then# Do we have an tagged version? If so, latesttagdistance == 1if [ "`hg log -r . --template '{latesttagdistance}'`" = "1" ]; thenid=`hg log -r . --template '{latesttag}'`printf '%s%s' -hg "$id"elsetag=`printf '%s' "$hgid" | cut -d' ' -f2`if [ -z "$tag" -o "$tag" = tip ]; thenid=`printf '%s' "$hgid" | sed 's/[+ ].*//'`printf '%s%s' -hg "$id"fifi# Are there uncommitted changes?# These are represented by + after the changeset id.case "$hgid" in*+|*+\ *) printf '%s' -dirty ;;esac# All done with mercurialreturnfi# Check for svn and a svn repo.if rev=`LANG= LC_ALL= LC_MESSAGES=C svn info 2>/dev/null | grep '^Last Changed Rev'`; thenrev=`echo $rev | awk '{print $NF}'`printf -- '-svn%s' "$rev"# All done with svnreturnfi
}commit_info="$(scm_version)"
if test -z "${commit_info}" ; then
cat <<EOM >${INFO_DIR}
#define GIT_COMMIT_INFO "null"
EOMelse
cat <<EOM >${INFO_DIR}
#define GIT_COMMIT_INFO "${commit_info}"
EOM
fi解析:
这里做了两处修改,一是原本判断用户必须保证执行编译时环境路径处于仓库的根目录下。这句if判断其实只需要帮我确认内核源码存在于git仓库下即可,所以去掉第一个条件。
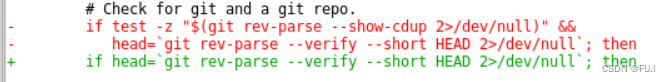
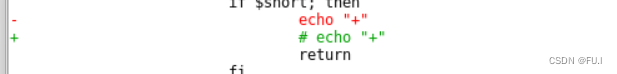
二是+号是我们不要的
//这里主要定义生成的提交号文件路径,使用头文件用*.lst做后缀是默认git会忽略这个后缀的文件,如果没有忽略就自行加入忽略文件即可
INFO_DIR=../../../../kernel/linux-5.4/include/dt-bindings/cpuinfo.lst//获取提交号
commit_info="$(scm_version)"//这行代码使用了cat命令结合<<和一个标记(这里是EOM,可自定义)来创建一个临时的文件输出,然后重定向到${INFO_DIR}指定的文件中。这种方式可以让你在脚本中直接写入多行文本。
//简单说就是将#define GIT_COMMIT_INFO "$(scm_version)"写入到指定的文件${INFO_DIR}中
if test -z "${commit_info}" ; then
cat <<EOM >${INFO_DIR}
#define GIT_COMMIT_INFO "null"
EOMelse
cat <<EOM >${INFO_DIR}
#define GIT_COMMIT_INFO "${commit_info}"
EOM
fi然后我们在源码的setlocalversion脚本最后添加执行我们的新创建脚本即可,内核编译会执行到我们自己创建的脚本。
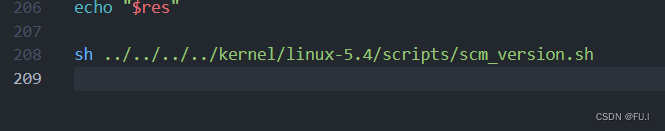
最后还要在setup.c中添加提交号重定向的文件。

3、验证:

从设备树查看提交号
1、修改设备树,添加提交号, 并引入提交号重定向文件。
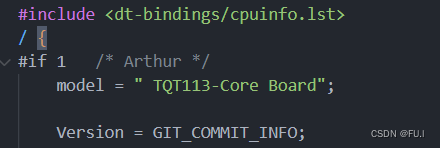
2、验证 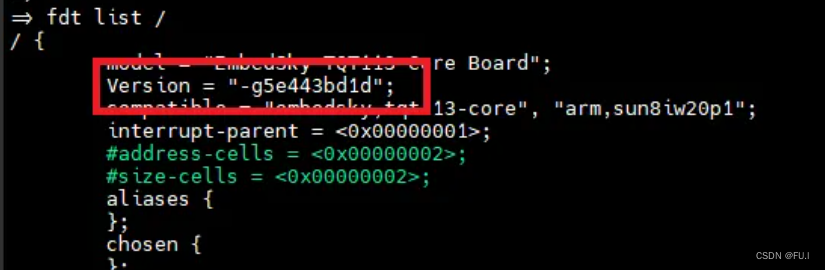
uboot版本号获取提交号
1、uboot设置:
CONFIG_LOCALVERSION_AUTO=y可以用命令:make ubootrelease验证一下,如果没有就要完善一下脚本,见下。
2、完善<sdk>/brandy/brandy-2.0/u-boot-2018/scripts/setlocalversion脚本,完整版如下:
scm_version()
{local shortshort=falsecd "$srctree"if test -e .scmversion; thencat .scmversionreturnfiif test "$1" = "--short"; thenshort=truefi# Check for git and a git repo.if head=`git rev-parse --verify --short HEAD 2>/dev/null`; then# If we are at a tagged commit (like "v2.6.30-rc6"), we ignore# it, because this version is defined in the top level Makefile.if [ -z "`git describe --exact-match 2>/dev/null`" ]; then# If only the short version is requested, don't bother# running further git commandsif $short; then# echo "+"returnfi# If we are past a tagged commit (like# "v2.6.30-rc5-302-g72357d5"), we pretty print it.if atag="`git describe 2>/dev/null`"; thenecho "$atag" | awk -F- '{printf("-%05d-%s", $(NF-1),$(NF))}'# If we don't have a tag at all we print -g{commitish}.elseprintf '%s%s' -g $headfielseprintf '%s%s' -g $headfi# Is this git on svn?if git config --get svn-remote.svn.url >/dev/null; thenprintf -- '-svn%s' "`git svn find-rev $head`"fi# Check for uncommitted changesif {git --no-optional-locks status -uno --porcelain 2>/dev/null ||git diff-index --name-only HEAD} | grep -qvE '^(.. )?scripts/package'; thenprintf '%s' -dirtyfi# All done with gitreturnfi# Check for mercurial and a mercurial repo.if test -d .hg && hgid=`hg id 2>/dev/null`; then# Do we have an tagged version? If so, latesttagdistance == 1if [ "`hg log -r . --template '{latesttagdistance}'`" == "1" ]; thenid=`hg log -r . --template '{latesttag}'`printf '%s%s' -hg "$id"elsetag=`printf '%s' "$hgid" | cut -d' ' -f2`if [ -z "$tag" -o "$tag" = tip ]; thenid=`printf '%s' "$hgid" | sed 's/[+ ].*//'`printf '%s%s' -hg "$id"fifi# Are there uncommitted changes?# These are represented by + after the changeset id.case "$hgid" in*+|*+\ *) printf '%s' -dirty ;;esac# All done with mercurialreturnfi# Check for svn and a svn repo.if rev=`LANG= LC_ALL= LC_MESSAGES=C svn info 2>/dev/null | grep '^Last Changed Rev'`; thenrev=`echo $rev | awk '{print $NF}'`printf -- '-svn%s' "$rev"# All done with svnreturnfi
}验证:

这篇关于Linux-笔记 全志平台镜像中添加git提交号的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







