本文主要是介绍ioctl.h 分析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
ioctl.h 分析
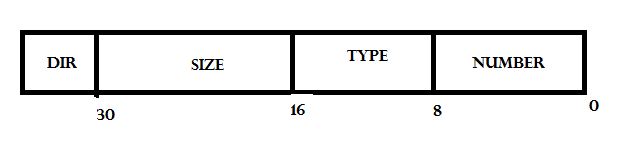
我自己画了个解析图。。。不要嫌弃丑啊。。。哈哈
type
The magic number. Just choose one number (after consultingioctl-number.txt ) and use it throughout the driver. This field is eight bits wide (_IOC_TYPEBITS).
number.
The ordinal (sequential) number. It’s eight bits ( _IOC_NRBITS) wide.
direction
The direction of data transfer,if the particular command involves a data transfer. The possible values are _IOC_NONE (no data transfer), _IOC_READ, _IOC_WRITE, and _IOC_READ|_IOC_WRITE(data is transferred both ways). Data transfer is seen from the application’s point of view; _IOC_READ means reading from the device, so the driver must write to user space. Note that the field is a bitmask,so _IOC_ READ and _IOC_WRITE can be extracted using a logical AND operation.
size
The size of user data involved.The width of this field is architecture dependent, but is usually 13 or 14 bits.You can find its value for your specific architecture in the macro _IOC_SIZEBITS. It’s not mandatory that you use the size field—the kernel does not check it—but it is a goodidea.Proper use of this field can help detect user-space programming errors and enable you to implement backward compatibility if you ever need to change the size of the relevant data item. If you need larger data structures, however,you can just ignore the size field. We’ll see how this field is used soon.
#ifndef _UAPI_ASM_GENERIC_IOCTL_H
#define _UAPI_ASM_GENERIC_IOCTL_H/* ioctl command encoding: 32 bits total, command in lower 16 bits,* size of the parameter structure in the lower 14 bits of the* upper 16 bits.* Encoding the size of the parameter structure in the ioctl request* is useful for catching programs compiled with old versions* and to avoid overwriting user space outside the user buffer area.* The highest 2 bits are reserved for indicating the ``access mode''.* NOTE: This limits the max parameter size to 16kB -1 !*//** The following is for compatibility across the various Linux* platforms. The generic ioctl numbering scheme doesn't really enforce* a type field. De facto, however, the top 8 bits of the lower 16* bits are indeed used as a type field, so we might just as well make* this explicit here. Please be sure to use the decoding macros* below from now on.*/
#define _IOC_NRBITS 8
#define _IOC_TYPEBITS 8/** Let any architecture override either of the following before* including this file.*/#ifndef _IOC_SIZEBITS
# define _IOC_SIZEBITS 14
#endif#ifndef _IOC_DIRBITS
# define _IOC_DIRBITS 2
#endif#define _IOC_NRMASK ((1 << _IOC_NRBITS)-1) //0xff
#define _IOC_TYPEMASK ((1 << _IOC_TYPEBITS)-1) //0xff
#define _IOC_SIZEMASK ((1 << _IOC_SIZEBITS)-1) //0x3fff
#define _IOC_DIRMASK ((1 << _IOC_DIRBITS)-1) //0x3/*这部分是NR TYPE SIZE DIR 段在32bit数据中储存位置相对于起始0位置的偏移量*/
#define _IOC_NRSHIFT 0
#define _IOC_TYPESHIFT (_IOC_NRSHIFT+_IOC_NRBITS) //0x8
#define _IOC_SIZESHIFT (_IOC_TYPESHIFT+_IOC_TYPEBITS)//0x10
#define _IOC_DIRSHIFT (_IOC_SIZESHIFT+_IOC_SIZEBITS)//0x1E/** Direction bits, which any architecture can choose to override* before including this file.*/
/*io 读写权限宏*/
#ifndef _IOC_NONE
# define _IOC_NONE 0U
#endif#ifndef _IOC_WRITE
# define _IOC_WRITE 1U
#endif#ifndef _IOC_READ
# define _IOC_READ 2U
#endif/*_IOC 适用于将dir, type nr size 这四个信息合成到一个32bit的数据中*/
#define _IOC(dir,type,nr,size) \(((dir) << _IOC_DIRSHIFT) | \((type) << _IOC_TYPESHIFT) | \((nr) << _IOC_NRSHIFT) | \((size) << _IOC_SIZESHIFT))#ifndef __KERNEL__
#define _IOC_TYPECHECK(t) (sizeof(t))
#endif/* used to create numbers */
#define _IO(type,nr) _IOC(_IOC_NONE,(type),(nr),0)
#define _IOR(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_READ,(type),(nr),(_IOC_TYPECHECK(size)))
#define _IOW(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_WRITE,(type),(nr),(_IOC_TYPECHECK(size)))
#define _IOWR(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_READ|_IOC_WRITE,(type),(nr),(_IOC_TYPECHECK(size)))/*一下三个BAD结尾的宏定义我也没看明白为什么最后一个参数是sizeof(size) 就得跟一个BAD*/
#define _IOR_BAD(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_READ,(type),(nr),sizeof(size))
#define _IOW_BAD(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_WRITE,(type),(nr),sizeof(size))
#define _IOWR_BAD(type,nr,size) _IOC(_IOC_READ|_IOC_WRITE,(type),(nr),sizeof(size))/* used to decode ioctl numbers.. *//*从32bit的数据中解码出DIR TYPE NR SIZE,很简单没啥讲的*/
#define _IOC_DIR(nr) (((nr) >> _IOC_DIRSHIFT) & _IOC_DIRMASK)
#define _IOC_TYPE(nr) (((nr) >> _IOC_TYPESHIFT) & _IOC_TYPEMASK)
#define _IOC_NR(nr) (((nr) >> _IOC_NRSHIFT) & _IOC_NRMASK)
#define _IOC_SIZE(nr) (((nr) >> _IOC_SIZESHIFT) & _IOC_SIZEMASK)/* ...and for the drivers/sound files... */#define IOC_IN (_IOC_WRITE << _IOC_DIRSHIFT)
#define IOC_OUT (_IOC_READ << _IOC_DIRSHIFT)
#define IOC_INOUT ((_IOC_WRITE|_IOC_READ) << _IOC_DIRSHIFT)
#define IOCSIZE_MASK (_IOC_SIZEMASK << _IOC_SIZESHIFT)
#define IOCSIZE_SHIFT (_IOC_SIZESHIFT)#endif /* _UAPI_ASM_GENERIC_IOCTL_H */

这篇关于ioctl.h 分析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!