本文主要是介绍C++ 享元模式 (FlyWeight Pattern),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
//UtilTool.h
//工具头文件
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
//UObject.h
//根基类,本想多写一些东西的,奈何时间不允许#include "UtilTool.h"
class UObject
{
public :
UObject(string name, string Description) :Name(name), Description(Description) { Id += 1; };
static long long GetId();
string GetName();
string GetDescription();
bool SetName(string name);
bool SetDescription(string des);
inline void ShowUObject()
{
cout <<"<--Id-->"<<Id<< "<--Name-->" << Name << "," << "<--Description-->" << Description <<endl;
}
private:
static long long Id;
string Name;
string Description;
};
//Texture.h
#include "UObject.h"
class Texture:UObject
{
public:
Texture(int width =1024, int height =1024) :UObject(NULL, NULL),mWidth(width),mHeight(height) {};
Texture(string name, string des, int width, int height) :UObject(name,des),mWidth(width),mHeight(height){}
int mWidth;
int mHeight;
inline void ShowTexture()
{
UObject::ShowUObject();
cout << "<--mWidth-->" << mWidth << "<--mHeight-->" << mHeight << endl;
}
}
//Mesh.h
#include "UObject.h"
class Mesh:UObject
{
public:
Mesh(string anim=NULL,string skt=NULL):UObject(NULL,NULL),Animation(anim),Skeleton(skt){};
Mesh(string name, string des, string anim, string skeleton):UObject(name,des),Animation(anim),Skeleton(skeleton){};
string Animation;
string Skeleton;
inline void ShowMesh()
{
UObject::ShowUObject();
cout << "<--Animation-->" << Animation << "<--Skeleton-->" << Skeleton << endl;
}
};
//RootTree.h
#include "UObject.h"
#include "Mesh.h"
#include "Texture.h"
#include "ResourceFactory.h"
class RootTree:UObject
{
public:
RootTree(string name,string des):UObject(name,des)
{
if(name.length()!=0)
mTreeMesh = ResourceFactory::GetMesh(name);
mTreeTexture = ResourceFactory::GetTexture(name);
}
void ShowRootTree();
private:
Mesh* mTreeMesh;
Texture* mTreeTexture;
};
//ResourceFactory.h
#include "UtilTool.h"
class Mesh;
class Texture;
typedef pair<string, Mesh> PairMesh;
typedef pair<string, Texture> PairTexture;
class ResourceFactory
{
private:
static map<string, Mesh> *mMapMeshs;
static map<string, Texture>*mMapTextrues;
~ResourceFactory() { if(mMapMeshs!=NULL)delete mMapMeshs;if(mMapTextrues!=NULL) delete mMapTextrues; }
public:
static Mesh* GetMesh(const string& name);
static Texture* GetTexture(const string& name);
};
//UObject.cpp
#include "UObject.h"
long long UObject::Id = 0;
long long UObject::GetId()
{
return Id;
}
string UObject::GetName()
{
return Name;
}
string UObject::GetDescription()
{
return Description;
}
bool UObject::SetName(string name)
{
Name = name;
return true;
}
bool UObject::SetDescription(string des)
{
Description = des;
return true;
}
//RootTree.cpp
#include "RootTree.h"
void RootTree::ShowRootTree()
{
if (!RootTree::UObject::GetName().empty())
cout << "RootTree :" <<RootTree::UObject::GetName()<< "====================" << endl;
if(mTreeMesh!=NULL)
mTreeMesh->ShowMesh();
if(mTreeTexture!=NULL)
mTreeTexture->ShowTexture();
}
//ResourceFactory.cpp
#include "UtilTool.h"
#include "Mesh.h"
#include "Texture.h"
#include "ResourceFactory.h"
#include "UObject.h"
map<string, Mesh>* ResourceFactory::mMapMeshs = new map<string, Mesh>();
map<string, Texture>* ResourceFactory::mMapTextrues = new map<string, Texture>();
Mesh* ResourceFactory::GetMesh(const string& name)
{
map<string, Mesh>::iterator itor;
itor = (*mMapMeshs).find(name);
if (itor != mMapMeshs->end())
{
return &itor->second;
}
else
{
Mesh* mesh = new Mesh("Mesh 0"+to_string(UObject::GetId()),"This is "+to_string(UObject::GetId())+"th Mesh","Basic Anim","root");
mMapMeshs->insert(PairMesh(name,*mesh));
return mesh;
}
}
Texture* ResourceFactory::GetTexture(const string& name)
{
map<string, Texture>::iterator itor;
itor = mMapTextrues->find(name);
if (itor != mMapTextrues->end())
{
return &itor->second;
}
else
{
Texture* texture = new Texture("Texture 0" +to_string(UObject::GetId()), "This is " + to_string(UObject::GetId()) + "th Mesh", 1024,1024);
mMapTextrues->insert(PairTexture(name,*texture));
return texture;
}
}
//test .cpp
#include "RootTree.h"
int main()
{
string firstTree("aspen");
string firstTreeDes("Populustremula");
RootTree rt1(firstTree,firstTreeDes);
rt1.ShowRootTree();
string SecondTree("peach");
string SecondTreeDes("Eattingquickly");
RootTree rt2(SecondTree,SecondTreeDes);
string ThirdTreeDes("shsodf");
string ThirdTree("banana");
RootTree rt3(ThirdTree,ThirdTreeDes);
string FourthTree("aspen");
string FourthTreeDec("dfasdfa");
RootTree rt4(FourthTree,FourthTreeDec);
rt2.ShowRootTree();
rt3.ShowRootTree();
rt4.ShowRootTree();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
项目目录结构:
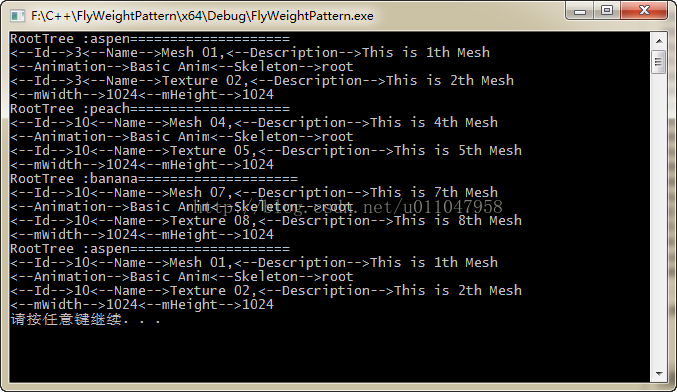
执行结果:
这篇关于C++ 享元模式 (FlyWeight Pattern)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!