本文主要是介绍基于多模态MRI中深层语义和边缘信息融合的脑肿瘤分割 | 文献速递-深度学习肿瘤自动分割,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Title
题目
Brain tumor segmentation based on the fusion of deep semantics and edge information in multimodal MRI
基于多模态MRI中深层语义和边缘信息融合的脑肿瘤分割
01
文献速递介绍
医学图像分割是医学图像处理领域的重要课题。其中,脑肿瘤分割旨在从图像中定位多种类型的肿瘤区域,对临床实践具有重要意义。由于磁共振成像(MRI)在提供软组织高分辨率解剖结构方面的良好能力,它在诊断和治疗脑肿瘤疾病中被广泛应用。为了获得准确分割所需的全面信息,通常需要在脑肿瘤分割中使用具有不同成像参数的多模态MRI扫描。常用的模态包括液体衰减反转恢复(FLAIR)、T1加权(T1)、对比增强T1加权(T1ce)和T2加权(T2)。不同模态的图像捕获了不同的病理信息,并且它们可以有效地相互补充,这在分割多种类型的脑肿瘤区域(如水肿(ED)、坏死和非增强肿瘤(NCR/NET)以及增强肿瘤(ET))中起着至关重要的作用。图1展示了用于脑肿瘤分割的多模态MRI的示例。为简单起见,只选择了整个扫描的一个切片。图1(a)显示了领域专家提供的地面真相(GT)分割标签。绿色、黄色和红色分别表示ED、ET和NCR/NET区域。从图1(b)到(e)可以看出,不同模态的特征差异显著。例如,FLAIR模态可以很好地捕获具有明显边缘或边界的ED区域,而T1ce模态在检测具有高对比度的肿瘤核心(即ET和NRC/NET的联合)方面更为有效。
Abstract
摘要
Brain tumor segmentation in multimodal MRI has great significance in clinical diagnosis and treatment. Theutilization of multimodal information plays a crucial role in brain tumor segmentation. However, most existingmethods focus on the extraction and selection of deep semantic features, while ignoring some features withspecific meaning and importance to the segmentation problem. In this paper, we propose a brain tumorsegmentation method based on the fusion of deep semantics and edge information in multimodal MRI, aimingto achieve a more sufficient utilization of multimodal information for accurate segmentation. The proposedmethod mainly consists of a semantic segmentation module, an edge detection module and a feature fusionmodule. In the semantic segmentation module, the Swin Transformer is adopted to extract semantic featuresand a shifted patch tokenization strategy is introduced for better training. The edge detection module isdesigned based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and an edge spatial attention block (ESAB) ispresented for feature enhancement. The feature fusion module aims to fuse the extracted semantic and edgefeatures, and we design a multi-feature inference block (MFIB) based on graph convolution to perform featurereasoning and information dissemination for effective feature fusion. The proposed method is validated on thepopular BraTS benchmarks. The experimental results verify that the proposed method outperforms a numberof state-of-the-art brain tumor segmentation methods.
多模态MRI中的脑肿瘤分割在临床诊断和治疗中具有重要意义。利用多模态信息在脑肿瘤分割中起着至关重要的作用。然而,大多数现有方法都专注于提取和选择深度语义特征,而忽视了一些具有特定意义和重要性的特征,这些特征对于分割问题至关重要。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于多模态MRI中深层语义和边缘信息融合的脑肿瘤分割方法,旨在更充分地利用多模态信息进行准确的分割。所提出的方法主要由语义分割模块、边缘检测模块和特征融合模块组成。在语义分割模块中,采用Swin Transformer来提取语义特征,并引入了一种移位块标记策略以进行更好的训练。边缘检测模块基于卷积神经网络(CNNs)设计,并提出了边缘空间注意力块(ESAB)以进行特征增强。特征融合模块旨在融合提取的语义和边缘特征,我们设计了基于图卷积的多特征推理块(MFIB)来进行特征推理和信息传播,以实现有效的特征融合。所提出的方法在流行的BraTS基准数据集上进行了验证。实验结果验证了所提出的方法优于许多最新的脑肿瘤分割方法。
Method
方法
The framework of the proposed brain tumor segmentation methodis shown in Fig. 2. It is mainly composed of a semantic segmentationmodule, an edge detection module and a feature fusion module. The semantic module adopts an improved Swin Transformer block to extractdeep semantic features from multimodal MRI scans including FLAIR,T1, T1ce and T2. The edge detection module aims to extract edgefeatures by employing a convolutional network as the backbone anddesigning edge spatial attention blocks (ESABs) for feature enhancement. Considering the modal characteristics of MRI modalities, onlyFLAIR and T1ce are selected as the input of the edge detection module.The feature fusion module consists of several multi-feature inferenceblocks (MFIBs), aiming to fuse the semantic features obtained from thesemantic segmentation module and the edge features obtained fromthe edge module at multiple levels. To reconstruct the segmentationresult, a successive expanding decoder that is widely adopted in theU-Net-like architectures is employed. For the edge detection task, theresult is directly obtained by bilinear interpolation. For the featurefusion model, the output includes both an edge detection result and asegmentation result. To train the network, the semantic segmentationmodule and edge detection module are first trained individually. Then,the output of the feature fusion module is used to supervise the trainingof the entire model.
所提出的脑肿瘤分割方法的框架如图2所示。它主要由语义分割模块、边缘检测模块和特征融合模块组成。语义模块采用改进的Swin Transformer模块从包括FLAIR、T1、T1ce和T2在内的多模态MRI扫描中提取深层语义特征。边缘检测模块旨在通过使用卷积网络作为骨干,并设计边缘空间注意力块(ESABs)来增强特征,从而提取边缘特征。考虑到MRI模态的特征,仅选择FLAIR和T1ce作为边缘检测模块的输入。特征融合模块由多个多特征推理块(MFIBs)组成,旨在在多个级别上融合从语义分割模块获得的语义特征和从边缘模块获得的边缘特征。为了重建分割结果,采用了在U-Net类似的架构中广泛采用的连续扩展解码器。对于边缘检测任务,结果直接通过双线性插值获得。对于特征融合模型,输出包括边缘检测结果和分割结果。为了训练网络,首先单独训练语义分割模块和边缘检测模块。然后,特征融合模块的输出用于监督整个模型的训练。
Conclusion
结论
This paper proposes a novel deep learning-based brain tumor segmentation method by jointly utilizing deep semantics and edge information in multimodal MRI. To achieve this target, three functionalmodules are designed. Specifically, we present a semantic segmentationmodule based on an improved Swin Transformer by introducing theshifted patch tokenization strategy for better training. In addition, aCNN-based edge detection module is designed to extract edge features from the input MRI scans. Finally, we present a feature fusionmodule by designing a multi-feature inference block based on graphconvolution to fuse the deep semantic edges and specific edge features.Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the key components designed in our method. Moreover, the proposed method achievesbetter performance when compared with some state-of-the-art methodson the BraTS benchmarks. Future work may focus on exploring thefeasibility of some other specific features for brain tumor segmentationand extending the proposed approach to other semantic segmentationproblems.
这篇论文提出了一种新颖的基于深度学习的脑肿瘤分割方法,通过联合利用多模态MRI中的深度语义和边缘信息来实现。为了实现这一目标,设计了三个功能模块。具体来说,我们提出了一个基于改进的Swin Transformer的语义分割模块,通过引入移位块标记策略来实现更好的训练。此外,设计了一个基于CNN的边缘检测模块,用于从输入的MRI扫描中提取边缘特征。最后,我们设计了一个基于图卷积的多特征推理块的特征融合模块,用于融合深度语义边缘和特定边缘特征。实验结果证明了我们方法中设计的关键组件的有效性。此外,与一些最新方法相比,所提出的方法在BraTS基准数据集上取得了更好的性能。未来的工作可能集中在探索其他特定特征对于脑肿瘤分割的可行性,并将所提出的方法扩展到其他语义分割问题上。
Figure
图

Fig. 1. An example of multimodal MRI for brain tumor segmentation. (a) The ground truth (GT) segmentation label provided by domain experts (the green, yellow and redrepresent edema (ED), enhancing tumor (ET), and necrosis and non-enhancing tumor (NCR/NET), respectively). (b) The FLAIR modality. (c) The T1 modality. (d) The T1cemodality. (e) The T2 modality. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend,
图1. 用于脑肿瘤分割的多模态MRI示例。(a)领域专家提供的地面真实(GT)分割标签(绿色、黄色和红色分别表示水肿(ED)、增强肿瘤(ET)和坏死和非增强肿瘤(NCR/NET))。(b)FLAIR模态。(c)T1模态。(d)T1ce模态。(e)T2模态。

Fig. 2. The framework of the proposed brain tumor segmentation method. It mainly consists of three modules: a semantic segmentation module, an edge detection module and afeature fusion module.
图2. 所提出的脑肿瘤分割方法的框架。它主要由三个模块组成:语义分割模块、边缘检测模块和特征融合模块。

Fig. 3. The architecture of a Swin Transformer block with the shifted patch tokenization strategy. Both W-MSA and SW-MSA are multi-head attention, which represent the regularwindow and the shifted window, respectively.
图3. 具有移位块标记策略的Swin Transformer块的架构。W-MSA和SW-MSA均为多头注意力,分别代表常规窗口和移位窗口。

Fig. 4. The architecture of the edge spatial attention block (ESAB) designed for edge feature enhancement.
图4. 为边缘特征增强设计的边缘空间注意力块(ESAB)的架构。

Fig. 5. The architecture of the multi-feature inference block (MFIB) for feature fusion. (a) The whole architecture of the 𝑖th MFIB. (b) The specific structure of graph convolution.
图5. 用于特征融合的多特征推理块(MFIB)的架构。(a) 第i个MFIB的整体架构。(b) 图卷积的具体结构。
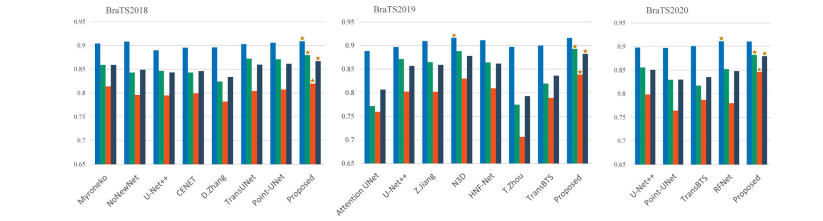
Fig. 6. Performance comparison of different brain tumor segmentation methods on the metric Dice. The best-performed method in each case is marked by a star.
图6. 不同脑肿瘤分割方法在Dice指标上的性能比较。在每种情况下表现最佳的方法用星号标记。

Fig. 7. Performance comparison of different brain tumor segmentation methods on the metric HD. The best-performed method in each case is marked by a star.
图7. 不同脑肿瘤分割方法在HD指标上的性能比较。在每种情况下表现最佳的方法用星号标记。

Fig. 8. Visual effect comparison of brain tumor segmentation results obtained by different methods. The green, yellow and red indicate ED, ET and NCR/NET regions, respectively.
图8. 使用不同方法获得的脑肿瘤分割结果的视觉效果比较。绿色、黄色和红色分别表示水肿(ED)、增强肿瘤(ET)和坏死和非增强肿瘤(NCR/NET)区域。

Fig. 9. Performance comparison of different segmentation methods in terms of tumor boundary accuracy.
图9. 不同分割方法在肿瘤边界准确度方面的性能比较。

Fig. 10. Visual effect comparison of segmentation results obtained by different models in the ablation study
图10. 使用消融研究中不同模型获得的分割结果的视觉效果比较
Table
表
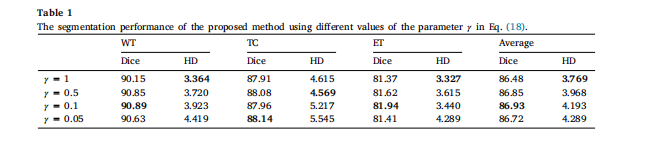
Table 1The segmentation performance of the proposed method using different values of the parameter 𝛾 in Eq. .
表1 使用方程中不同参数γ的提出方法的分割性能。
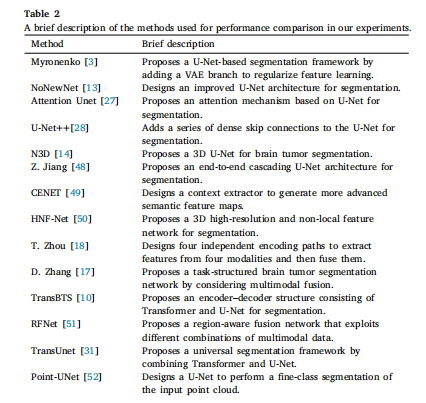
Table 2A brief description of the methods used for performance comparison in our experiments.
表2 在我们的实验中用于性能比较的方法的简要描述。

Table 3Objective evaluation results of different brain tumor segmentation methods on the BraTS2018 benchmark.
表3 不同脑肿瘤分割方法在BraTS2018基准数据集上的客观评估结果。

Table 4Objective evaluation results of different brain tumor segmentation methods on the BraTS2019 benchmark
表4 不同脑肿瘤分割方法在BraTS2019基准数据集上的客观评估结果。
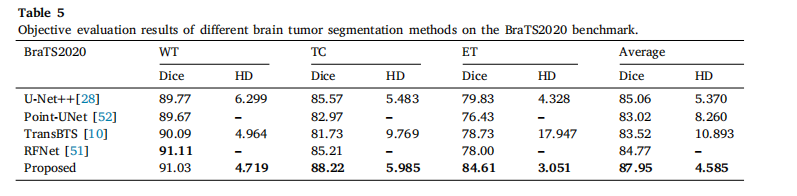
Table 5Objective evaluation results of different brain tumor segmentation methods on the BraTS2020 benchmark.
表5 不同脑肿瘤分割方法在BraTS2020基准数据集上的客观评估结果。
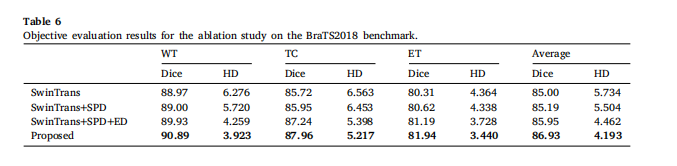
Table 6Objective evaluation results for the ablation study on the BraTS2018 benchmark
表6对BraTS2018基准数据集进行消融研究的客观评估结果
这篇关于基于多模态MRI中深层语义和边缘信息融合的脑肿瘤分割 | 文献速递-深度学习肿瘤自动分割的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






